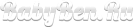
Not a single person is safe from injuries. First aid, these are the skills that everyone should ideally possess. I suggest you get acquainted with the rules for first aid for various types of bleeding.
The content of the article
- Emergency assistance algorithm for bleeding: Ways to stop bleeding
- Temporary way to stop bleeding
- Types of bleeding and first aid for bleeding
- First aid for bleeding for bruises and fractures
- Inquisition for arterial bleeding
- Venous bleeding, signs and first aid
- Emergency assistance in capillary bleeding
- Assistance in nasal bleeding
- First aid for gastrointestinal bleeding
- Uterine bleeding, help
- How to provide help with bleeding: tips and reviews
- Video: First aid for bleeding
Emergency assistance algorithm for bleeding: Ways to stop bleeding
With any type of bleeding, it is extremely important to provide assistance in time in time in time to avoid critical blood loss, which is possible with serious injuries and damage. To provide first aid, use the following algorithm:
- Make sure that you and the victim are safe (at a safe distance from the roadway, away from fragments, etc.)
- Call for help and call an ambulance
- Check consciousness
- If possible, put on gloves
- Free the affected area from clothes
- Determine the type of bleeding
- Try to stop bleeding
- If necessary and in the absence of contraindications, anesthetize
- Psychologically support the victim before help arriving

The need for first aid for bleeding
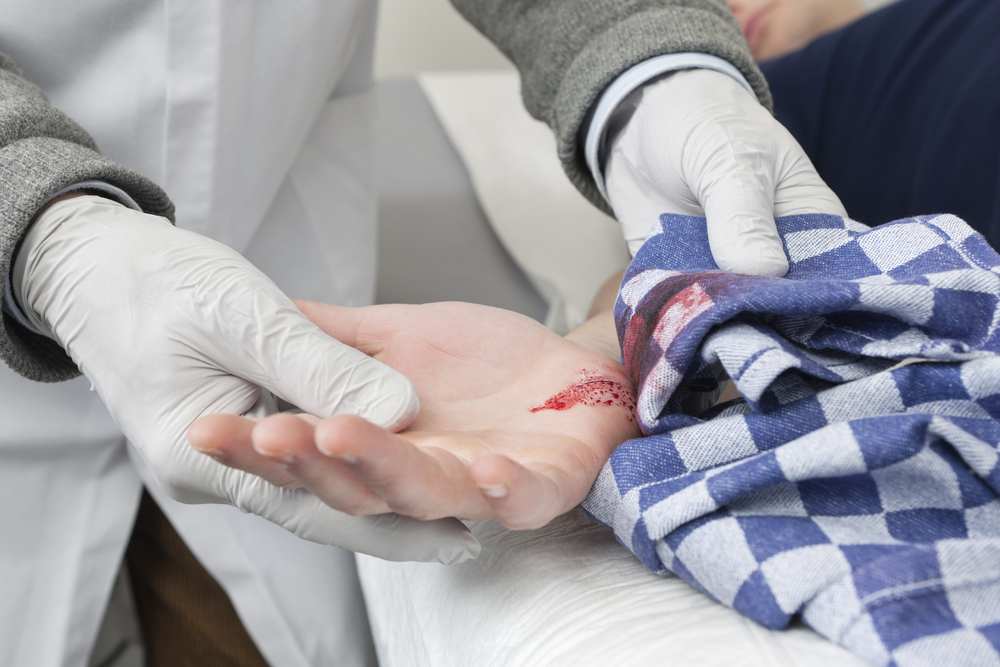
Temporary way to stop bleeding
The method of stopping bleeding depends on its type and cause. First, we determine the nature of the bleeding: the amount of blood and the intensity of its flow. If there is a lot of blood, then there is a danger of blood loss and the main goal is to close the wound with a pressure bandage.
If there is a small amount of blood, then rinse the wound before avoiding infection before applying the dressing. If you see that blood flows with a fountain, you need to apply a tourniquet as soon as possible.
And now I suggest that you familiarize yourself with the methods of temporary stopping of bleeding:
- raising the limb or injured area - to achieve out the outflow of blood from the injured area. If the limb is injured, raise it if the wound is located on the body - put it on the opposite side
- putting the bandage - the dressing must necessarily exert pressure on the wound. To achieve this on a napkin laid on the wound, place the roller from the bandage, then tightly bandage
- the use of cold to the injured area is often used for internal bleeding
- tampon insertion into the wound - used for arterial bleeding in the limbs in the presence of a deep wound
- squeezing the arteries is the fastest and most effective way to stop. Press the artery with your fingers in the area between the wound and the heart so that the blood stops flowing to the injured area. Use this method on the artery area, as close to the skin as possible. The disadvantages of pushing are rather painful sensations
- burning - used for damage to large arteries
- flexion in the joint - causes vascular overflow and reduction of blood flow to the wound
Methods of temporary stopping bleeding
Types of bleeding and first aid for bleeding
Bleeding are five types that differ in danger:
- Capillary bleeding is the most “harmless” bleeding, which practically does not pose a threat to human life and health. Occurs with injections, abrasions, small cuts and scratches
- Venous bleeding - poses a serious threat in the absence of first aid for a long time. Blood in dark color, flows slowly, at the same speed
- Arterial - one of the most dangerous bleeding due to quick blood loss. You can recognize the blood of scarlet color, which, when flowing pulsates, is pulsed with a fountain
- Parenchymal bleeding - occurs with penetrating wounds and injuries of internal organs. You can recognize it by blood from a wound, blood -soaked clothes or blood near the victim
- The internal is the most dangerous type of bleeding due to untimely recognition. It mainly occurs during injuries and bruises of internal organs. It is possible to determine the presence of internal bleeding only pain at the place of injury (which may not be) and signs of blood loss (weakness, thirst, vomiting, fainting, pallor, weak pulse, rapid breathing)
Types of bleeding
First aid for bleeding for bruises and fractures
As a result bruise Bleeding from the nose may begin. In severe cases, internal bleeding is possible. You can determine the likelihood of the latter by the following signs:
- Rapid pulse
- Low pressure
- Pallor
- Pain in the abdomen
- In some cases, a bruise is visible
- In case of damage to the stomach or esophagus, vomiting may be very dark blood
- The bowel moved is indicated by the tar
- Blood foam cough speaks of light injury
In the presence of internal bleeding, attach the cold to the injured area, calm the victim. In the case of a lung injury, give a person a half -blue position, in other cases, lay on an even surface until an ambulance arrives.
Important: if you suspect internal bleeding, in no case do not feed and do not give the victim, you can not give medications.
Fractures There are open and closed. With a closed fracture with a clearly expressed bruise, immobilize the injured part and attach the cold until hospitalization.
Open fractures carry great danger due to the rupture of soft tissues and the formation of an open wound. After you fix the limb, treat the wound and stop bleeding. The method of stopping depends on the type of bleeding.
IMPORTANT: If you need to apply a tourniquet with a fracture, do it for the shortest possible time
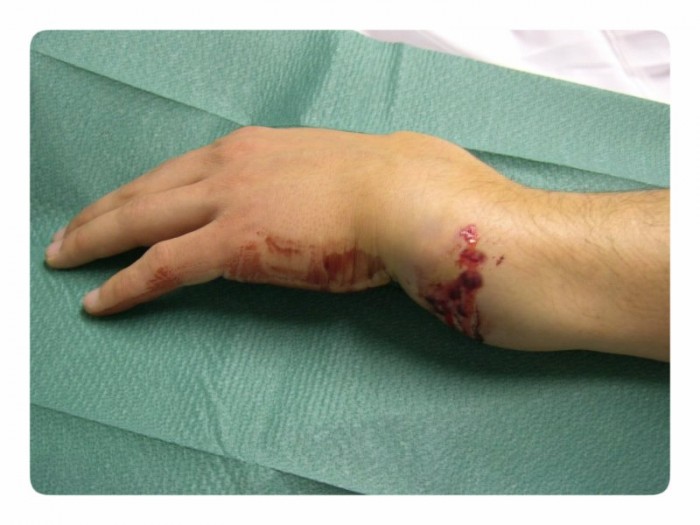
Bleeding with a fracture
Inquisition for arterial bleeding
Arterial bleeding is extremely dangerous due to the danger of quick and severe blood loss. For example, with a strong wound, a liter of blood can result in a matter of minutes. Therefore, it is necessary to stop it as quickly as possible. For example, you should not spend precious time searching (possibly unsuccessful) sterile bandage. Use what is at hand.
The most important thing is to slow down the loss of blood, so the first thing you must do is to squeeze the artery. Then prepare the victim for transportation to the hospital and impose a tourniquet.
Important: the tourniquet can be on the victim for no more than 30 minutes in winter and 1 hour in the summer. If the help has not arrived yet, carefully and, most importantly, slowly remove it until the blood circulation is restored, then apply again
Arteries and a way of pressing:
- Sleepy - press the palm behind the neck, and hold the artery with your fingers, do not try to press the wound with both hands - blood is unlikely to stop in this way, and you can strangle the person
- Front - holding the lower jaw with your palm, click the artery with your fingers at the junction of the upper and lower jaw
- Temporal - click on the artery in front of the ear of the ear
- Submitted - the artery that is located behind the collarbone press to the first rib. This is a rather difficult task, so if possible, take away the victim's hand back
- Shoulder - there are no special nuances in pressing, the artery is easily accessible
- Axillary - make efforts, clamping the artery, it is located deep enough
- Podged - press in a popliteal fossa, without making much effort
- Femoral - large artery, press it to the pubic bone
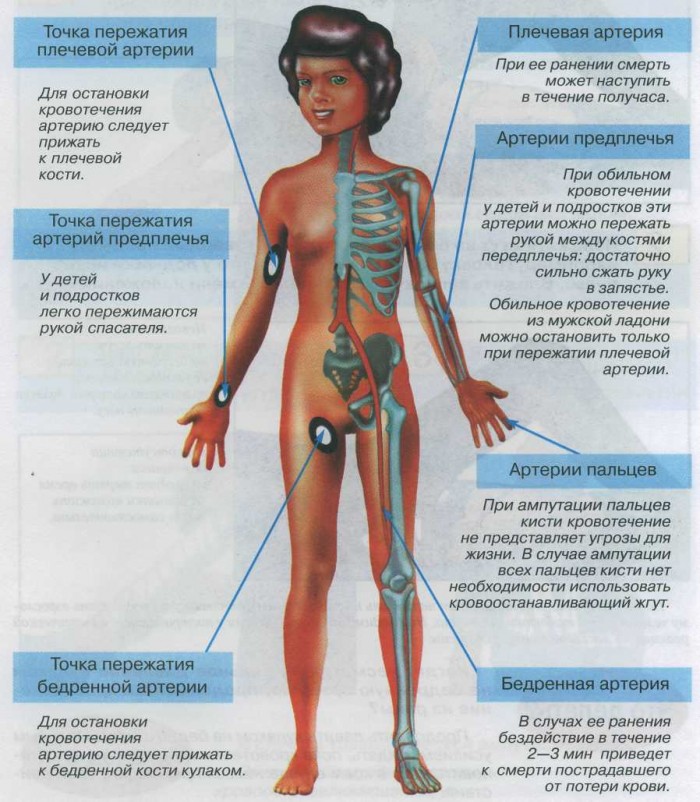
Places of contingent of arteries
How to properly apply a tourniquet:
- The tourniquet should be 3-5 cm above the wound
- Be sure to apply it on clothes or put it under the tourniquet of fabric
- Stretch the tourniquet and wrap 2-3 times around the limb, fix it
- Wrap the injured limb with clothes or fabric
- Under the tourniquet, be sure to put a note with the exact time of applying the tourniquet so that it is immediately visible. It is even more reliable to write time on the forehead of the victim
- With proper imposition of a tourniquet, you should not feel the pulse below the tourniquet
Instead of a tourniquet, you can use a rubber hose, belt, bandage, tie and other improvised materials with the exception of thin inelastic objects, for example, laces, thin rope, etc. In the case of the use of rag improvised bundles, fix them with a loop, under the knot of which place a stick. With its help, you can tighten the bandage qualitatively. Strengthen the position of the stick to avoid untwisting the burning of the tourniquet.
Important: apply a tourniquet only in case of bleeding from the shoulder or femoral artery, but not to the area of \u200b\u200bthe middle third of the shoulder and the lower third of the thigh.
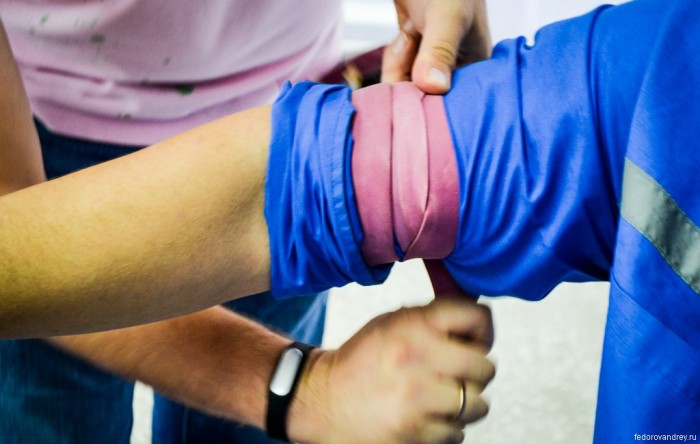
Burning for arterial bleeding
Venous bleeding, signs and first aid
With venous bleeding, blood flows evenly. It poses a threat to blood loss in the absence of timely assistance. In addition, if the wound is located on the neck or in the chest area there is a risk of air entering the vein when inhale, which leads to death.
Do not try to rinse the wound or remove excess from it (fragments, dirt, etc.) and in no case do not touch the resulting blood clots and blood clots. Your task is to apply a bandage to stop bleeding as soon as possible
- Treat the area around the wound or wipe with a damp cloth
- Put a napkin on the wound, a piece of fabric or a blank handkerchief
- Close a deep wound with a swab
- Fix the napkin with a bandage
- Apply direct pressure on the wound with a small roller from the bandage
- Put a tight bandage
- Give the injured limb an elevated position
Important: if the bandage is gradually impregnated with blood, then you have imposed it incorrectly, but you should not remove it. Wind several layers of bandage from above to increase the pressure on the wound.
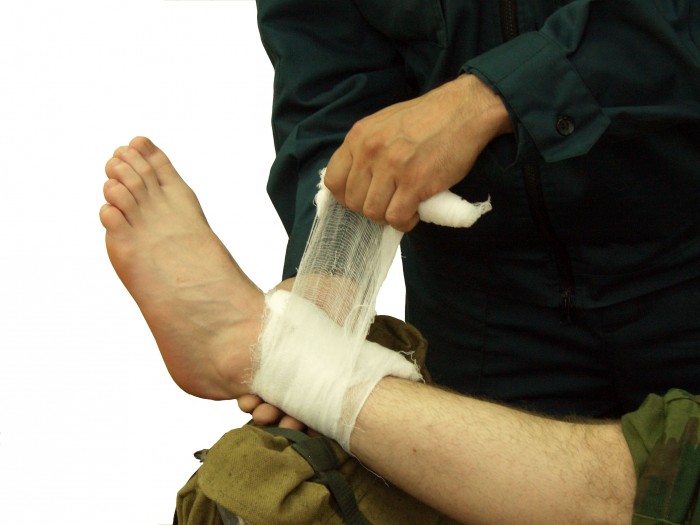
Pressure dressing
There are a number of recommendations for the correct and effective application of the dressing:
- After applying the bandage, the injured part of the body should be in the same position as during its applied
- If you bandage your hand, bend it at the elbow
- When applying a bandage on the leg, bend it at the knee, the foot should be at an angle of 90 °
- MOT WILL BINT from left to right, in addition, each new round must close half the previous one
Emergency assistance in capillary bleeding
Capillary bleeding occurs with small cuts, scratches, abrasions, small wounds. Blood flows slowly, often drops. After a while, blood turns off, and bleeding may stop independently.
- Treat damage with an antiseptic
- If necessary, put a clean bandage
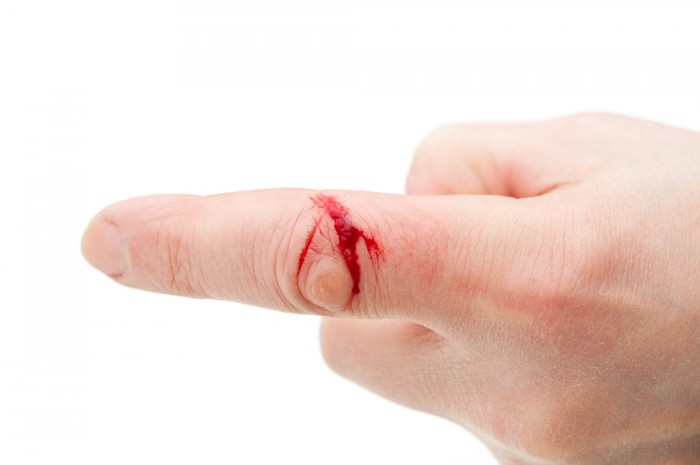

Capillary bleeding
Assistance in nasal bleeding
Nasal bleeding is referred to special cases of external bleeding. If you are faced with this case, do the following:
- Calm the victim
- Attach the cold to the nose
- Place the swab or press the napkin in the nasal cavity
- Ask the victim to tilt his head
- Call an ambulance if in 15 minutes bleeding does not stop
Important: do not let the victim throw his head away, blood can enter the respiratory or digestive paths, and bloody vomiting may occur.
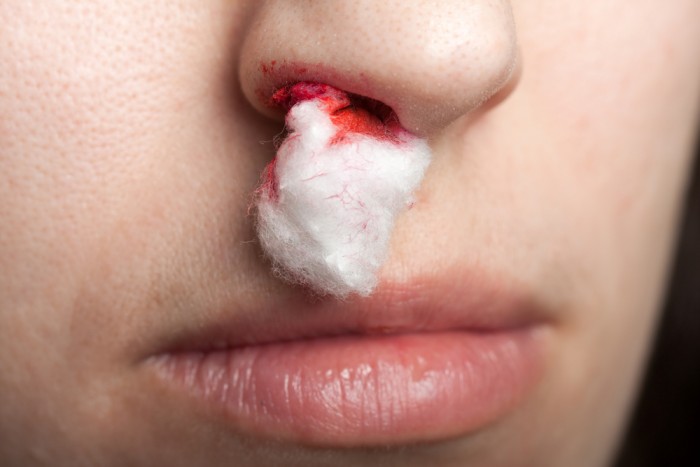
Tamponade with nasal bleeding
First aid for gastrointestinal bleeding
Gastric bleeding can occur due to ulcers, tumors, poisoning (due to abundant vomiting), severe bruises, entering the esophagus or stomach of an outsider. You can recognize by the following signs:
- Vomiting with very dark blood
- Dark tar -shaped chair
- May attend the pain syndrome
- Confusion
- Pallor
- Sharp weakness, flickering before eyes, fainting
- General signs of blood loss
With this type of bleeding, it is extremely important to provide qualified medical care as soon as possible as soon as possible, before that you can take some steps:
- Raise the person's foot in a lying position a little
- If you have vomiting, turn your head to one side
- Put the cold on the stomach
- Calm the victim
Important: in no case do not let the victim eat, drink, medications.
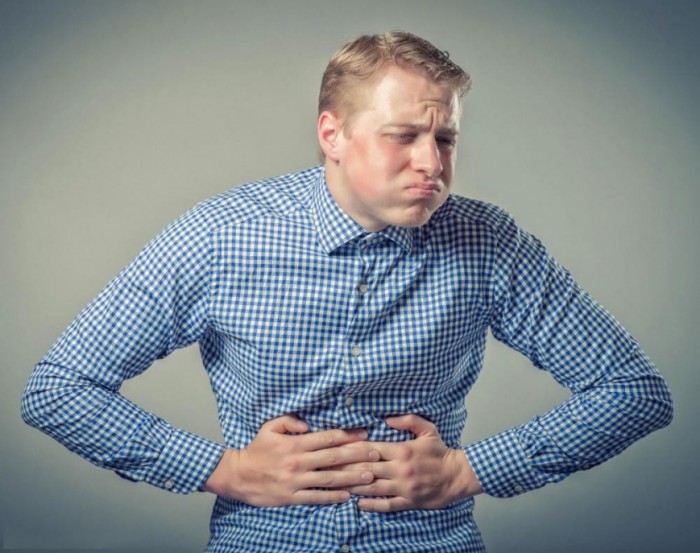

Gastrointestinal bleeding
Uterine bleeding, help
Symptoms of bleeding:
- Pallor
- Vomiting or nausea
- Blood release from the genitals
- Rapid pulse
In case of suspicion of uterine bleeding, it is urgent to deliver the victim to the hospital, and before the arrival of assistance:
- Give the body a horizontal position, lift your legs a little
- Put the cold on the stomach
- Constantly let's drink (water, juice, rosehip decoction, tea are suitable)
Important: in no case do not let the warm bath or put the heating pad on the stomach.
Uterine bleeding
How to provide help with bleeding: tips and reviews
- Do not rinse the wound with antiseptics or water, exceptions are cases when caustic substance got into the wound
- Do not use ointments and powders
- Do not remove anything from the wound, whether it be fragments, dirt or blood clots. You can provoke an increase in bleeding
- Do not remove the bandage that was saturated with blood
- Clean the skin around the wound with strong contamination. Cleaning, move from the wound, make sure that nothing gets into it
- You can not bandage over the harness. The hospital may not notice him
- Apply a tourniquet only with emergency, it can lead to irreversible health damage, as it completely covers the nutrition of tissues and bones
- Keep the material (bandage, napkins, fabric) with which you stopped blood for medical workers. This can help correctly assess the scale of blood loss
- If you managed to stop bleeding, seek medical help to properly treat the wound and avoid infection. If you suspect a significant blood loss, seek help immediately