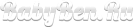
What is Epstein-Barr or mononucleosis virus? Symptoms and treatment of the Epstein-Barr virus. Diagnosis and decryption of tests for the Epstein-Barr virus.
The content of the article
- What is the danger of Epstein-Barr virus?
- Epstein-Barr virus as a causative agent of infectious mononucleosis
- How is the Epstein-Barr virus transmitted?
- Symptoms of the Epstein-Barra virus in adults and children
- Epstein-barra virus during pregnancy
- Epstein-Barr virus, diagnostics
- Antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus
- The norm of the Epstein-Barr virus
- How to treat Epstein-Barr virus medication?
- Folk treatment of the Epstein-Barr virus
- Video: Epstein-Barr virus
The Epstein-Barra virus is a viral disease provoked by a fourth-type herpes virus. Almost ninety percent of the population of the entire planet is infected with this virus. Many patients do not even suspect the presence of herpes virus in their body. The fact is that the primary infection of a person is not accompanied by any symptoms and manifestations. A person may not even feel any discomfort.
What is the danger of Epstein-Barr virus?

What is the danger of Epstein-Barra's virus?
In most cases, infection with this virus does not lead to serious complications. However, not all so simple. In people with weak immunity, herpes virus can provoke a number of complex diseases. First of all, the Epstein-Barr virus is a provocateur of the appearance of infectious mononucleosis in a person. In addition to this disease, in his power to cause a lot of other complications in the human body, such as:
- diabetes
- rheumatoid arthritis
- chronic fatigue syndrome
- hasimoto thyroiditis
- angiimmunoblastic liphenopathy
- anemia
- hemophagocytic syndrome
- immune thrombocytopenic purple
- DIC-syndrome
- hepatitis
- jaundice
- syndrome "Alice in Wonderland"
- pericarditis
- myocarditis
- duncan disease
- hairy leukoplakia oral cavity
- Berkitt lymphoma
- timoma
- nazopharyngeal carcinoma
- cancer tonsils
- bella syndrome
- nediferinocial cancer of the nasopharynx
- lymphomas of the central nervous system
- encyfolite
- stomach cancer
- meningitis
- testament cancer
- cancer Guine-Barre
- obstructive disease of the respiratory tract
- myelitis
Epstein-Barr virus as a causative agent of infectious mononucleosis
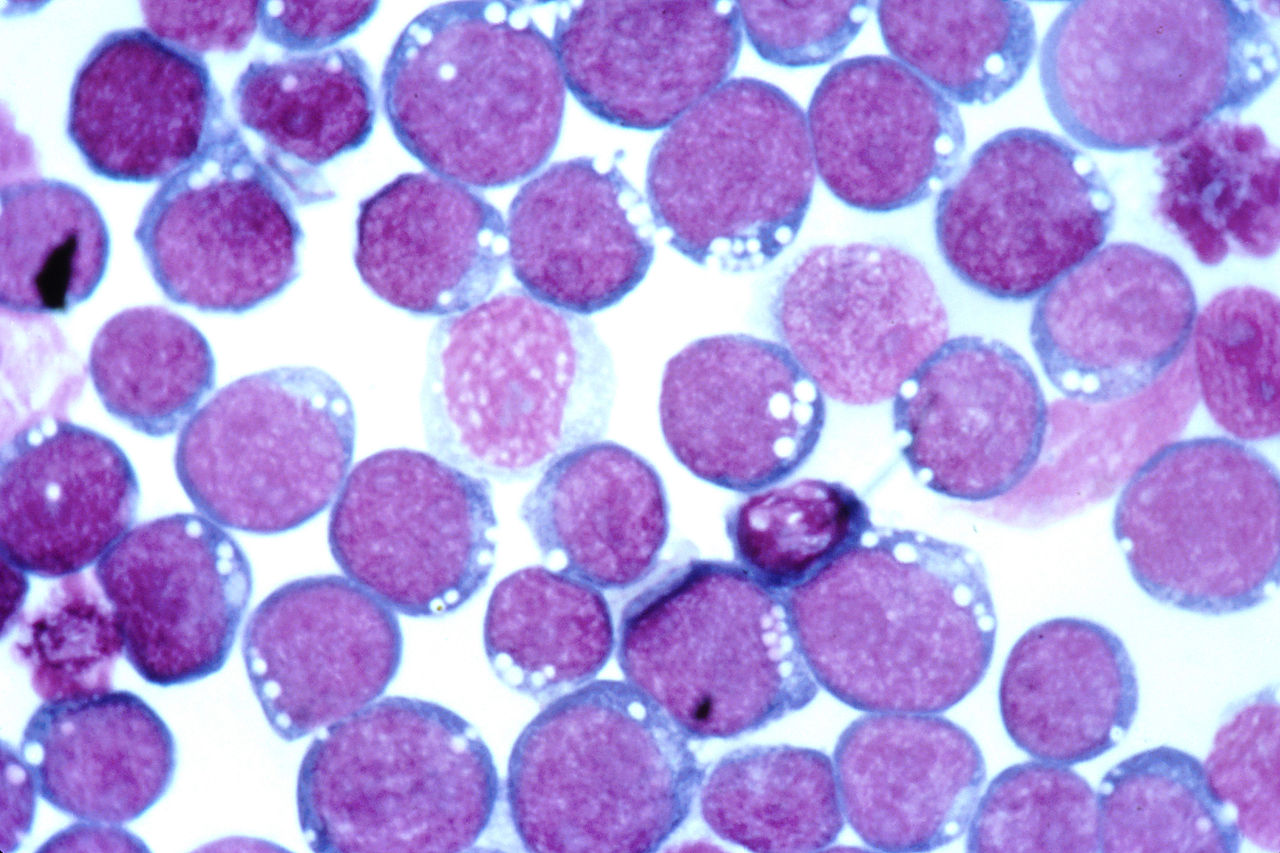
Epstein-barra virus as a causative agent of infectious mononucleosis
- Infectious mononucleosis is provoked by the penetration of the Herpes Epstein-Barra virus into the human body. Most often, children under the age of ten are subject to this disease. Infection with this virus occurs in the team from other sick children
- Over time, infectious mononucleosis can result in chronic mononucleosis
- Treatment of such a disease can be carried out at home. If for a long period of time to overcome the disease at home or the baby has become worse, such a child must be sent for treatment to a hospital conditions
How is the Epstein-Barr virus transmitted?

How is the Epstein-Barra virus transmitted?
The Epstein-Barra virus can be transmitted from a sick person with a healthy airborne or domestic way. Also, this disease can be infected with blood transfusion or sexual contact.
Most often, the herpes virus is called "kisses of kisses." This is really true. The most common methods for transmitting the virus are:
- kisses
- sex
- using a common cup, plate and devices
- using one linen
- personal hygiene products (razor, soap bar, washcloth)
- blood transfusion
- bone marrow transplantation
- intrauterine infection
After the Epstein-Barra virus infection, a person can spray the virus and infect others to them for a year and a half.
Symptoms of the Epstein-Barra virus in adults and children

Symptoms of the Epstein-Barra virus in adults and children
The main features of the Epstein-Barra virus are:
- heat
- weakness
- lymphadenopathy
- rashes on the body
- herpic formations on the skin
- nasal congestion
- labored breathing
- sore throat
- muscle pain
- increase in the liver and spleen
All these signs are very similar to the symptoms of tonsillitis. That is why the second name of infectious mononucleosis is monocytic tonsillitis.
Epstein-barra virus during pregnancy

Epstein-barra virus during pregnancy
- The Epstein-Barra virus during pregnancy is dangerous only if before pregnancy a woman was not ill with this disease and first accommodated with his carrier, being in an interesting position. Infection with this virus during pregnancy can be dangerous for the fetus and its development
- If a woman has already been ill with mononucleosis until pregnancy, then antibodies to this virus will be present in her blood, because it will not do any harm even during pregnancy
- A very important stage in preparation for pregnancy is the delivery of appropriate tests to determine the presence of antibodies to the Epstein-barra virus in the woman's body. If she does not have any antibodies, then during pregnancy she should be extremely neat and exclude random contacts so as not to become infected with this quite dangerous for pregnant women
Epstein-Barr virus, diagnostics
Diagnosis of the Epstein-Barra virus
You can diagnose the Epstein-Barr virus using the following studies:
- A general blood test can show an increase in leukocytes, an inflamed indicator of ESR, a decreased or increased level of platelets, a drop in hemoglobin levels, and the presence of atypical mononuclear. All these indicators may indicate the possible presence of herpes virus in human blood
- Biochemical blood test is able to identify such signs of a virus as an increased level of ALT, AST, LDH, Bilirubin, alkaline phosphotase, the presence of acute phase proteins (fibrinogen, SRB)
- Immunological studies show a picture of the state of immunoglobulins and interferon
- Serological studies are the most accurate method for diagnosing mononucleosis. This type of diagnosis is able to identify the presence of antibodies in the blood to the virus
- DNA analysis is carried out by a fence of such research material as saliva, a smear from the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract, cerebrospinal fluid. In the listed materials in laboratory studies, the Herpes virus is searching for DNA
Antibodies to the Epstein-Barr virus
Antibodies to the Epstein-Barra virus
During the infection of the human body, the Epstein-Barr virus and its reproduction in the human blood, the following antibodies begin to be produced:
- IGM antigens - begin to be produced in the blood, but the first signs of the disease begins. Their presence will be noticeable with one hundred percent probability at the very beginning of the disease. The highest indicators of IGM antibodies from the first to the sixth week after infection. Three weeks after infection, their indicator will fall a little, and six months later they will disappear completely
- IgG class antigens can also be detected very early - one week after infection. Their indicator becomes maximum in the second month of infection. The titer of these antibodies decreases closer to the time of recovery, but their presence will manifest itself in the analyzes for several more years after the disease
- Antibodies to the IGG class nuclear antigen, as a rule, begin to appear by the time of recovery. Such antibodies remain in the blood for many years after infection
The norm of the Epstein-Barr virus

The norm of the Epstein-Barra virus
- If during laboratory tests in the blood only antibodies of the IgG and EBNA IgG class were found, this suggests that the person is in contact with the virus, but at the moment it is absolutely healthy
- If during the analysis antigens of the IgG and IGM class were detected, and there was no EBNA IgG antibodies, then this may indicate the acute phase of the disease
- If the analyzes showed only IGM antibodies, then this indicates the volume that the infection is at an early stage of its development
- If during the analysis all three types of antigens were discovered, this indicates the current persistent infection
How to treat Epstein-Barr virus medication?
How to treat Epstein-Barra virus medication?
A strictly defined treatment for the Epstein-Barr virus does not exist. With infectious mononucleosis, the patient needs to provide peace and abundant drink. High temperature in this case can be shot down with antipyretic drugs. In some cases, the patient is prescribed hormonal (glucortic), antiviral or antibacterial drugs. It is also possible to prescribe immunoglobulins, interferons and antihistamines.
If cancerous conditions were developed as a result of mononucleosis, then antitumor therapy may be prescribed to the patient.
Folk treatment of the Epstein-Barr virus

Folk treatment of the Epstein-Barra virus
In folk medicine, there are several ways to treat the Epstein-Barra virus:
- Coconut oil is an excellent means of combating sore throat. In addition, it contributes to the exit of toxins from the human body
- Apple vinegar helps strengthen immunity, overcome the infection and enrich the body with vitamins and minerals
- Astral in the form of tincture or tea
- Ginger tea
- Tea from herbal gathering (mint, coltsfoot, calendula, chamomile, Duma and ginseng root)
- Green tea with lemon
- Echinacea infusion
- A decoction of cabbage is prepared on the basis of cut leaves of fresh cabbage flooded with water. Such a mixture must be put on fire and boiled for ten minutes. Then the decoction must be cooled and taken overnight and in the morning one hundred grams
- Infusion of ginseng
- Ginseng, fir or juniper can be lubricated with an inflamed throat