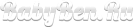How to take tests for feces correctly? Features of collecting feces in children and adults. What is the results of the tests indicated? The article will highlight these issues in detail.
The content of the article
- How to collect feces for analysis and hand over an adult, child, baby?
- How much feces do you need to analyze an adult and a child?
- How to take a fecal analysis during pregnancy?
- What is the analysis of the feces: a jar for fecal tests
- Is it possible to collect a fecal analysis in the evening?
- How much can feces be stored for analysis in the refrigerator?
- General analysis of feces - decryption, norm
- Biochemical and bacteriological analysis of feces for dysbiosis - decoding, norm
- Kala analysis for the copper - decryption, norm
- Hidden blood analysis - decryption, norm
- Analysis of feces for eggs of worms, helminths - decryption, norm
- Analysis of feces for carbohydrates in infants - decryption, norm
- Kala analysis for Calprotetin - decryption, norm
- Analysis of feces for parasites - decryption, norm
- Calais analysis and scraping for enterobiosis - decryption, norm
- Calais analysis for the simplest
- Helicobacter Pilori Helicobacter Analysis
- Calais analysis for dysentery
- Calais analysis for pancreatic elastasis - decryption, norm
- Calais analysis for UPF (conditionally pathogenic flora) - salmonellosis
- Analysis of feces for sensitivity to antibiotics - decryption, norm
- Allergens analysis - decryption, norm
- Calais analysis for rotavirus - decryption, norm
- Fecal analysis for opisthorchiasis - decryption, norm
- What does yeast mushroom mushrooms mean in the analysis of Kala?
- What does starch mean in the analysis of Kala?
- What does a citrobacter mean in the analysis of feces?
How to collect feces for analysis and hand over an adult, child, baby?
Laboratory examination of feces is an important step for the correct diagnosis of the disease. Deciphering the analysis of feces often helps the doctor confirm the alleged diagnosis and choose the optimal course of the patient's treatment.
Cala is the final product of the breakdown of food products as a result of the biochemical processes of the gastrointestinal tract. The study of excrement can identify pathological foci throughout the digestive path, starting from the stomach, ending with the rectum.
Calais analysis helps the doctor in the correct diagnosis of the disease
Calais analysis is prescribed in cases:
- complaints about the work of the gastrointestinal tract: insufficient enzymatic activity of gastric juice and pancreas, bad digestion
- infectious processes of the digestive tract when infected with pathogenic microorganisms, mushrooms, viruses, simple parasites
- bleeding caused by a number of gastrointestinal diseases: sampling ulcers of the stomach and intestines, varicose veins of the esophagus, stomach, intestines, and neoplasms
Before the laboratory study of feces, the following recommendations should adhere to:
- Feces are collected in clean and dry containers after spontaneous defecation
- Fecal masses must be sent to a laboratory study within 12 hours after bowel movements in order to avoid distorting the results of the analysis
- It is not recommended to use feces for analysis after an enema and the use of suppositories, as well as after consuming a number of drugs containing iron, bismuth, barium
- On the eve of laboratory tests, you should eat, adhering to the balanced content of carbohydrates, fats and proteins to obtain reliable results
- For the reliability of the analysis, impurities of water and urine in feces are unacceptable
Important: during menstruation, women should refrain from passing feces for analysis, so as not to distort the results.

In older children, you can collect feces for analysis of clean pots
Features of collecting feces for infants and older babies
- In infants, feces are placed in a special container from a disposable diaper or diaper after defecation. The bowel movements are collected from the surface of the absorbent material, without curettage from the depths
- If the baby has a liquid chair, you can try to collect feces from the oilcloth, waiting for the baby to emptie
- Do not feed the baby intensively before passing the analysis and force him to empty. The feces can be collected the day before, observing the usual regime of the child’s day. The only requirement will be - storing it in a well -closed container in the refrigerator
- Older children can be collected by feces from the pot, having previously washed it with soda or neutral soap (children). Then rinse the pot with running water and dry well. Synthetic detergents and cleaning products should not be used to process the pot
How much feces do you need to analyze an adult and a child?
To study feces, you need to fill out a container for collecting analysis for 1 \\ 3 volumes. These are approximately 10 g of feces or 2 teaspoons for adults and kids after a year.
It is enough for infants and children up to 12 months to collect about 5 g of bowel movements (1 teaspoon).
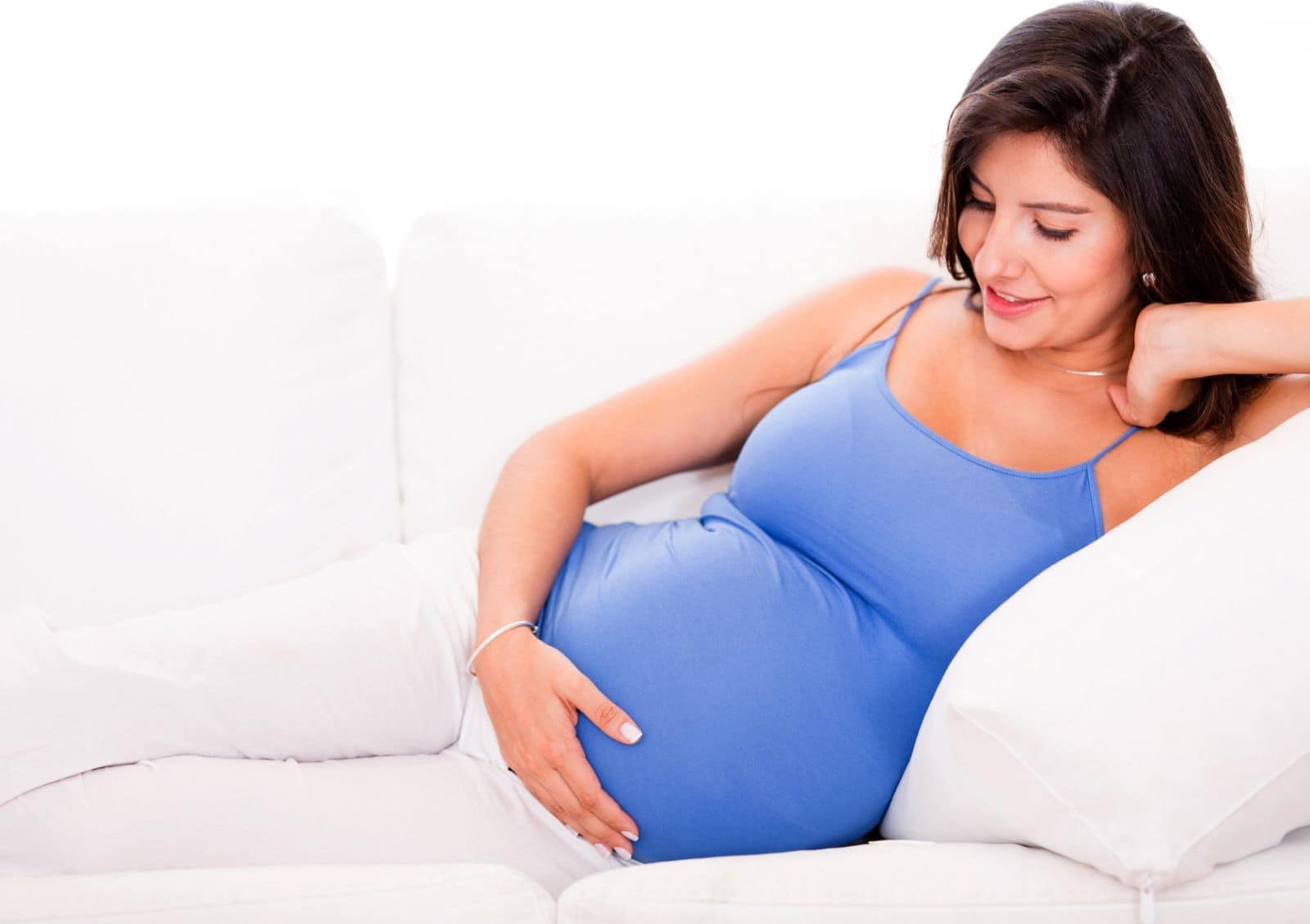

Helminths analysis is mandatory for pregnant women
How to take a fecal analysis during pregnancy?
The analysis of feces for the identification of helminths is mandatory when registering a pregnant woman for registration in a antenatal clinic. The doctor, with the issuance of a referral for the analysis, must advise the future mother how to prepare and collect a fecal analysis correctly.
The requirements for collecting bowel movements for pregnant women are the same as for other categories of patients and are described in detail above.
Important: pregnant women should not ignore the surrender of a fecal analysis. In time, the identified pathologies and their cure will help to be easier to come out of pregnancy and give birth to a healthy baby.
Calamin containers
What is the analysis of the feces: a jar for fecal tests
Modern requirements for passing fecal tests are to collect feces in a special plastic sterile container with a hermetic lid. Such containers can be purchased at the pharmacy network from different manufacturers at an affordable price.
Some laboratories allow the receipt of feces in glass containers of small volumes, provided that the container will be clean and dry. It should be borne in mind that special containers for collecting feces provide maximum safety of feces, and therefore a more reliable result.
Important: you should not confuse capacities for collecting urine with containers for feces. The latter have a special spatula for the convenience of fake feces.

The delivery of feces collected in the evening, provided that the proper storage is permissible
Is it possible to collect a fecal analysis in the evening?
An ideal biomaterial for laboratory research is a freshly shaped morning feces delivered to the laboratory within three hours after the collection.
As a rule, it is not always possible to collect feces in the morning, especially for breast babies and older children.
Therefore, it is permissible to collect feces the night before, provided that the proper storage. It is best to place the container in a cool place, for example, in the refrigerator, and in the morning to take it to the laboratory.
How much can feces be stored for analysis in the refrigerator?
It is allowed to store the collected feces in the refrigerator for 6-8 hours at a temperature of 4-8 degrees. The feces should be stored in a special plastic container with a tightly fitted lid. It is unacceptable to freeze feces and its maintenance on the shelf from the side of the refrigerator door. It is best to keep the container on the middle shelf.
General analysis of feces allows a gastroenterologist to get important information about the work of the patient's gastrointestinal tract
General analysis of feces - decryption, norm
A coprogram or general analysis of feces is an important non-invasive laboratory examination method in gastroenterology, which allows you to reliably study the gastrointestinal tract, in time to detect pathological areas of the digestive system and choose the right path of treatment.
Important: a coprological study of feces is a necessary tool for making a reliable diagnosis, so you should not refuse to conduct this analysis if the doctor prescribed it.
Detailed decryption of a general analysis of feces is set out in the article below.
Biochemical and bacteriological analysis of feces for dysbiosis - decoding, norm
Dysbiosis or intestinal dysbiosis occurs as a result of a change in the quantitative and qualitative ratio of the flora, setting the human body due to any adverse factors.
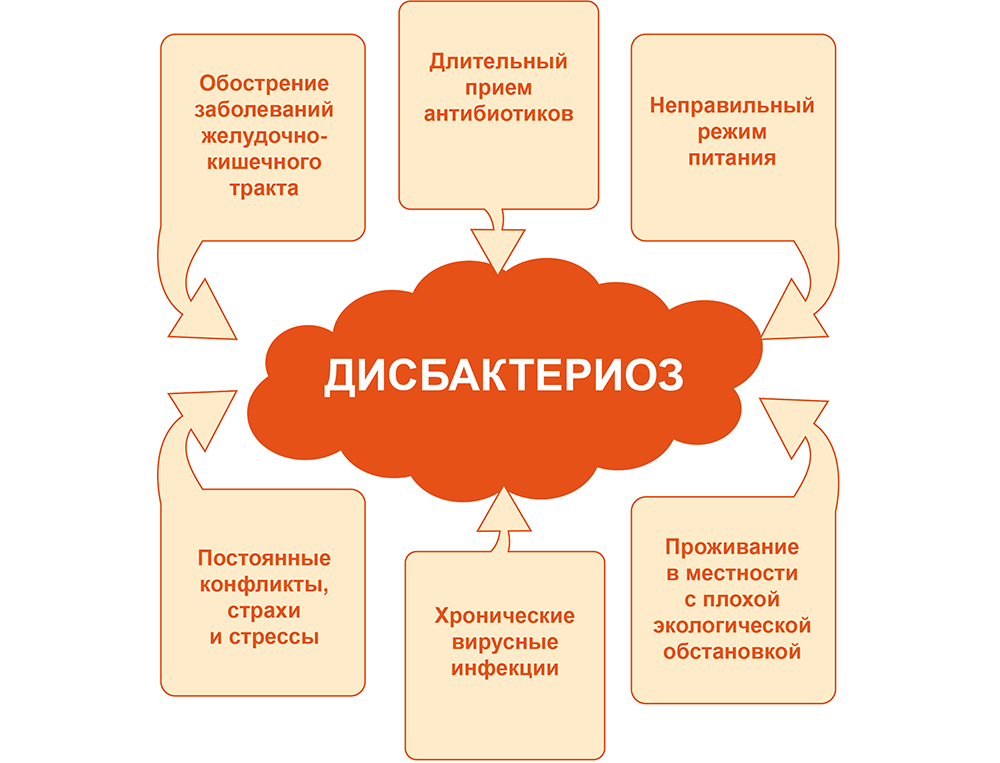
Factors causing dysbiCherioch
The microbiological intestinal imbalance can be determined by studying feces on the flora and the identification of pathogenic microorganisms in it. Analysis of feces for dysbiosis is carried out in the following cases:
- long -term intestinal disorders
- after the treatment of intestinal infections (salmonellosis, shigellosis, etc.) and prolonged antibiotic therapy
- allergic processes
- immunodeficiency states
Children of the first year of life are conducted by fecal examinations for dysbiosis in the following indications:
- intrauterine intoxication
- artificial feeding after birth
- intolerance to mother's milk
- frequent colds
- the disproportionality of weight gain
- stomatitis, thrush

Sowing feces on a nutrient medium
- Three before the passage of feces for dysbiosis should refrain from taking antibiotic drugs, alcohol and acute foods
- For analysis, it is enough to collect about 2 g of feces (half a teaspoon)
- The feces for this analysis should be freshly made and delivered to the laboratory in a sterile container for 2-4 hours, using a refrigerant at a temperature of 2-8 degrees
- Microbiological examination of feces is carried out after sowing the studied biological material on the nutrient medium and its further thermal restoration
- With the help of biochemical and microbiological examination of feces for dysbiosis, it is possible to identify the quantitative and qualitative composition of microorganisms inhabiting the patient’s intestines, compare them with reference (normal) indicators, as well as to identify unacceptable pathogenic flora: salmonella, shigella, percanite, etc.
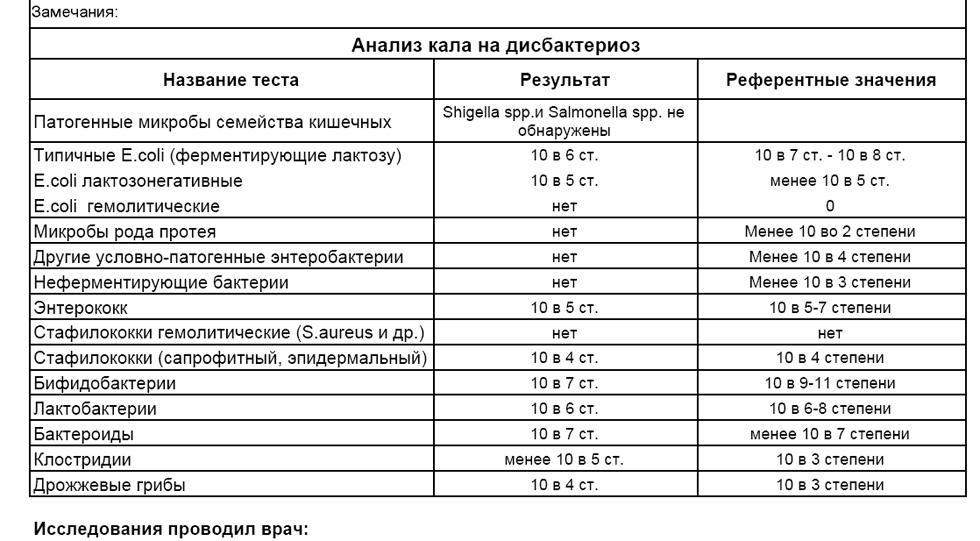
Kala analysis for dysbiosis
The absence or insufficient amount of beneficial intestinal flora (lactobacilli, bifidobacteria, E. coli) can state about dysbiosis and prescribing the appropriate treatment.
Study of feces for dysbiosis, video

Coprogram research
Kala analysis for the copper - decryption, norm
Coproprogram is a laboratory study method of feces that helps identify problems in the digestive tract. The results of the analysis allow you to detect:
- pathology of digesting and enzymatic gastrointestinal tract activities
- the presence of inflammatory foci throughout the intestinal tract
- the presence of cysts, helminths and their eggs, protozoa and other parasites
- a reliable picture of microflora
Copological analysis includes three stages of the study of feces:
- macroscopic
- chemical
- microscopic

The daily diet of products affects the quantity, shape and consistency of feces
Macro -study
- Quantity Feces with a balanced diet is 100-200 g. The use of plant foods increases the amount of feces, and excess meat, with a high protein content, reduces the volume of bowel movements. The norm of feces of the baby is an average of 70-90 grams
- Form Kala normally has a cylindrical design
- Consistency Kala is determined by the products used. According to reference indicators, the feces have a decorated structure, soft and homogeneous. Infants, on the contrary, have unformed bowel movements with a viscous and sticky structure. The amount of water, mucus and fats affect the density of feces
- Color Human bowel movements forms the gall pigment - stercobilin, which gives Kalu brown tint
Important: the products used affect the color of feces. Food containing dyeing pigments can change the color of bowel movements. It should be remembered that iron -containing drugs, activated carbon, beets, dominance in the diet of dairy or meat products can affect staining feces during analysis.
- Smellprotein foods are given by protein food, namely, the components of its decay: Indol, Scatol, phenol
- Pus, mucus, blood: The detection of these components can serve as a signal of serious gastrointestinal diseases

In the laboratory
Chemical analysis
- Fecal reaction (pH) In terms of norm, it is neutral or slightly alkaline (6.8-7.6). In children-breasts, stingy reaction is characterized by the feces due to the features of the nutrition in this age period. PH discrepancies with reference norms mean pathological changes in digestion associated with diseases of the stomach and individual intestinal segments
- Squirrels should not be detected in feces according to regulatory indicators
- Hidden blood, identified in feces, serves as a marker for internal bleeding and pathological processes of the digestive tract
- Bile pigments (Bilirubin, Surcobilin) \u200b\u200b- important indicators of chemical study of feces to establish the diagnosis of many diseases: hepatitis, inflammation of the bile ducts, acute pancreatitis. These pathologies are often associated with fracture of color due to a reduction in the amount of stormobilin
Important: a small amount of bilirubin is allowed in the feces of newborn children. Upon reaching about 9 months, this pigment disappears from the feces of the child.

Study of feces under a microscope
Micro -medical investigation
The analysis of feces under a microscope makes it possible to detail the diagnosis of the disease at the micro level.
- Detritus - amorphous particles of digested food with the remains of epithelial and bacterial cells. Detection of detrites during the examination is considered the norm, which indicates a healthy digestion
- Muscle fibers, elements of connective tissue and intestinal mucosa shells(leukocytes, epithelium cells, red blood cells, eosinophils). The detection of these components may indicate various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
IMPORTANT: normally, leukocytes should be absent in bowel movements. A large number of white blood cells in the absence of mucus should alert specialists about the possible pararectal abscess in the wall of the rectum.
- Digested fiber, starch and iodophilic flora permissible in minor volumes. Explicit accumulation of these components indicates various pathologies throughout the gastrointestinal tract
- Neutral fat, fatty acids and their salts Often detected in bowel movements. Traces of fatty components are acceptable, but their noticeable quantities indicate insufficient biles, weak contraction of the small intestine, pancreatic pathology

The norms of analysis of feces of infants differ from indicators of children of the older age category due to the characteristics of the nutrition
Important: in the feces of the babies feeding on breast milk, the presence of neutral fat in the form of small drops is permissible.
- Microflora, discovered in feces, makes it possible to determine useful, conditionally pathogenic and pathogenic microorganisms in qualitative and quantitative indicators
- Helminths, their eggs, protozoa and other parasites, identified in bowel movements, require an urgent output from the body
- Charcot-Liden crystals, hemosiderin and oxalate calcium, discovered in the analysis, carry information about possible helminthic invasions, amoebic dysentery, intestinal bleeding, functional disorders of the digestive tract
Important: feces of adults should not contain calcium oxalate crystals according to regulatory indicators. In small-breasts, a non-essential amount of these formations in feces is allowed.
Copropram reference
|
Index |
Reference values |
| Consistency |
Dense, decorated, solid, soft |
| Form |
Designed, cylindrical |
| Smell |
Fecal, sour |
| Color |
Light brown, brown, dark brown, yellow, yellow-green, olive |
| Reaction |
Neutral, slightly acidic |
| Blood |
No |
| Slime |
Absent, a small amount |
| The remains of undigested food |
Absent |
| The muscle fibers are changed |
Large, moderate, small amount, absent |
| The muscle fibers are unchanged |
Absent |
| Detritus |
Absent, small, moderate, large |
| Plant fiber is digested |
Absent, a small amount |
| Fat neutral |
Absent |
| Fatty acid |
Absent, a small amount |
| Soap |
Absent, a small amount |
| Intracellular starch |
Absent |
| The starch is extracellular |
Absent |
| Red blood cells |
0 — 1 |
| Crystals |
No |
| Iodophilic flora |
Absent |
| Clostria |
Absent, a small amount |
| Yeast -like mushrooms |
Absent |
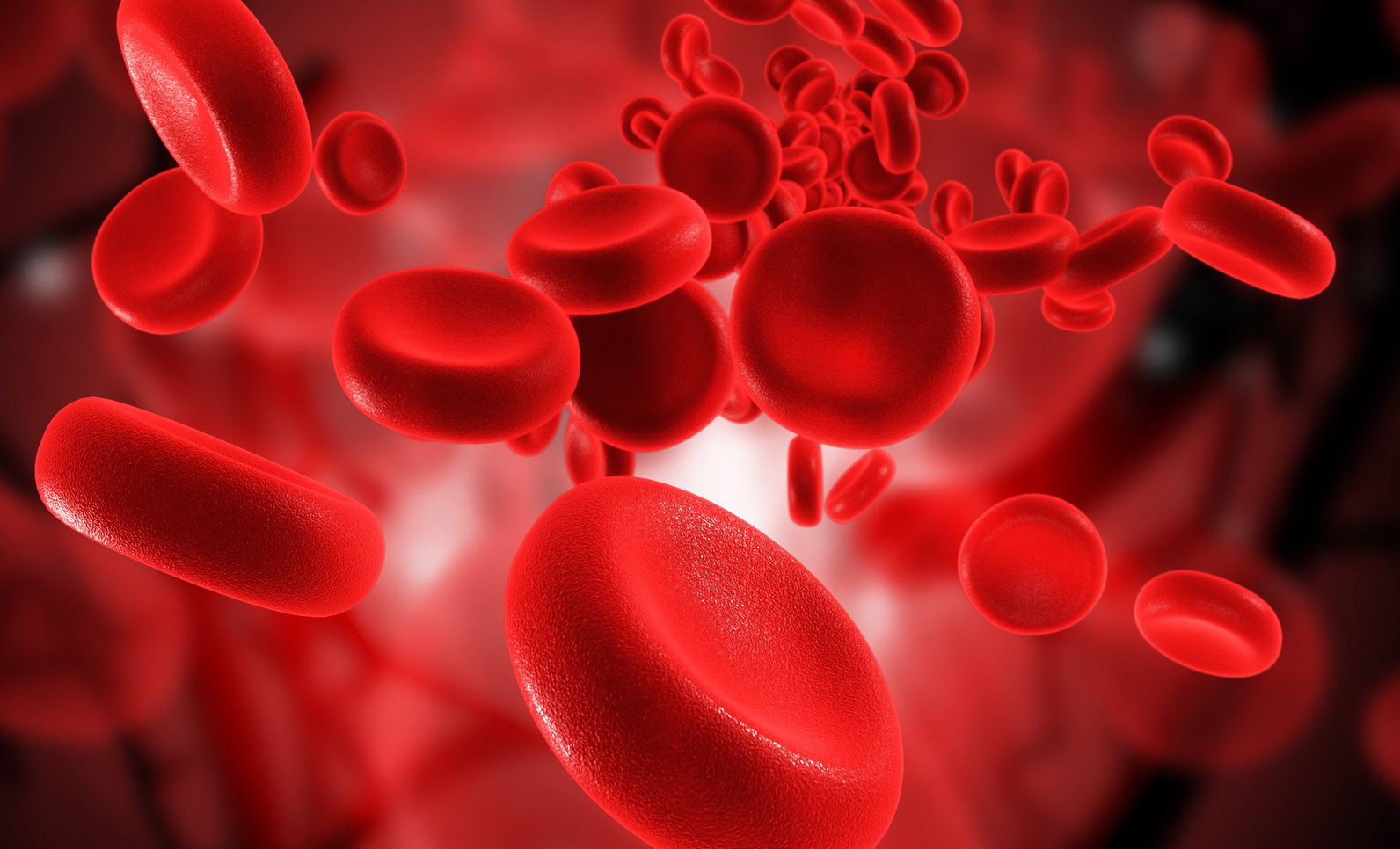
Blood cells under a microscope
Hidden blood analysis - decryption, norm
- Invisible bleeding of internal organs is a great danger to human life. In time, the identified bleeding of the stomach or individual segments of the intestinal tract makes it possible to avoid severe consequences due to blood loss, make a reliable diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment
- The essence of laboratory research is to identify abnormal hemoglobin with destroyed red blood cells in the lower intestinal segments. The scientific terminology of research is called gasoline breakdown or gregersen's technique
- The analysis is so sensitive and accurate that it makes it possible to detect even minor amounts of hemoglobin contained in the meat eaten by the patient on the eve of the examination

Iron -containing products
- Therefore, before the analysis for hidden blood, special training should be undergoing. A week before the study, the use of iron -containing drugs, hematogen, drugs containing bismuth and laxative medicines is prohibited
- 3 days before the analysis, it is recommended to observe a diet that does not contain products with blood components: animal and poultry meat, fish, offal (liver, kidneys, heart, light). You should also refrain from using apples, spinach and beans
Important: on the eve of the test of hidden blood, such studies and procedures as fibrogastoscopy, irrigoscopy, etc. should not be carried out, associated with the ability to damage the mucous membrane and cause even minor damage to bleeding. It is not recommended even to brush your teeth in order to avoid bleeding gums.
Analysis of feces for eggs of worms, helminths - decryption, norm
Important: the statistics of the WHO indicate 90% of the lesion of the population of the globe with helminths and the simplest parasites.

Children are most susceptible to helminthic invasions
The identification of helminths, their eggs and life products is an important task for maintaining the health of babies and the adult population.
Calais analysis allows you to identify helminth groups, which, by norm, should be absent in the human body:
- round worms or nematodes: Askarida, Krivolovka is duodenum, Vlasov, etc.
- ensalmers or nematodes: Leukhloridiy Parodox, cat and hepatic bicom, schistosoma
- ribbon worms or cestodes: wide tape, bull and pork tapeworm
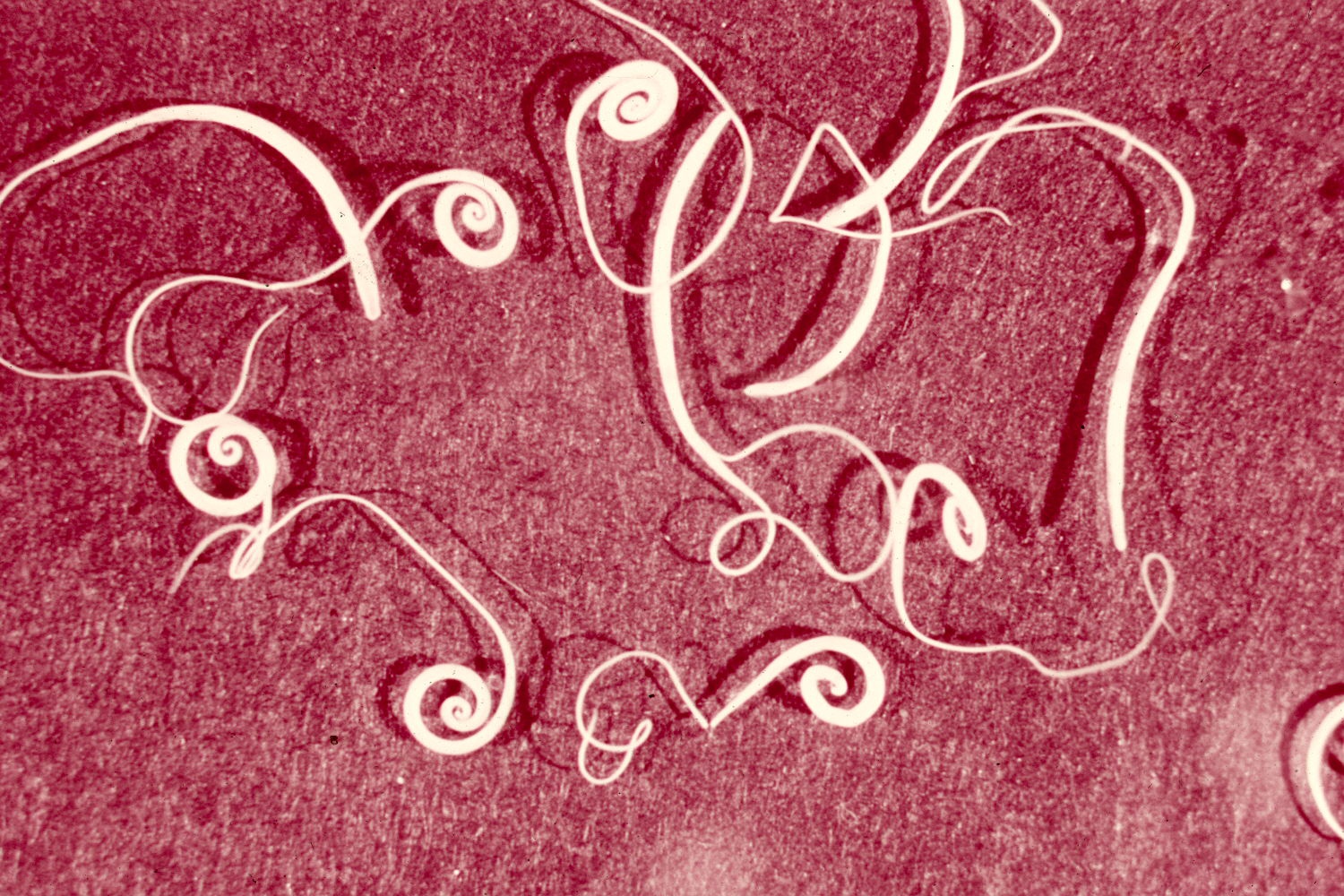
Helminths under a microscope
Analysis of feces for carbohydrates in infants - decryption, norm
- This study is often prescribed for babies with poor digestion, frequent regurgitation, poor weight gain, diarrhea, colic, vomiting. The analysis allows you to identify lactase deficiency and other abnormal processes in the absorption and splitting of carbohydrates in the baby. The scientific name for a laboratory study for carbohydrates is called benedict method
- A small volume of feces (at least 5 grams) should be determined in the laboratory within 4 hours after collection in a special container for collecting analysis
- Normally, the carbohydrate indicator must correspond to: 0-0.25% for babies up to a year
- Results exceeding 0, 25% are considered deviations from small: 0.3-0.5% to medium: 0.6-1%. A significant deviation from reference indicators is the indicator above 1%.

Calais study helps to identify many diseases
Kala analysis for Calprotetin - decryption, norm
- Calais analysis allows you to identify calprotectin (protein synthesized by leukocytes). The higher its concentration, the more leukocytes is in the intestinal tract
- This indicator helps to diagnose many diseases: chronic dyspepsia, fistulas and cracks of the rectum, crown disease, irritable intestine, etc.
- Reference indicators of calprotectin: 0-10 ng/ml. Indications above the norm are taken under control and are carefully analyzed by specialists with subsequent treatment
Analysis of feces for parasites - decryption, norm
To identify parasites in the human body is most significantly through the analysis of feces. Methods of laboratory tests allow you to detect a variety of helminths, giardia, toxocar, anquilostomic, echinococcus, etc.
The reason for the laboratory examination of feces on parasites is the following complaints:
- headache
- nausea
- loss or increased appetite
- intestinal disorders
- night rattle with teeth
- skin rashes
- itching in the anus
The analysis of feces allows you to identify the type of parasites settled in the body, their number and choose the best way to remove them with medication and other methods.

Hand hygiene - prevention of children's helminthic invasion
Calais analysis and scraping for enterobiosis - decryption, norm
Infection with pinworms or enterobiosis - The most common helminthic disease among children.
- Enterobiosis is caused by moving parasitic small worms - pinworms having a pointed tail (the name is associated with this). They reach sizes up to 1 cm in length and can be found with the naked eye in feces
- The pinworms are activated at night and are able to crawl into the rectum and lay eggs in the skin folds. At the same time cause severe anus, anxiety and a discomfort state
- The consequences of infection with pinworms are dangerous and, as a rule, have severe health consequences, especially for the child's body. This is not only night itching and combing, but also the likelihood of developing dysbiosis, disorders of the gastrointestinal system, intoxication, allergies, insomnia, nervous breakdowns
- In girls, cuts can penetrate the genitals and cause inflammatory and infectious processes in the form of thrush, vulvovaginitis
- The identification of pinworms is important for preventing infection with enterobiosis of a large group of children in children's groups. The study of feces for enterobiosis is carried out:
- when complaining of suspicion of infection with cuts
- as a preventive analysis when visiting children's groups, a pool, hospitalization of a child, registration of a medical book, etc.
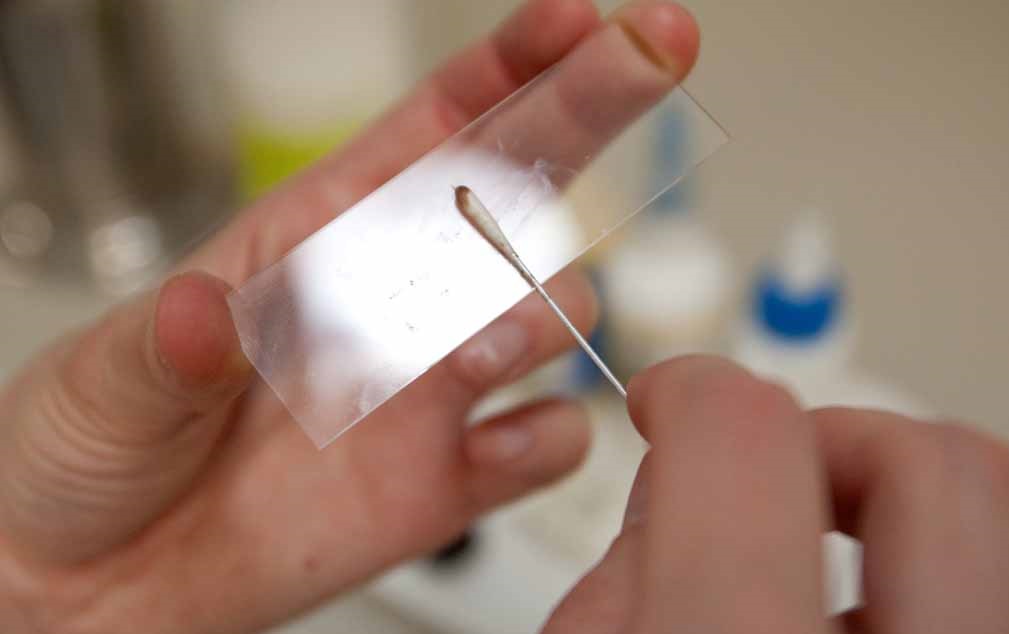

Scraping to enterobiosis
An analysis for enterobiosis is carried out by the method of study of feces and by scraping.
A smear or scraping is carried out in the morning after waking up. Do not wash or wash the anus area and adjacent skin folds to avoid distorting the results of the analysis. It is not recommended to carry out scraping after defecation.
How to scrap on enterobiosis with tape
- Take adhesive tape about 2 cm wide and cut off a tape 5-6 cm long from it
- Sticking the side of the tape, press the tape to the surface of the skin near the anus. Repeat the application several times with the same side of the tape
- Glue the tape tape with sticky side to the surface of the object glass
- The assembled scraping to take to the laboratory within 2 hours
How to scrap on enterobiosis with a cotton swab
- Moisten the usual cotton stick with one of the solvents: water, physiological solution (0.9% sodium chloride solution), glycerin or petroleum jelly
- Draw a stick around the anus, pushing the buttocks
- Place a stick with a biomaterial in a clean and dry container (you can use a urine container)
- Take the assembled smear to the laboratory in the near future
Tips and their eggs should be absent in a healthy person according to normative indicators.
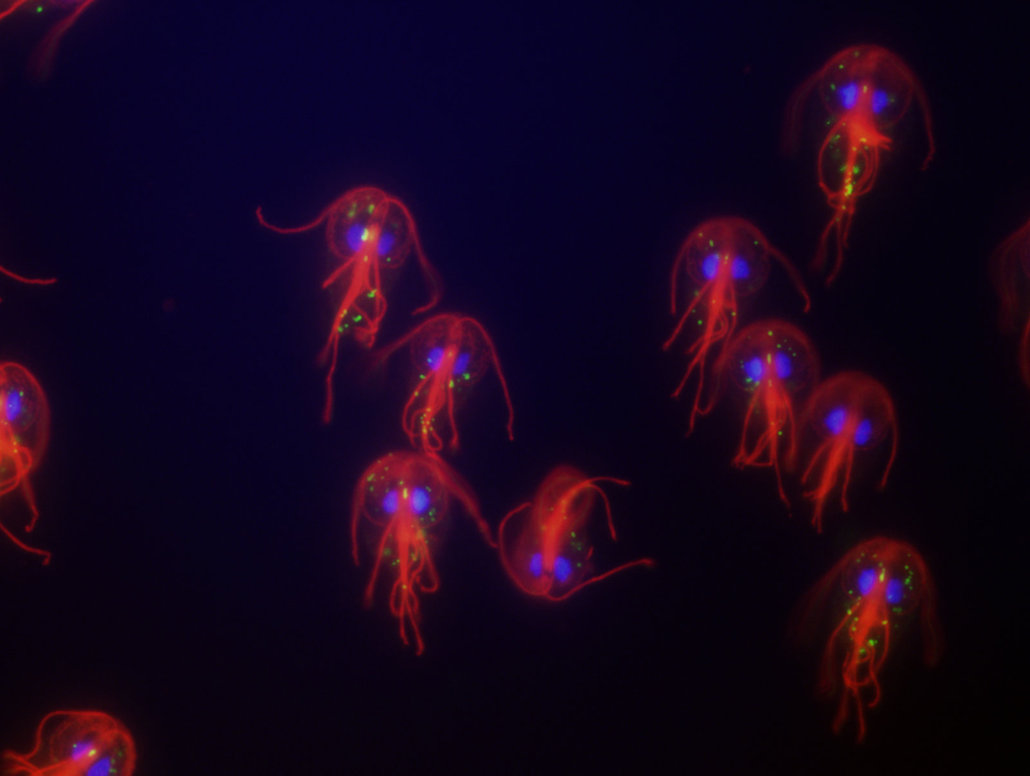
Lambia under a microscope
Calais analysis for the simplest
If you suspect infection with the simplest (dysentery amoeba, lamblia, balance), the patient is given a direction for the study of feces.
The protozoa, identified as a result of analysis, serve as a marker for a comprehensive study of the patient and prescribing optimal treatment.
- Dysenteria amoebacauses a serious illness - amoebiasis. This parasite sets in the walls of the intestine, causing numerous long -healing ulcerations for long
- Lamblia The gall bladder of a person and the small intestine are inhabited
- Establishing balanTidia parasitizes in the intestinal tract, causing diseases such as colitis that passes into severe ulcerative forms
For research, feces are taken with delivery to the laboratory in the near future.
Normally, these types of protozoa should be absent.
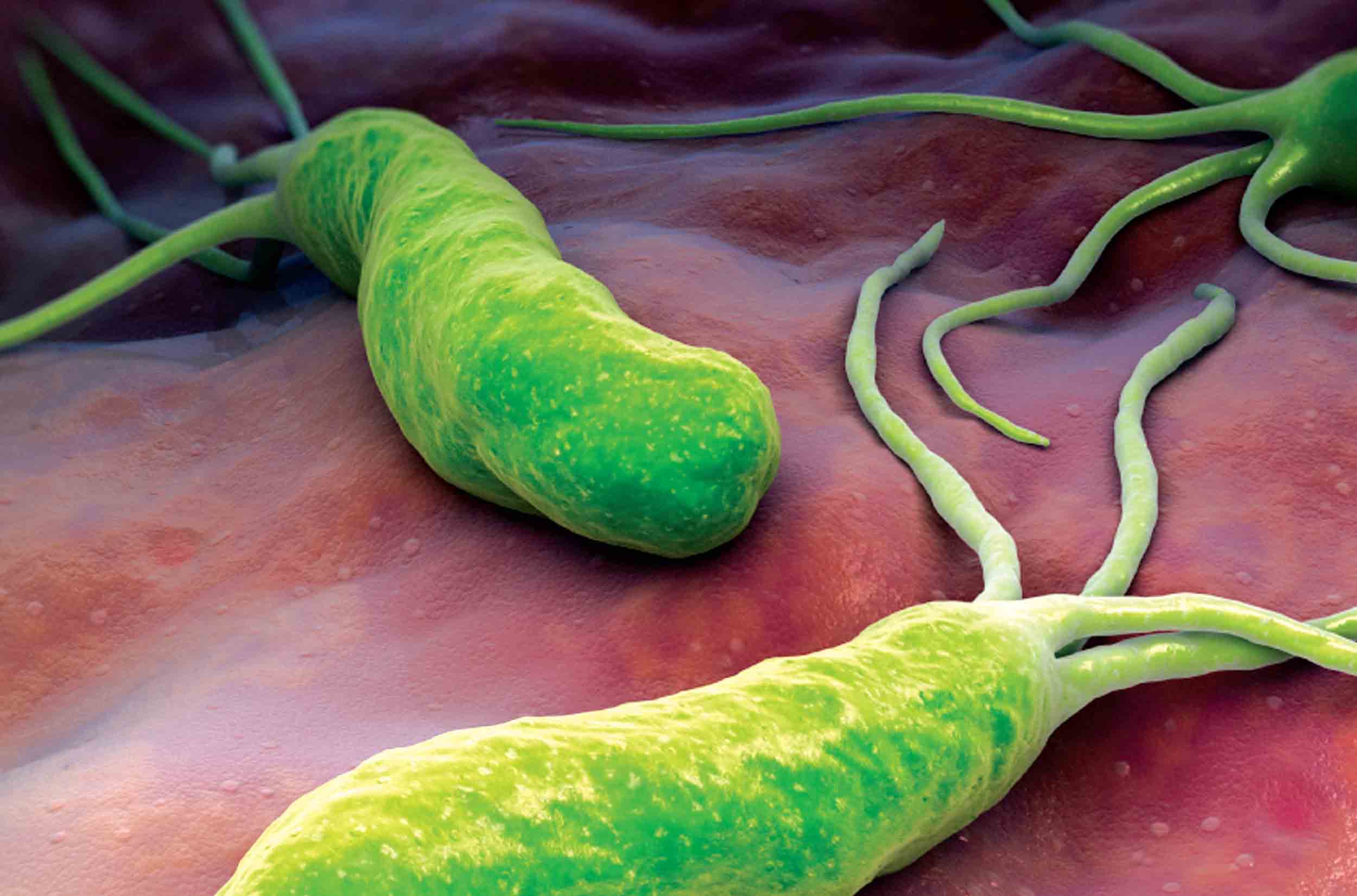
Helicobacter Pilori (Helicobacter Pilori) with an increase
Helicobacter Pilori Helicobacter Analysis
The analysis of feces for the presence of the pathogen Helicobacter Pilori is auxiliary. It is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis in case of suspicion of the presence of this spiral bacterium in the body.
The analysis is carried out no earlier than 30 days after the course of antibiotic therapy.
Calais analysis for dysentery
This type of analysis of bowel movements is carried out in case of suspicion of dysentery, which is caused by microorganisms from the detachment shigell. Collection of feces does not require special recommendations. The study of feces for dysentery is carried out within 5 days.
Calais analysis for pancreatic elastasis - decryption, norm
The performance of the pancreas will help to analyze feces for pancreatic elastasis. The study is carried out with suspicion:
- on Crohn's disease and cystic fibrosis, in children with impaired digestion
- pancreatitis
- diabetes
- neoplasms of the pancreas
Pancreatic elastasis is a pancreatic enzyme that breaks down the dietary protein and stands out with feces in unchanged condition, having passed the digestive tract.
The norm is the indicator-200-500 mg of elastasis in 1 g of feces. The shift of the indicator in one direction or another indicates the malfunctions of the pancreas.
Salmonellosis can be confirmed by the analysis of feces
Calais analysis for UPF (conditionally pathogenic flora) - salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is a severe toxicoic infectious disease of the gastrointestinal tract. The smallest gram -negative sticks are actively moved through flagella and transmitted through animal products (eggs, milk, meat, sausage products).
The identification of the pathogen is important in the correct diagnosis and prescribing the correct treatment.
Important: the collection of feces for analysis should be done before the treatment with antibiotics, so as not to hide the true picture of the disease.
Analysis of feces for sensitivity to antibiotics - decryption, norm
The bacteriological sowing of feces for sensitivity to antibiotics helps the attending physician correctly prescribe treatment with antibiotic drugs to certain types of pathogens of intestinal infections.
The identification of intestinal flora, conditionally pathogenic and pathogenic microorganisms, deviations from reference indicators, control over the effective effect of prescribed antibacterial drugs are important links in the treatment of gastrointestinal infections.
The regulatory indicators of the flora during the bacterials are indicated in the following table
| Children under 1 year old | Older children | Adults | |
| Bifidobacteria | 1010–1011 | 109–1010 | 108–1010 |
| Lactobacteria | 106–107 | 107–108 | 106–108 |
| Escherichia | 106–107 | 107–108 | 106–108 |
| Bacteroids | 107–108 | 107–108 | 107–108 |
| Peptustroptococci | 103–105 | 105–106 | 105–106 |
| Enterococci | 105–107 | 105–108 | 105–108 |
| Saprophytic staphylococci | ≤104 | ≤104 | ≤104 |
| Pathogenic staphylococci | absent | absent | absent |
| Clostria | ≤103 | ≤105 | ≤105 |
| Candida | ≤103 | ≤104 | ≤104 |
| Pathogenic enterobacteria | absent | absent | absent |
Allergens analysis - decryption, norm
The coprogram is an important factor in the diagnosis of allergic diseases. This is especially true for kids. At the first signs of allergic manifestations from the first days of a child’s life, you should consult a specialist.
The general analysis of feces, the study of feces for carbohydrates and dysbiosis are additional diagnostic methods in the establishment of allergies. The laboratory study of feces when identifying allergic processes becomes more informative after the child reaches 5-6 months.

Calais analysis for rotavirus infection
Calais analysis for rotavirus - decryption, norm
- “Intestinal flu” or rotavirus infection is a fairly common disease with a high degree of infection and severe complications. The disease can be picked up by airborne droplets, through water, dirty hands, vegetables, fruits
- Symptoms of the disease are similar to many diseases: high temperature, frequent and liquid stool, nausea, vomiting. To identify the pathogen and prescribe the correct and immediate medical treatment, a diagnostic study of feces should be carried out
- Biomaterial (feces) is collected according to general requirements and is investigated for the presence of rotaviruses and adenoviruses
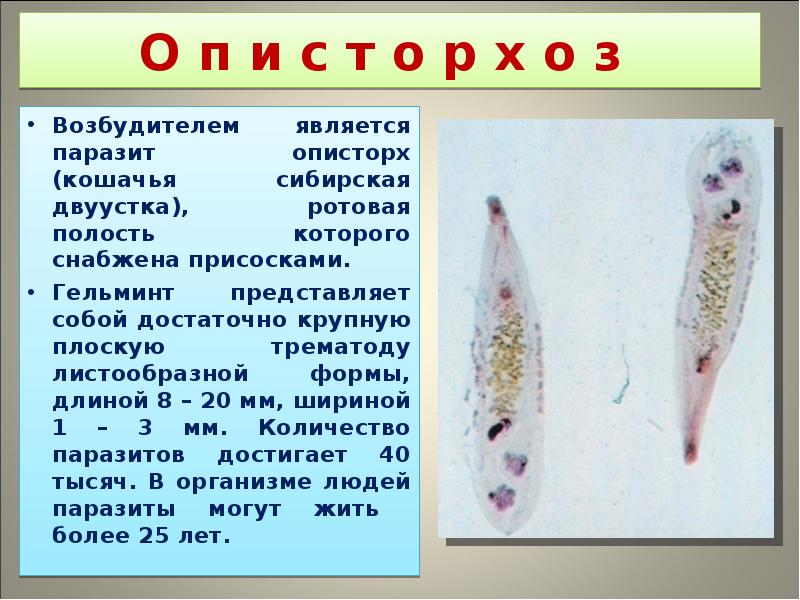
Opistorchoz
Fecal analysis for opisthorchiasis - decryption, norm
- Opisthorchiasis is a serious illness that occurs when the bile and hepatic ducts and pancreas are damaged with a small parasite-subservative- a cat -catfish. The disease lasts a long time with frequent exacerbations and possible cancer damage to the liver and pancreas
- It is unusually difficult to recognize and determine the diagnosis of the disease due to the lack of specific complaints and symptoms of the disease. Studies of feces at different stages of the disease on method of Fuulleborne and Goryachev make it possible to identify the pathogen
- Analysis for opisthorchiasis is prescribed for chronic inflammation of the bile ducts, acute pancreatitis, and neoplasms in the liver
What does yeast mushroom mushrooms mean in the analysis of Kala?
Very often, for various reasons, a violation of the balance of intestinal microflora occurs. Long-term treatment with antimicrobial drugs, weakening of the immune system, malnutrition and many other factors lead to an imbalance of intestinal flora and an increase in the proportion of conditionally pathogenic microorganisms.
Identification in the feces of yeast mushrooms of the genus Candida above reference indicators (›10 4) may indicate the developed intestinal candidiasis and prescribing immediate treatment.
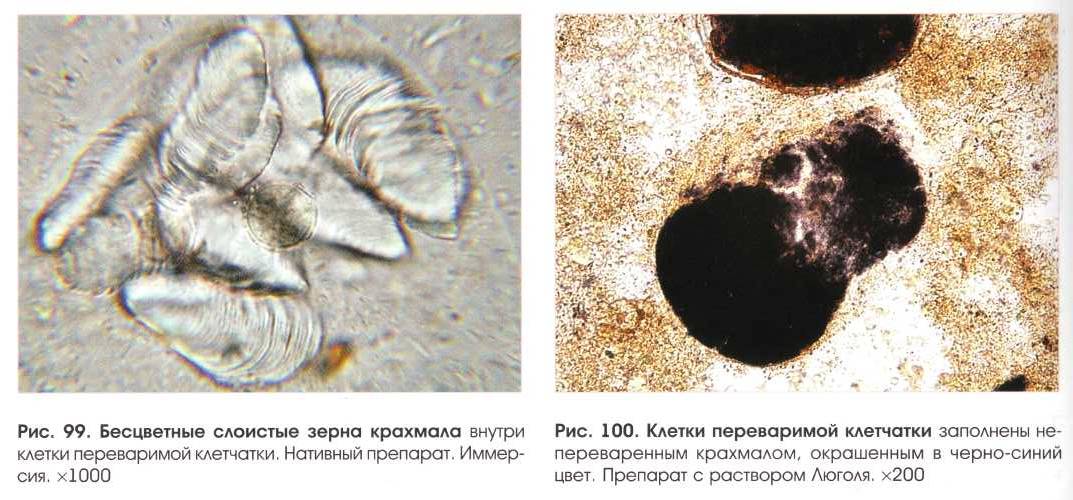
Undigested starch grains in feces under a microscope
What does starch mean in the analysis of Kala?
- The study of the coprogram contains the identification of starch intracellular and extracellular. For reference values, starch should not be present in the bowel movements
- The presence of intracellular starch indicates insufficient digestive function and possible processes of decay and fermentation in the intestines. According to physiological standards, cell membranes should be destroyed under the influence of digestive enzymes, and their contents are completely split and absorbed
- Extracellular starch in feces is undigested starch grains from damaged plant cells. The non -acquired starch may indicate a low function of the amylase enzyme or accelerated evacuation of food along the intestinal tract

Currently, the bacterium of the citrobacter is the main source of nosocomial infections
What does a citrobacter mean in the analysis of feces?
- Anaerobic bacterium Citrobacter of the Enterobacteria family is part of a human conditioned-pathogenic flora. Exceeding referential indicators of the pathogen indicates dysbiosis with a possible serious infectious intoxication of the body, requiring immediate drug treatment
- Citrobacter is the most common causative agent of nosocomic angiogenic infections and urinary tract infections. This tiny microbe is able to cause outbreaks of purulent infections, gastroenteritis, toxicoinfections, mass poisoning in hospitals and children's institutions
- Citrobacter is detected when sowing feces for dysbiosis in a total examination for the presence of conditionally pathogenic enterobacteria: enterobacter, Klebsiella, Morganella, Proteus, etc. The reference norm of these microorganisms by should exceed indicator 10 4 in 1 g of feces