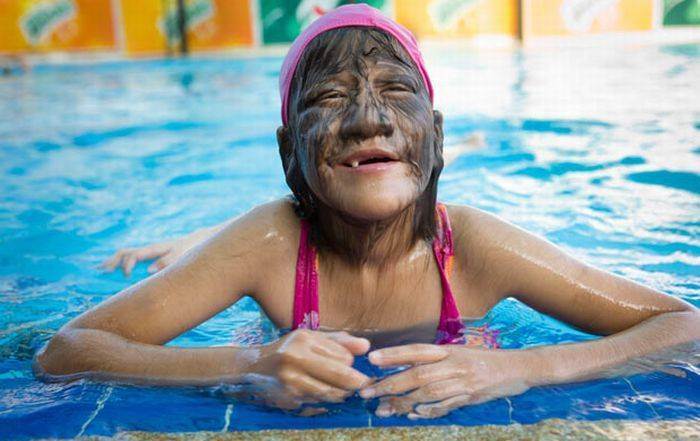
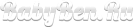Excessive hairy, or hypertrichosis, not only aesthetic problem. Perhaps the human body has a genetic failure or serious pathological processes proceed.
The content of the article
- Signs and causes of hypertrichosis. Is hypertrichosis inherited?
- Hypertrichosis in children: boys and girls
- Video: Increased hairy in women and men - how to get rid of unwanted hair?
- Hypertrichosis in men: on the face, ear sink, on the body
- Hypertrichosis in women: on the face, ear sink, on the body
- Increased hairy in girls: hirsutism
- Video: Hirsatism in women
- Flip hypertrichosis
- Acquired hypertrichosis
- Treatment of hypertrichosis
- Video: Hypertrichosis or werewolf syndrome
The whole body of a person is covered with hair. The head and the genitals are long, brightly painted and gestured, the superfluous arcs and eyelids are bristly. In other parts of the body, the hairs are short, thin and very bright, almost invisible, fluffy. However, it happens that in those areas of the body where there should be a fluff, hard dark hair begins to grow, sometimes even similar to wool. This condition is called hypertrichosis.
Signs and causes of hypertrichosis. Is hypertrichosis inherited?
The scientific term "hypertrichosis" is of Greek origin and means excessive (beyond measure) hairy. Men are more susceptible to this phenomenon (the disease is gripped with sex), but it is also found in women (more often acquired).
- The hair on the head and body of a person was previously not too fairly called atavism. But it is proved that even today they perform a protective function, protecting individual parts of the body and their heads from overheating, hypothermia, injuries, so on
- When the child undergoes intrauterine development, his whole body is covered with primary hairs (germs, or lanugo), which by 8-9 months of pregnancy, and sometimes secondary (fluff) turn into hairs soon. Hard long hair appears on the head of the baby during the first year of life, but it happens that the baby is born already with a hairstyle
- In the period of puberty in men and women in the genitals, under the mouses, less often on the inner part of the hips, legs, forearms, the stomach appear hormone-dependent terminal hair. The fact is that the hair onion guns in these places very violently react even to a slight increase in testosterone production and reborn
Important: With hypertrichoz, terminal hair may appear on the body anywhere, even where the hair follicles are indifferent to testosterone
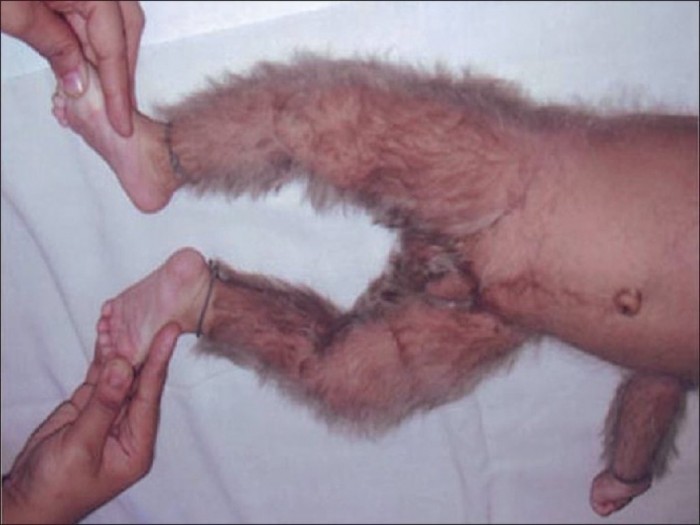
Hypertrichosis is very often congenital.
By the nature of the causes that contribute to excessive hairiness, hypertrichosis is classified on:
- congenital (universal, if the hair is covered with the whole body, and local, if terminal hair appeared on certain parts of the body)
- acquired
By the way, exactly the hair was reborn into terminal, ailment happens:
- pushkov
- organic
- lumbar-sacral
- unwearing
- symptomatic
- yatrogenic
Important: Previously, people with hypertrichoz were called "wolves" or "lions". They were afraid and could drive out of the villages. Hairy people often became artists "Circus freaks"

The causes of pathology are:
- Heredity and disruption of the development of the fetus. It is known that hypertrichosis is inherited by the male line (adhesion with chromosome y). It may also be a symptom of the pathology of the development of nervous and bone fetus systems, manifest itself in the syndrome of congenital deformity (for example, alcoholic). Mutation can also occur due to intrauterine infection or due to the reception of the future mothers of drugs prohibited during pregnancy
- Endocrine diseases and jumps of hormone levels. Hypertrichosis is not necessarily manifested in newborns. "Unnecessary" hair may appear during puberty, during pregnancy, due to diseases of the endocrine glands
- Benign and malignant tumors of endocrine glands, mammary glands and head
- Stress
- Reception of certain medicines
- Infectious diseases, including venereal
- Injuries
- Frequent shave and depilation
- Inflammatory processes
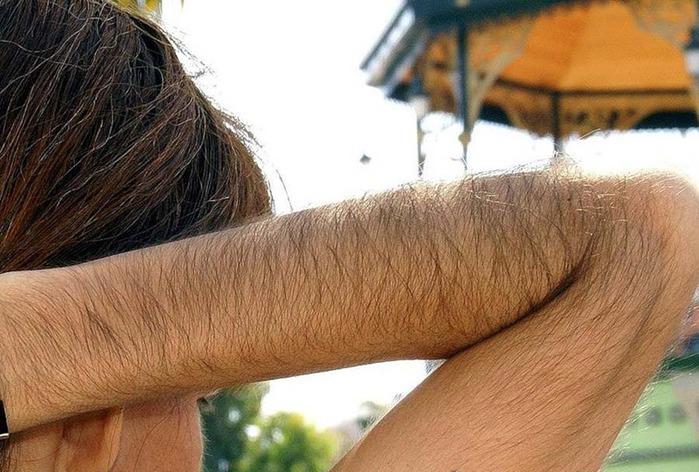

Congenital malformations, endocrine diseases, frequent shave, stress - some of the causes of hairiness.
The main symptom of hyperitrichoz is the growth of hair where they should not be.
Hyperitrichoz in children: boys and girls
In a newborn child, especially if he is born ahead of time, the body can be covered with lanugo hairs, which soon roll out. But sometimes, doctors observe the transformation of epithelial tissue into tissue with hair follicles where hairyness should not be ethnic and age -related signs, as well as the laws of nature.
A premature child can be born with Lanugo. This is not a disease.
Important: in this case, you can suspect a genetic disorder in a child. He needs to conduct appropriate tests to identify the corresponding pathology
Acquired hairy in older children can occur due to the disease:
- bullous epidermalization
- brain injuries
- brain tumors
- fungal skin disease
- epilepsy
- diseases of the glands of internal secretion
Important: in girls and boys, the presence of hair under mice, on the genitals, on the legs, forearms, stomach, back and shoulders is not the norm. The same can be said about the hairs not to the chin, cheeks, upper lip
Having discovered signs of hypertrichosis in a child, parents should show it to a specialist:
- genetics
- dermatologist
- endocrinologist
- neuropathologist
- children's gynecologist (for girls)
Children with congenital hypertrichosis.
The treatment of hairy in children depends on whether it is innate or acquired:
- If the hypertrichosis is hereditary, nothing can be done, except to mechanically remove unwanted hairs, choosing the most acceptable method for the child, for example, electro -power
- If the disease occurs throughout life, it is necessary to eliminate its cause (treatment with hormones, for example)
Important: hypertrichosis gives rise to complexes and other psychological problems in the child: not like others, a boy or a girl is teased at school. It is important for parents to behave as delicately as possible during the search for the cause of pathology and treatment of hypertrichosis. In no case should the child show his fear or excitement
Also, parents should not independently remove excess hairs from the baby, Brey or plucking them. Such mechanical procedures will only aggravate the problem.
VIDEO: Increased hairy in women and men - how to get rid of unwanted hair?
Hypertrichosis in men: on the face, ear sink, on the body
Excess hair in men can be associated with one of the above reasons, as well as because of:
- excess of testosterone
- alcoholism
Testosterone - Steroid hormone - Androgen, synthesized in men in the testicle and adrenal cortex. It is responsible for the functioning of the male sexual system, muscle mass in men. Its increased development can be associated with:
- diseases listed above endocrine glands
- violations of metabolism
- reception of hormonal drugs
- reception of steroids in athletes increasing muscle mass
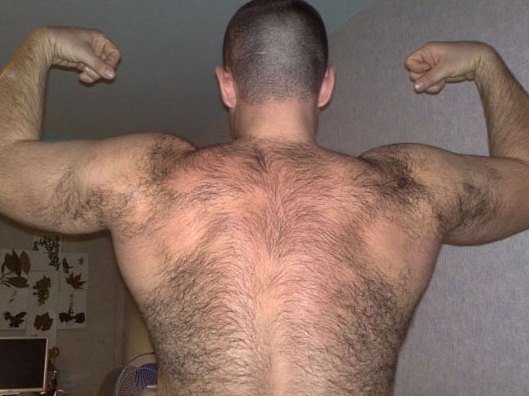
Hypertrichoz in a man due to the overstero testosterone.
This pathology is characterized by the appearance of unwanted hair on the body, in the ears, on the face. Wherein:
- on the head hair, on the contrary, fall out
- men can show attacks of unreasonable aggression
- he complains of headache
- he is tormented by insomnia
It is impossible to ignore the problem. Necessary:
- pass analyzes for hormones
- refuse to receive steroids
- correct the reception of hormonal drugs
- get consultation of an endocrinologist about the treatment of diseases of the testicles or adrenal glands
IMPORTANT: According to statistics, the hyperitrihosis suffer 14 men out of 100
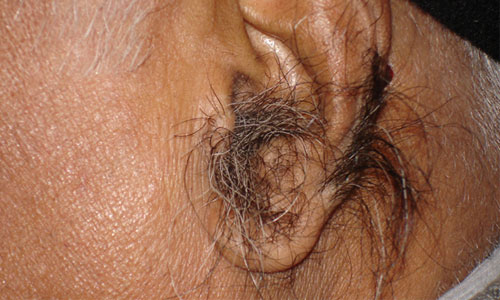
Hair in the ears in a man.
Hypertrichoz in women: on the face, ear sink, on the body
If the increased hairiness is not hereditary, it may arise from a woman in two very important periods of her life:
- In adolescence (from 12 to 17 years). Usually, hair command on the neck, back, chest, stomach, the legs and hips of the girl is associated with a violation of important endocrine glands - adrenal and ovarian bark
- In the menopausal period. In the second half of life, a woman in the body occurs the strongest hormonal storm. All glands of internal secretion are rebuilt. The level of female hormones is constantly jumping. A couple of years after the onset of menopause, the hair of a woman can appear above the upper lip (mustache), on the cheeks, in the chin area, in the nose or ears
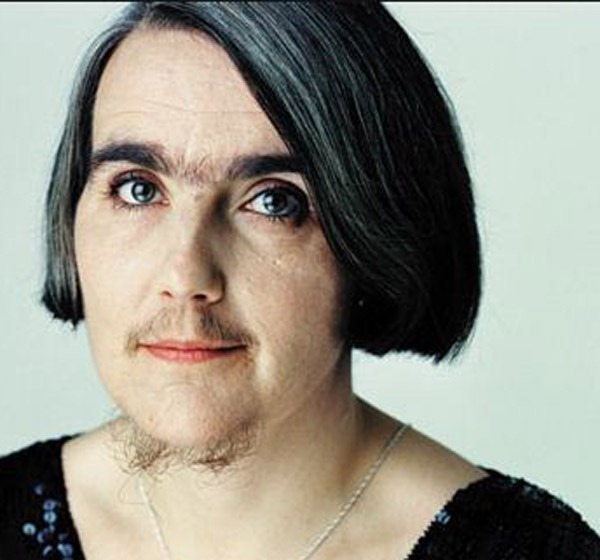

Climacteric hypertrichosis.
Important: If a woman in childbearing has sharply grown hair in unexpected places, it may have polycystic ovarian syndrome. Need to do ultrasound and get a consultation of the gynecologist
Increased hair in girls: Girsutism
Beard, mustache, chest and leg hair - secondary sexual sign in men, which appears during their sexual maturity under the influence of androgen hormones. So the nature has ordered that women's and men's hormones are synthesized in the organisms of both sexes. And if suddenly it happens that the concentration of male hormones in the blood of a woman rises, it can develop excessive oversight. Such a phenomenon is called girsutism.
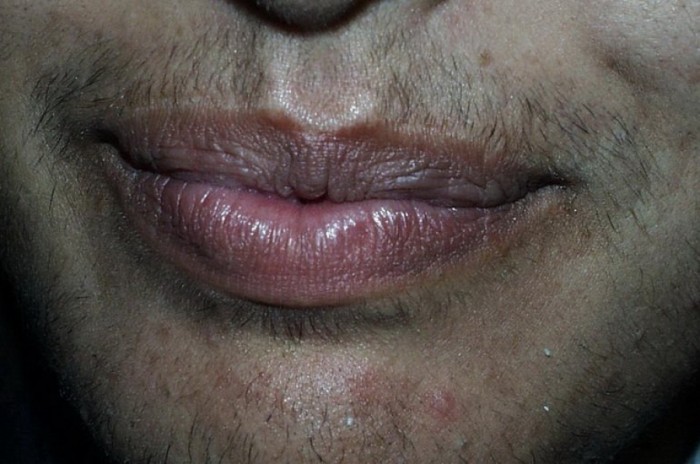
A mustache and beard in a woman.
In addition to the growth of hair where they should not be, a woman is worried:
- menstrual cycle violations up to amenorrhea
- infertility
- increase muscle mass
- dry vagina
- breast Reduction
- raising libido
- voice changes (it becomes lower and rougher)
Important: one hair removal is not solves the problem of hirsutism. It should be seen for the cause of the work of the pituitary gland, ovarian or adrenal glands, the reception of hormonal drugs, and eliminate it
The girl should stop shy to his hairiness and turn to the endocrinologist, as well as pass tests for the content in blood serum:
- testosterone
- androstandion (ovarian hormone)
- dehydroepiyndrosterone (adrenal hormone)
- other men's hormones
Usually, hirsutism is fairly easy to treat. It is necessary to treat the diseases of the endocrine glands, provoked by the exhaust. The girl also suggests a course of treatment with oral contraceptives.
Video: Girsutism in women
Pushchy hypertrichosis
Pushkovy hypertrichosis is diagnosed in the case of rebirth of light and short powder hair into dense and pigmented. For several months, they are capable of growing at a length of 10-15 cm. Such "wool" covers the whole body and face of a person, except for his palms and feet.
IMPORTANT: scientists are notified by sad pattern - after a few months or years in a person with a powder hypertrichoz diagnose cancer
Tumor, most often, amazes:
- lungs
- colon
- the gall bladder
- bladder
- milk glands
Acquired hypertrichosis
Acquired hairiness, as mentioned above, is a few species:
- Traumatic. The most common example is a frequent shave or stitching, when terminal hard hairs are growing on the skin instead of the gun on the skin. A similar can also occur due to the wearing of plaster or leucoplasty, long-term use of ointments and creams with an irritant effect. Haired sometimes turn scars and scars
- Drug. Hair growth is provoked by the reception of glucocorticosteroids, anabolics, androgen. These are: psoralyn, psoriazine, diazoxide, danazole, cyclosporine, others. Hypertrichosis can be caused by anti-tuberculosis streptomycin
- Symptomatic. In this case, the extension of unnecessary places is not a separate disease, but a symptom of another pathology. For example, tuberculosis in children can appear between the blades. Excessive hair growth is also observed in diabetes mellitus, Ashara syndrome - TEER, Porphyry, dermatomyositis, brain tumor diseases, other
- Neurogenic. The cause of neurogenic hypertrichosis is an injury to the spinal cord or any nerve
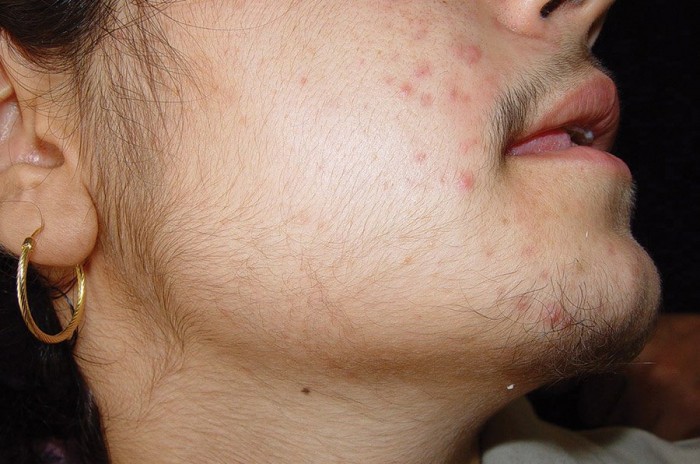
Ashara Tier Syndrome.
Treatment of hypertrichosis
Unfortunately, congenital hypertrichosis in children, men and women is not treated. Only modern cosmetic methods help to get rid of unwanted hair: laser, photo and electro -power.
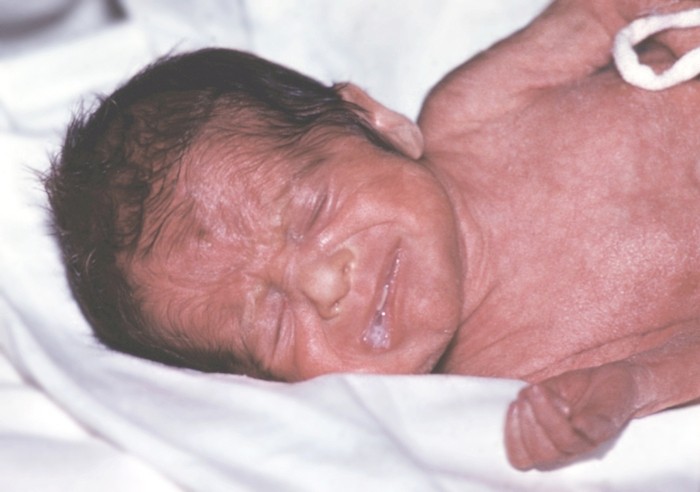
Important: an example of congenital hypertrichosis are three sisters of Sangli from India. All three were born hairy and already in adulthood passed the procedure of laser hair removal
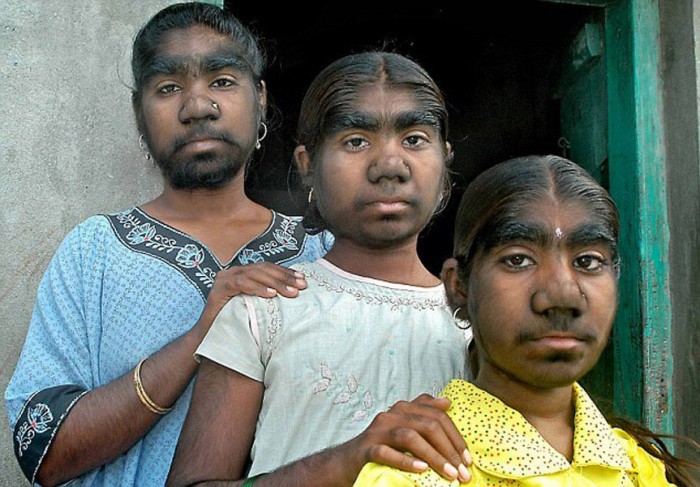

Sisters Sangli, patients with congenital hairy.
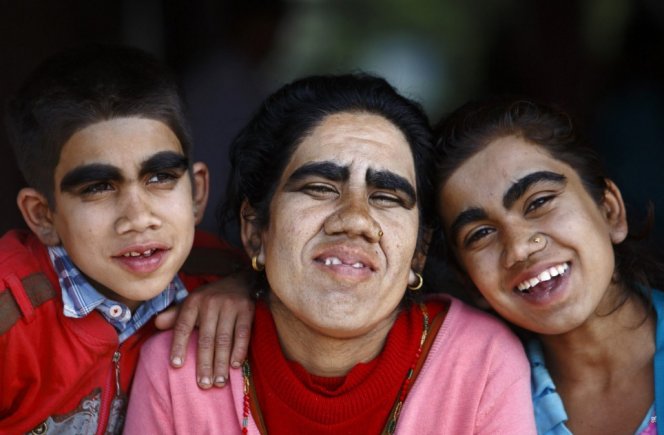

Sisters Sangli after laser hair removal.
The acquired hypertrichosis is treated with the elimination of its cause and symptomatically.