Why do children get viral hepatitis? What are the symptoms of these liver diseases? Is it possible to recover from hepatitis A, B and C? Are the vaccinations from hepatitis effective.
The content of the article
- Viral hepatitis: symptoms and causes in children. How is hepatitis A and B transmitted? How is hepatitis C transmitted?
- Video: Viral hepatitis
- Symptoms of hepatitis A in children
- Symptoms of hepatitis B in children
- The main symptoms of hepatitis C in children
- Video: Hepatitis A. Viral hepatitis with symptoms treatment. Chronic hepatitis B symptoms. How to treat hepatitis with
- Hepatitis treatment
- Is it worth making a child vaccine from hepatitis? Vaccination from hepatitis A and in children. Graft from hepatitis C for children
- Video: Viral hepatitis - the school of Dr. Komarovsky
Viral hepatitis is a group of very serious infectious diseases, during which the liver is inflamed, increases in size and ceases normally. According to people's prevalence, these diseases are in third place after respiratory and intestinal infections. Doctors beat the alarm - more than half of those who suffer from hepatitis of one form or another are children.
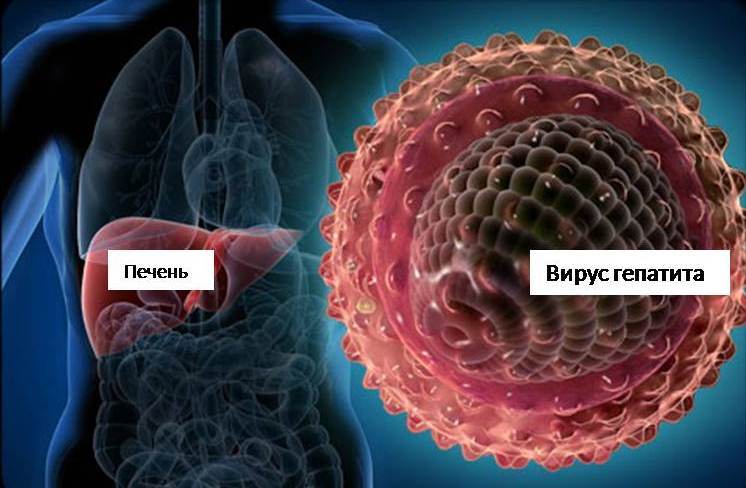
Viral hepatitis: symptoms and causes in children. How is hepatitis A and B transmitted? How is hepatitis C transmitted?
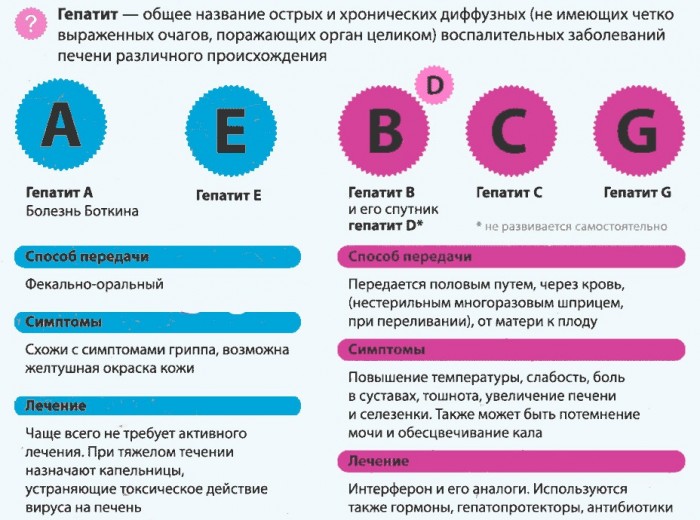
Viral hepatitis is a generalized name of a group of diseases. In total, 8 viruses provoking inflammatory liver disease are known. Most often found:
- hepatitis A (up to 70% of patients with hepatitis children suffer from this form)
- hepatitis B (about 11% of the total number of hepatitis in children)
- hepatitis C.
- hepatitis D (rarely meets independently, usually, accompanying hepatitis B)
Also there are hepatitis E, F, G, SEN, TTV, but they are diagnosed much less frequently and today not fully studied.
Important: The liver can be inflamed not only because of infection. In the hotel group, hepatitis noncommunicable - autoimine and toxic
Forms of hepatitis, most common in children.
There are vigorous forms of hepatitis in children by the method of infection with a virus, manifestation of symptoms, adorable treatment and outcome. But regardless of the competitive type of causative agent, hepatitis viruses in the body of a child or an adult behave in about the same:
- the virus penetrates the human body
- with blood flow, it is transported to the liver
- due to the special structure, the virus is easily attached to the hepatocyte wall
- RNA or DNA of the virus penetrate hepatocytes and embedded in its genome
- viruses multiply inside the cell, after which they leave it and amaze new hepatocytes
By spending an incredible amount of energy to reproduce the virus, the liver ceases to work normally, all its functions are disturbed.
General information about viral hepatitis.
Important: Viral hepatitis is highly contagious. Not only single cases of infection among children are recorded, but also outbreaks and even epidemics
A distinctive feature of all hepatitis viruses that are striking children and adults is their vitality outside the human body. Absolutely, all strains are successfully opposed to many environmental factors, such as:
- low and high temperatures
- dry air
- ultra-violet rays
- impact of certain chemicals
- other
Important: Virus provoking the inflammation of the liver can live half an hour at ambient temperature in plus 60 degrees
Hepatamiruses are transmitted to man to man. With all the forms of the disease, except hepatitis A, possibly passive virons.
Mechanisms of infection in certain types of hepatitis differ:
- Hepatitis A and E are transmitted fecal - orally: the virus is isolated with the feces and the urine of the patient and, due to the neglect of personal hygiene rules, it can get into the skin of a healthy person through a handshake, for example, children's toys, personal hygiene and life, and then in The mouth of the child (contact - household journey). If the virus falls into water or food, it can provoke an outbreak of the disease or even an epidemic. There is also a theory that hepatitis A can be transmitted and airborne droplets, but scientists are not convinced of this to the end
- Hepatitis B and C are transmitted through blood (C virus - and through other organism fluids). And to get infected, it must be literally one drop. Infection most often happens with poor quality medical manipulations: dental procedures, surgical operations, hemodialysis, blood transfusion, organ transplantation, other. Often the virus is transmitted from the mother to the child in the womb, through blood during childbirth, and strain C - with breast milk and, in rare cases, through saliva. These forms of the disease are terrible in that they have a long incubation period, at the end of which the patient is already infectious, and the hidden form of the flow (the absence of symptoms in humans does not mean that it does not distribute the virus). Child - Teenager can "pick up" hepatitis during manicure, piercing ears, piercing, tattoo application
Important: It is important for parents to engage in sex education and to tell them about the danger of sexually transmitted diseases and ways of protection against them. Hepatitis B and C are transmitted during sex
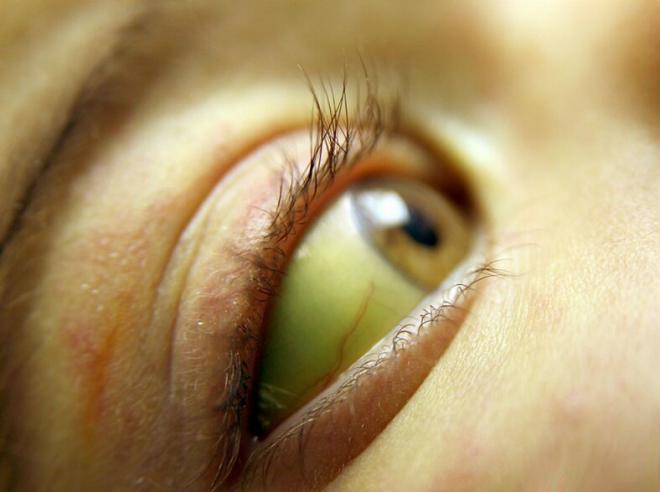

Jaundice in a child occurs with any form of viral hepatitis.
Noteworthy is the fact that infection of one form of hepatitis and its treatment does not mean immunity to another.
As symptoms manifest itself, they distinguish sharp and chronic inflammation of the liver in children.
All virus hepatitis in children are characterized by cyclical flow. Distinguish such periods of the disease:
- incubation
- barbecue
- icteric
- reconvision
In this case, the jaundice period can be attended (a typical form of hepatitis) and absent (latent or erased form). In shape and the disease always has symptoms.
Symptoms of hepatitis in children differs depending on what particular virus provoked it.
VIDEO: Viral hepatitis
Symptoms of hepatitis A in children
Despite the prevalence, hepatitis A in children (or the disease of Botkin, as it is also called) is the most harmless. It is good to treat and, if it is undertaken, passes without consequences.
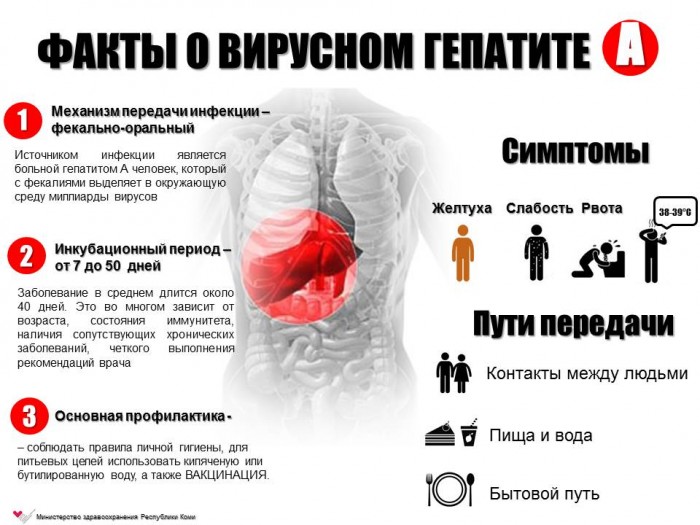
General Facts about Hepatitis A.
IMPORTANT: As a rule, hepatomirus and does not hit kids up to 1 year due to congenital immunity. And from 2 to 10 years, children are most susceptible to this disease: their innate immunity disappears, and comply with the rules of hygiene at this age more difficult
The incubation period at the hepatomirus A - from two weeks to one and a half months.
To suspect the disease of Botkin in a child in a set of rather typical symptoms:
- the child has an increase in temperature
- he has pain in the stomach and on the right in the hypochondrium
- its sick and tear
- the urine of the child becomes dark color and foam (compared with dark beer)
- his calm becomes light
- yellowee skin and eye scler appears
- the child appears weakness and other symptoms of viral intoxication
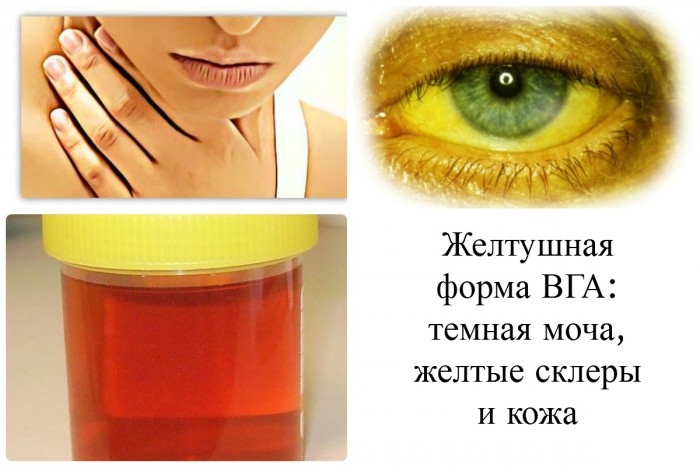
Symptoms of hepatitis A.
Toddler with such symptoms must urgently lead to the doctor. Pediatrician or infectious person:
- Increases the child to identify signs of jaundice, intoxication
- Pedpins the liver for its increase (there can be a spleen)
- He asked if the child was the last month in the children's team, did it contact with hepatitis A sick, was it in the village, on the river, was rested in southern countries
- Appoints clinical and biochemical analyzes of urine and blood
IMPORTANT: In the barn and jaundice periods of Botkin's disease, it is easy to identify on the presence of a high-title-specific immunoglobulin Anti - HAV IGM
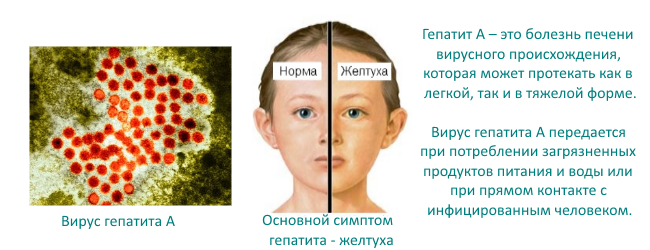
Hepatitis A virus and infection mechanism.
Botkin's disease ends with 1 child's death out of 1000. In this case, it flows lightning and causes liver necrosis. It can be argued that the cure of it occurs independently, since the complex of therapeutic measures is aimed at increasing the resistance of the children's body before viral infection and eliminate individual symptoms of the disease. Also during the treatment period, it is necessary to maintain detoxification and other liver functions.
Symptoms of hepatitis B in children
It often happens that hepatomirus in the child is infected back in the womb of Lee or breast age. Approximately 8 cases of 10 disease takes a chronic course, in 3 cases from 10 turns into cirrhosis of the liver or reborn hepatocytes into a dangerous malignant formation - primary hepatocellular carcinoma.
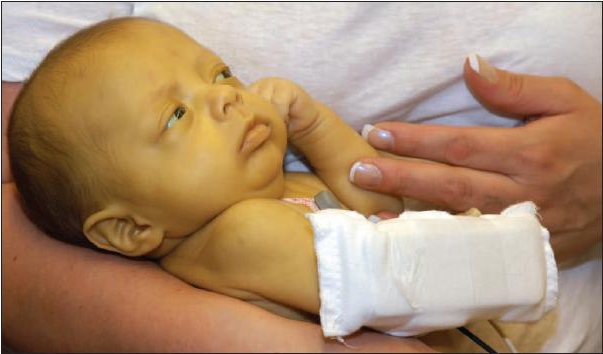
Hepatitis in the child can be infected with intrauterine, during childbirth or in infancy.
The disease is called parenteral or serum, as it is transmitted mainly through blood.
- Up to 10% of children with serum hepatitis are born with this disease. The virus penetrates them from the mother with a transplactation
- Infection is also possible in the process of childbirth, when the child contacts the mother's blood and other liquids of its body
- After the birth of hepatomirus in can get to the kid during his breastfeeding
- In the older childhood, it is possible to pick up whey hepatitis with a contact-household, in adolescent - sex
- Unfortunately, despite the complex of preventive measures, children are infected with hepatomirus in the conduct of medical or diagnostic procedures
Serum hepatitis has a variable incubation period. It can be 60 - 120 days and depends on:
- age of the child in which there was an infection
- ways of hitting hepatamirus in infusion
- the number of hepatomirus kid fell into the body
- fortress of immunity baby
The shortest incubation period will be in the case when infection occurred during blood transfusion.
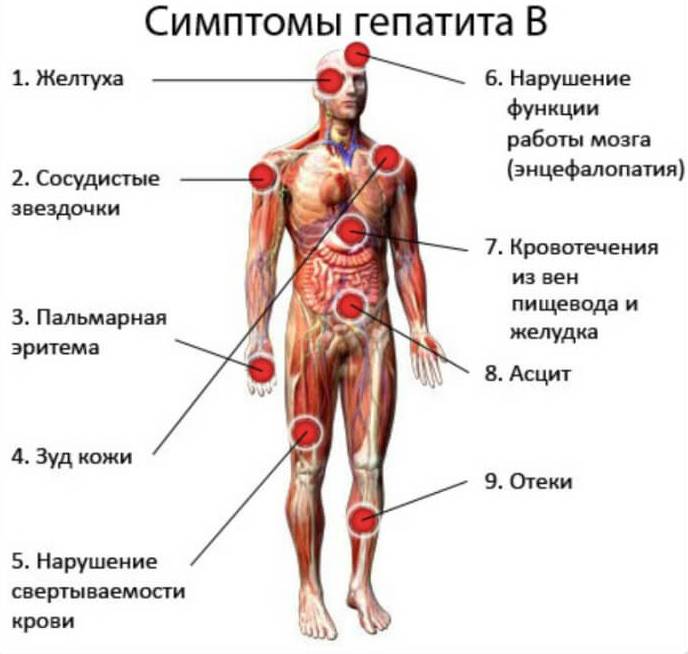
Symptoms of hepatitis V.
Important: often hepatitis in children flows hidden. It is detected by the presence of NVSAG, NREAG, anti-NVSAG IGM immunoglobulins and scar liver changes
Symptoms of different periods of serum hepatitis differ:
- Preicteric period. Within 2-4 weeks, the baby is showing signs of a general illness. He was listless and weak, not eating. The child appeared muscle and joint pain, skin rashes, indigestion, abdominal pain and vomiting. Babies often vomit, their colicky. Baby urine darkens, and feces, on the contrary, become bright
- Jaundice. When serum hepatitis, it can last from weeks to 2 months. Color of the skin, mucous membranes or eyes become intense yellow. The temperature rises. The liver and spleen are increased
- Recovery. Convalescence in children with serum hepatitis lasts 3-4 months. During this period, all the symptoms gradually fade
IMPORTANT: Most serum hepatitis takes an unfavorable outcome and becomes chronic. Chronic states physician if recovery does not occur within six months
The most dangerous form of hepatitis is given to infants. They often it is fraught with fatal outcome due to hepatic encephalopathy, failure and coma.
Typically, diagnosis of hepatitis B in children is not difficult. The disease is defined by the study of history, the results of laboratory tests. Diagnosis is based on the detected blood antigepatovirusnyh immunoglobulins, elevated bilirubin, increased transferase activity.
The main symptoms of hepatitis C in children
Hepatovirus C comprises RNA. He is very changeable and so quickly affects a large number of hepatocytes. Unfortunate consequences diseases are necrosis of hepatic parenchyma, active autoimmune response and liver fibrosis. The disease is often complicated by the diseases of other organs, as with the blood of hepatitis C virions are transported to the brain, heart and so on.
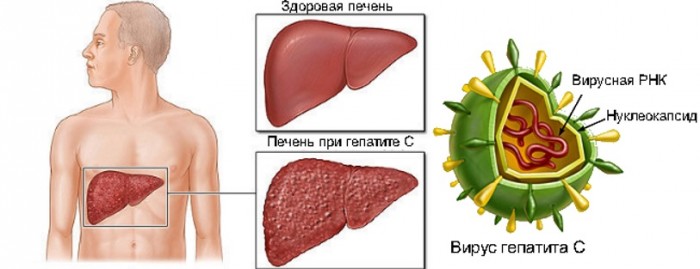
Hepatitis C virus causes necrosis of the liver or fibrosis.
Most often, children are infected hepatovirus C:
- in utero, at birth or in infancy from an infected mother
- during the diagnostic, therapeutic interventions, blood transfusion
- in adolescence, during unprotected sex
After the incubation period is over, which in this form of hepatitis lasts approximately 2 months, begins preicteric period in which the disease and makes itself felt first symptoms - asthenovegetative and dyspeptic syndrome, arthralgia and myalgia. Intoxication becomes pronounced.
With the advent of jaundice appear bright symptoms of inflammation of the liver:
- darkening of urine
- lightening stool
- temperature increase
- nausea and vomiting
- pain in the right hypochondrium
Chronicization of viral hepatitis C occurs in 20% of sick children. In this case, the disease does not pass within 6 months and longer. Its symptoms may not be, but the liver fibrosis continues.
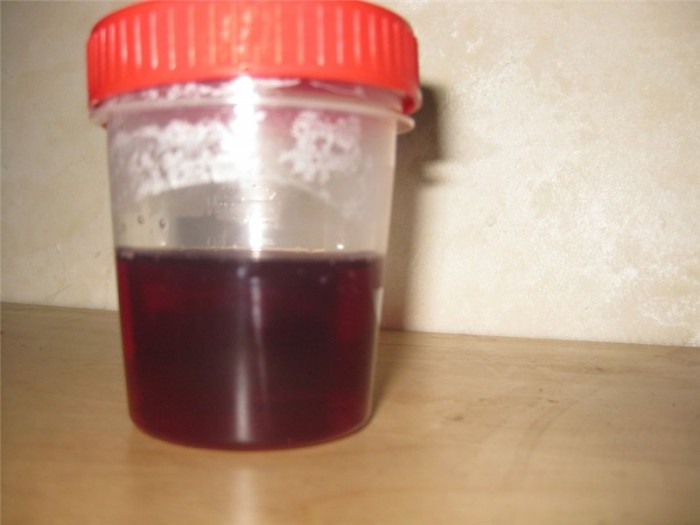

Urine in a child with hepatitis with darkens and begins to foam.
Danger for children represent possible:
- cirrhosis of the liver
- hepatic bleeding
- attachment of secondary bacterial infection
- development of hepatic insufficiency
As in the case of other forms of illness, hepatitis C is diagnosed according to the results of laboratory tests.
Video: Hepatitis A. Viral hepatitis with symptoms treatment. Chronic hepatitis B symptoms. How to treat hepatitis with
Hepatitis treatment
- As mentioned above, the child's body is able to cope with Botkin's disease independently, so the main task of treatment is to promote normal liver work
- It is necessary to make measures to facilitate the removal of the toxic substances produced by the virus
- Sick hepatitis and baby isolate, provide him with rest regime. It is introduced saline and glucose, hepatoprotectors and vitamins give drugs
- Also during illness, the child is on therapeutic diet table number 5
- Persons who were in contact with a child with Botkin's disease, if they have antibodies to hepatterns A, immunoglobulin are introduced in blood

The child with any form of hepatitis is hospitalized into an infectious hospital.
If the child has hepatitis in or s, the treatment will be more difficult. The child is mandatory hospitalized into an infectious office. He shows antiviral treatment with interferon. The patient is also prescribed:
- safety spasmolitis (drootaverin or but-shpa, papaverine)
- vitamins
- hepatoprotectors
- golden drugs
- if necessary - glucocorticosterlides
IMPORTANT: With a severe course of the disease caused by hepatamirus in or C, the child may need plasmferres and hemosorption
For a year after recovery from these forms of hepatitis, the child shows a dispensary observation.
If the baby manages to defeat hepatitis V viruses in or s, he has persistent lifelong immunity to them.
Is it worth making a child vaccine from hepatitis? Vaccination from hepatitis A and in children. Graft from hepatitis C for children
Doctors consider the question whether to instill a child from viral hepatitis, simply stupid. Their answer is unequivocal - yes. The fact is that alternative prevention of the disease, rather than immunization, does not exist.
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, the use of sterile or disposable medical equipment, other nonspecific preventive measures have not proven to be effective. At the same time, the vaccination gives 99% protection against hepatamirus for many years, and even for life.
Grappat from hepatitis and the child is made in the shoulder.
It is necessary to clarify, from what hepatitis you can instill a child when these vaccinations do.
To date, there are effective vaccines against the disease of Botkin and serum hepatitis.
- Vaccination against hepatitis A is not mandatory. But the doctors strongly recommend it to all children aged 2 to 10 years who have previously ill ill with Botkin's disease. A safe vaccine is introduced twice, the interval between vaccinations is half a year or a year. Injection is produced intramuscularly (children - in shoulder). Immunity to hepatomirus A in a graft child formed two weeks after the first vaccination and remains for 6 to 10 years
- Vaccination from hepatitis B is mandatory, it is entered into the vaccination calendar. The first dose of the baby vaccine should receive in the first 12 hours from the moment of birth, the second - in 1 month, the third is 6 months. Today, doctors in the maternity hospital are often reinsured and asked moms to write a rejection of vaccination against hepatterns V. In this case, the child receives the first vaccination from him in 1 month or later, after inspecting the pediatrician and neuropathologist. Then the second vaccination is performed with an interval of 1 month after the first, the third - with an interval of 5 months after the second. Injection is produced intramuscularly (children in the thigh). Vaccinations according to the scheme create a child immunity from this viral infection for 15 years
To date, recombinative drugs vaccinate from hepatitis in the child:
Combiotehe
- Regeva
- Endjherix B.
- Euvax B.

Roman - Vaccine against hepatitis V.
IMPORTANT: Allergic reactions of various types, Malgia, neuropathy, other adverse reactions that are extremely rare after vaccinations from hepatitis, it is a smaller risk for a child than the risk to infect severe viral disease
Grafs for children and adults from hepatitis C, unfortunately, does not exist. It is possible to conduct its prevention.