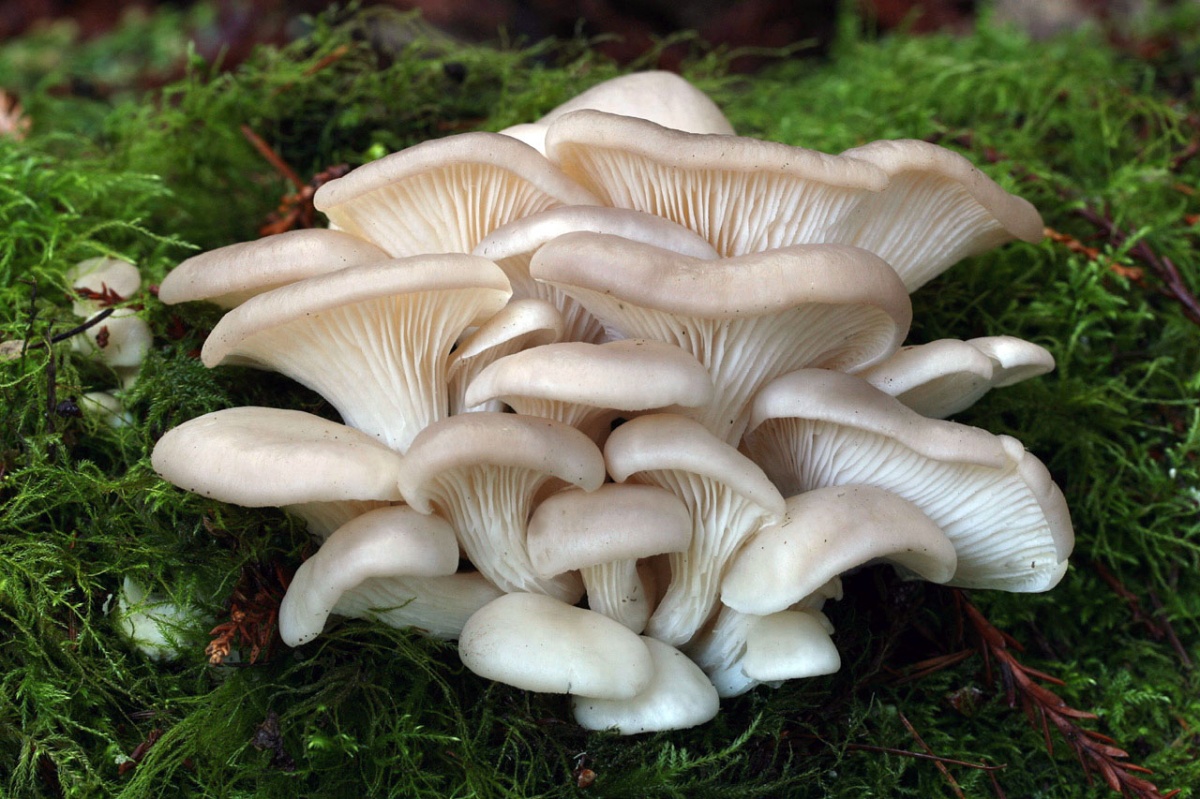
Options for growing oyster mushrooms at home.
The content of the article
- Methods of growing oyster mushrooms at home
- Where are the mushrooms of oyster mushrooms, on which trees?
- How, in what way to grow oyster mushrooms at home, in the country, garden area?
- Office grinding temperature
- Weekly diseases
- How to distinguish oyster mushrooms from casualties?
- Problems and errors when growing oyster mushrooms at home
- Video: growing oyster mushrooms at home
Growing a delicious oyster mushroom at home is not as difficult as many think. Having carefully studied the cultivation technology and acquires the necessary materials and equipment, you are guaranteed to get a crop of mushrooms with your own hand. We will consider the details and secrets of growing in the article.
Methods of growing oyster mushrooms at home
Exists two ways growing oyster mushrooms, each of which has its advantages and disadvantages:
Extensive- growing in natural conditions (in the garden, garden):
- Advantages: minimal financial costs, the crop can be harvested for several years.
- Disadvantages: Seasonality of the crop and great dependence on weather conditions.
For cultivation, use:
- logs
- old stumps
- branches
Intensive - artificially created conditions for accelerated development:
- the advantages are the rapid ripening of the product, the independence of the weather, the possibility of a crop in any season.
- disadvantages - significant investments, the obligatory presence of an equipped room with a necessary microclimate.
The role of the substrate is played by:
- the husk of the sunflower
- sawdust of trees of deciduous
- cobs and stems of corn
- straw

Oyster mushrooms at home
The main stages both methods of growing oyster mushrooms in home consider:
The acquisition of myceliumimportant indicators of which are:
- variety
- type (grain or in sticks)
- the percentage of grains
- growth rate
The heat treatment of the substratewhose purpose is:
- turn it with moisture
- provide air permeability
- disinfection of the material
Ways There are several such processing:
- xerothetermia - ferry with dry material
- pasteurization - steam with wet material
- hydrothermia - hot water
Creation of climatic conditions for mushroom growth:
- the period of incubation - germination of mycelium
- the cultivation period is the growth of fruit bodies
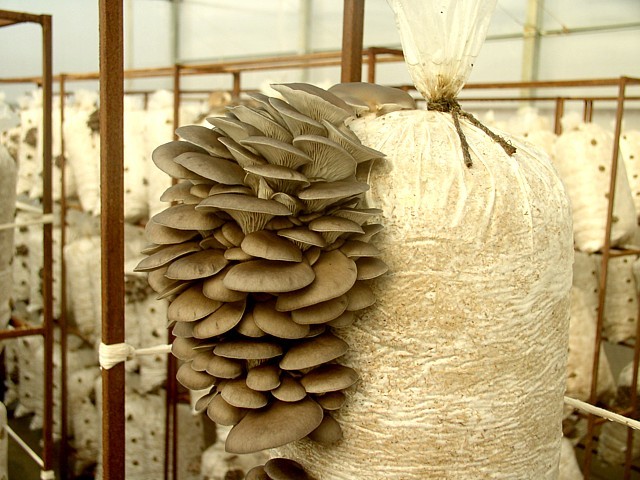
Where are the mushrooms of oyster mushrooms, on which trees?
Eye -This is a mushroom-sanprofit, that is, it feeds on components of the dead body. Therefore, it grows in large groups on lying trees, stumps, in the fault of the trunks.
Usually prefers this mushroom deciduous trees:
- osin
- kalina
- elm
- birch
- hornbeam
- poplar
However, the oyster mushroom can grow on conifers, penetrating into the northern forests. The nutritional value of the mushroom depends on which tree it grows on.

Mushrooms on trees
So, a larger amount of nutrients contains a product that has grown on a birch or aspen, and the smallest - the one that chose an oak. This mushroom begins to grow with a decrease in temperature - from mid -September to December. To find an oyster mushroom in the forest, mushroom pickers should not look at the feet, but at wood trunks, since such a mushroom loves a height.
How, in what way to grow oyster mushrooms at home, in the country, garden area?
In an apartment, it is not recommended to breed oyster mushroom in large volumes, since mushrooms require a special microclimate that is not suitable for humans. The small dimensions of our houses do not allow you to create the necessary conditions at the proper level.
Therefore, in the apartment you can grow a small crop of oyster mushrooms only as an experiment. Yes, and children, for sure, will captivate this process.
In the apartmentfor growing, it is recommended intensive method. For a substrate, use such a raw material:
- cardboard
- luzgu
- sawdust
- straw
As containers are used:
- polyethylene bags with a volume of 5 liters
- large plastic bottles
- plastic or wooden boxes
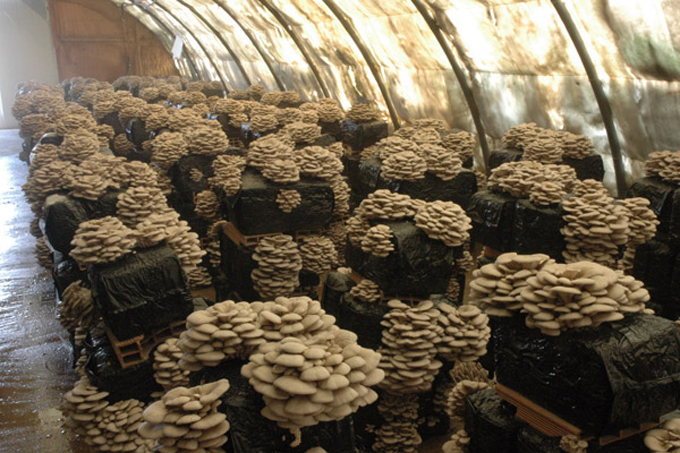

Oyster mushrooms at home
On garden plot Use extensive method growing. Choose a shady place for growing, where the direct sun does not fall. There are several main ways to organize mushroom beds:
On stumps:
- drill several holes in the old stump
- make a mycelium
- cover with straw or moss
- periodically water the soil around the stump
In the garden:
- drink a moat
- pour sand into it
- put boiled wheat or oats on top to create nutrient soil
- sprinkle bark and chips
- make mycelium
- lay out the bars soaked in water
- cover with straw on top
- in dry weather, water the moat
In the Polenitsa:
- small logs soak in water for about 3 days
- make grooves or holes
- make sowing material
- fold the logs on top of each other
- set the backups
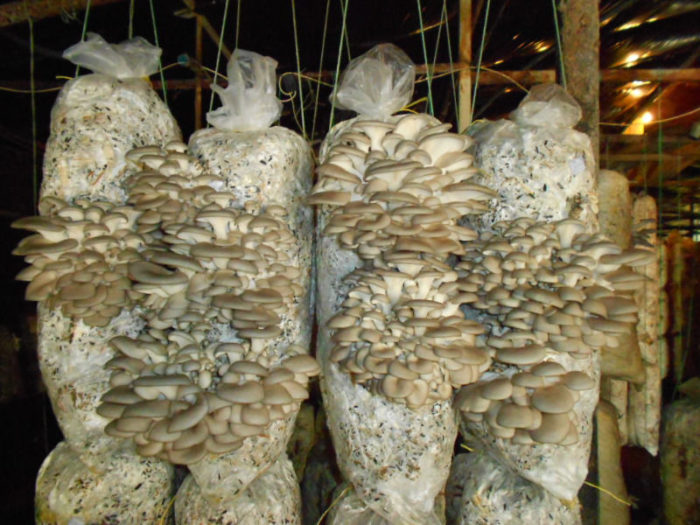

Growing oyster mushrooms
On dacha In the presence of free household premises, you can use any of them. To breed oyster mushrooms:
- basement
- barn
- garage
- cellar
- greenhouse
You can use both an extensive and intensive method and use various raw materials for the substrate.
Office grinding temperature
In natural conditions, oyster mushrooms begin to collect in May, in the summer the collection stops and resumes in September. That is, this mushroom ripens at low temperatures. These features are taken into account in industrial cultivation.
The temperature regime for the production of oyster mushrooms is very important and is set depending on the stage of development of mushrooms:
- storage of mycelium-at 3-4 ° C. Before laying in the substrate, it must be kept in the room for some time, where the blocks will be located during the growth of the mushroom lord.
- the incubation period-at 20-23 ° C. In this case, the temperature will be higher in the block itself. It is necessary to prevent changes in the temperature of the substrate above 30 degrees and below 21 ° C, since mycelium may die.
- the cultivation period is at 15-17 ° C. After the rudiments of the fungus appeared, the temperature must be reduced. At a temperature of up to 10 ° C, the oyster mushroom grows slowly, and her body will be dense and solid. With higher degrees (18 or more), mushrooms grow faster, but at the same time they are loose and bright.
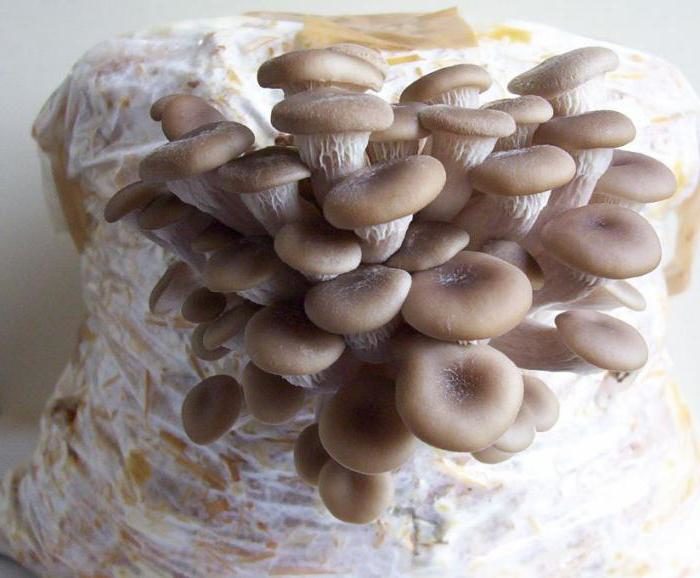

For growing oyster mushrooms, the correct temperature is needed
Violations of the cultivation technology and non -compliance with the temperature regime can lead to the death of the mushrooms and fruits.
Weekly diseases
When growing mushrooms, you need to know what diseases they can be subjected to. The most frequent oyster mushroom diseases:
- bacteriosis - spots of brown shades and an unpleasant odor appear on the fungus. The reason, as a rule, is the waterlogging of the substrate. Treatment is not amenable. Sick mushrooms must be disposed of.
- different types of mold (Trikhoderma, Muror, Penicilli) - the mold mushroom competes with the oyster mushroom for obtaining nutrients, as a result of which the mycelium slows down growth and gradually dies. The main reasons are the infection of the substrate or premises with spores of mold, non -compliance with climatic conditions.
- pathogenic mushrooms (verticillum, dactilium) - the hat is deformed. The reason is high humidity and temperature. In addition, infection with pathogenic organisms can occur through insects or poorly closed doors.
- viruses - fruit bodies have a shortened leg and thin hat. The reasons for the appearance of these diseases today are poorly studied.
Oyster mushrooms can attack viruses and fungi
In addition, oyster mushrooms can be damaged by parasite insects:
- mushroom mosquitoes
- gallines
- flies-humps
- ticks
The main reason for the appearance of insects is non -compliance with sanitary requirements in the room and improper processing of the substrate. The main measures to prevent fungal diseases are:
- thermal processing of raw materials for the substrate
- compliance with sanitary requirements
- checking mycelium for mold and parasites
- frequent washing of workwear
- protection of ventilation holes with special nets
- tightly closing doors to a room with mushroom blocks
How to distinguish oyster mushrooms from casualties?
In natural conditions, the oyster mushroom grows on trees and stumps. The fleshy hat at the mushroom is round and one -sided, the plates from it smoothly go to the leg. The color depends on the type of oyster mushroom: shades vary from lemon to gray.
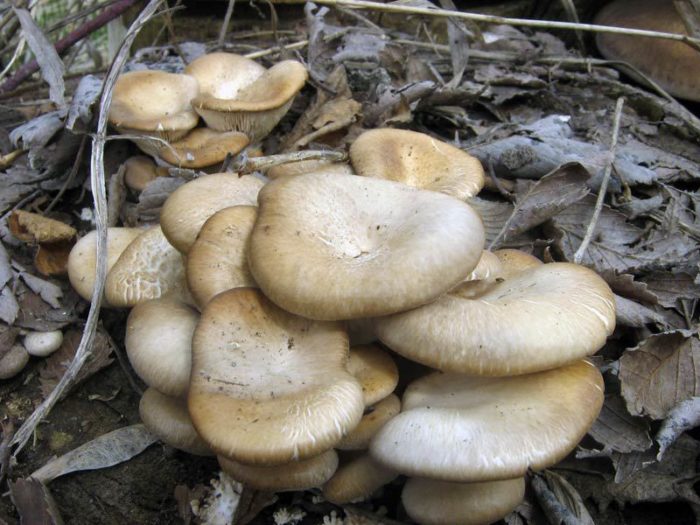

Eye
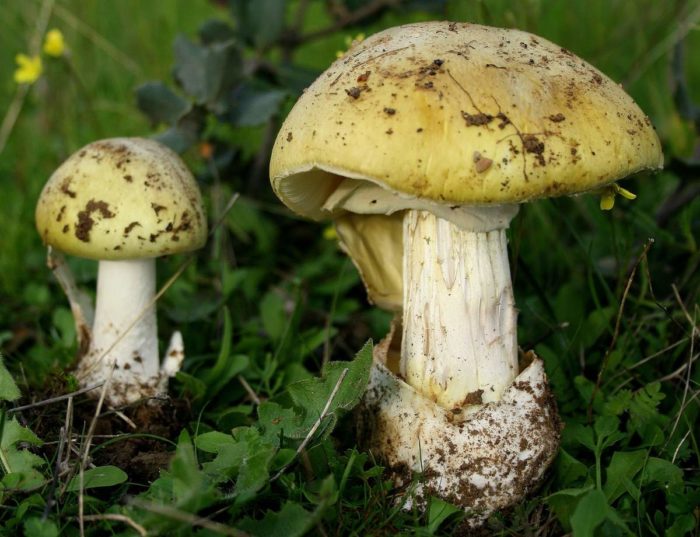

Toadstool
Fortunately, mushroom pickers may not be afraid to confuse this mushroom with double -hazardous doubles. There are practically no toxic mushrooms similar to oyster mushrooms in our regions. The oyster mushroom can be similar to some just inedible mushrooms (for example, with a pilot).
The main difference, thanks to which you can find out the oyster mushroom, is its improper -shaped hat, which has a certain surface. However, do not forget about the main rule of the mushroom pipe: if you doubt the definition of the mushroom, do not tear it.
Problems and errors when growing oyster mushrooms at home
Sometimes novice mushroom workers, having spent a lot of effort, time and finance, do not get the expected positive results and are disappointed in mushroom breeding. Consider the main mistakes that are often made at first:
- Poor raw materials for landing. When buying mycelium, pay attention to its appearance: it should have an orange color without black or green interspersed.
- Bad processing of the substrate. Inadequate pasteurization of the material can lead to infection of the substrate and mycelium.
- Non -compliance with microclimate. The temperature, humidity and good ventilation are the main factors of successful dilution, and they must be strictly adhered to.
- Insufficient amount of the stake in mycelium. Follow the proportions during landing-mycelium should be at least 4-5 %.

For a good harvest, you must follow the rules
- Non -compliance with hygiene requirements. Before monoculation, it is necessary to disinfect all surfaces, landing in gloves.
- Growing different strains in one room. It is impossible to create the necessary conditions for incubation and cultivation simultaneously in one room. Different periods need its own temperature regime.
- Parasites. Mushroom insects can start in the blocks, especially after the second harvest. It is recommended to hang adhesive tapes in the room for tracking. The affected block must be removed.
We also advise you to get acquainted with technologies for growing oyster mushroomsas well as useful information for novice businessmen in the field of mushroom growing.