Future mothers often hear the diagnosis - anemia, which is expressed in a decrease in the level of hemoglobin. In this article you will learn how such a diagnosis threatens and what measures should be taken with a reduced or increased level of hemoglobin in the blood.
The content of the article
- Anemia in pregnant women - low hemoglobin during pregnancy
- Symptoms and causes of low and reduced hemoglobin during pregnancy
- What is the danger of low hemoglobin during pregnancy? Effects
- How to increase, raise hemoglobin during pregnancy?
- Vitamins and dietary supplement to increase, raising hemoglobin
- Iron preparations that increase hemoglobin during pregnancy
- Pregnant nutrition for low hemoglobin
- Iron in products, table
- Iron rate during pregnancy
- Can there be a high hemoglobin during pregnancy?
- What to do if hemoglobin is increased during pregnancy?
- Drugs to reduce hemoglobin
- Video: reducing hemoglobin during pregnancy
As soon as a woman finds out about pregnancy, she immediately arises a number of questions related to her health status. When registering in a female consultation, they give a lot of directions for a wide variety of tests and research. One of the most important indicators is the level of hemoglobin, because the most common problem during pregnancy is its low level. Doctors diagnose anemia.
Anemia in pregnant women - low hemoglobin during pregnancy
Let's figure out what hemoglobin is and what function it performs in our body. Hemoglobin is a protein that is contained in red blood cells and serves for breathing tissues and internal organs, forming compounds with oxygen. In addition, it is he who stains the blood in red.
The normal indicator of the level of hemoglobin starts from 115g/l. If its concentration in the blood is lower, they say about anemia (anemia) of varying degrees:
- 90-110g/l-mild degree
- 80-90g/l-average degree
- ‹80 - severe degree
Hemoglobin in the blood
Symptoms and causes of low and reduced hemoglobin during pregnancy
With a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood, a woman can feel weakness, dizziness, shortness of breath may appear. With severe anemia, the likelihood of fainting increases. You can suspect anemia by a number of symptoms:
- Difficulty breathing
- Fainting and dizziness
- Increased fatigue
- Fragility of hair and nails
- Dry or pallor of the skin
- Cardiopalmus
- Headache, noise or bell in the ears
- Drowsiness
- Irritability, mood swings
- Changing taste sensations, strange addictions
Important: anemia can pass asymptomatic, and its symptoms are also suitable for a mass of other diseases. Do not diagnose yourself and do not self -medicate.
A decrease in hemoglobin in a pregnant woman is a completely expected and predictable phenomenon. During pregnancy, the blood volume in the body increases, and the concentration of red blood cells and, as a result, hemoglobin decreases.
There are a number of basic reasons that cause anemia:
- The most common is iron deficiency anemia. It occurs with a lack of iron in the blood due to inferior nutrition or lack of folic acid and vitamin B12, which are responsible for the absorption of iron by the body
- Multiple pregnancy - the mother’s body satisfies the constantly growing needs of children, including the need for gland
- Diseases of internal organs-liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract.
- Repeated pregnancy is less than three years later. A woman does not have time to make up for iron losses
- Strong toxicosis. The nausea and disorder of the stool leads to the removal of nutrients from the body, and the inability to eat fully does not allow to make up for their stocks
- Copper and zinc deficiency
- Reception of some drugs that can prevent hematopoietic function (for example, levomicetin, aminazine, cytostatics)
- Hormonal disorders
Important: in order to avoid anemia, it is best to take prevention measures at the pregnancy planning stage, taking vitamins and fully eating.

Symptoms of anemia
What is the danger of low hemoglobin during pregnancy? Effects
The course of pregnancy against the background of low hemoglobin fraught with many dangers and leads to negative consequences for both the health of the mother and the child in the womb and after birth:
- Hypoxia (lack of oxygen) of the fetus
- Hypotrophy - development delay, insufficient mass of the fetus
- The weakened immunity of the newborn
- Pathologies of the internal organs of the fetus
- The risk of miscarriage and premature birth
- Toxicosis up to the third trimester
- Complications during childbirth - bleeding, weakness
- Difficulties in recovery after childbirth

Complications with anemia
How to increase, raise hemoglobin during pregnancy?
Anemia in the last trimester is due to physiological changes in the body of a woman, and therefore does not need treatment. In addition, the treatment of anemia is a long process that can stretch for several months. Like any disease, the low level of hemoglobin is easier to prevent than to treat.
If you still need treatment, be patient. The elimination of this disease is in a complex approach. If you resort only to drug treatment, for example, treatment will last longer and will be less effective. Therefore, it is recommended to treat anemia comprehensively:
- Vitamin complexes
- Iron -containing drugs
- Proper full nutrition, which includes products containing iron
Vitamins and dietary supplement to increase, raising hemoglobin
- For the prevention of anemia, it is recommended to drink vitamin complexes (for example, Elevit, Perenvit or Vitrum) even at the stage of pregnancy planning or from its very beginning
- The deficiency of vitamins in the body leads to poorly assimilation of iron, therefore, with iron deficiency anemia, it is recommended to take folic and ascorbic acid
- With a deficiency of vitamin B12 of the pregnant woman, intramuscular injections are recommended, iron -containing drugs in this case are not prescribed
The effectiveness of taking dietary supplements is often questioned, but women often turn to this method of treatment. Among the biological additives to increase hemoglobin, AMWe's drugs are very popular.
Important: do not forget that dietary supplements are not an independent method of treatment, it should be taken only as an auxiliary remedy in combination with other drugs prescribed by the doctor.
Vitamins and dietary supplements
Iron preparations that increase hemoglobin during pregnancy
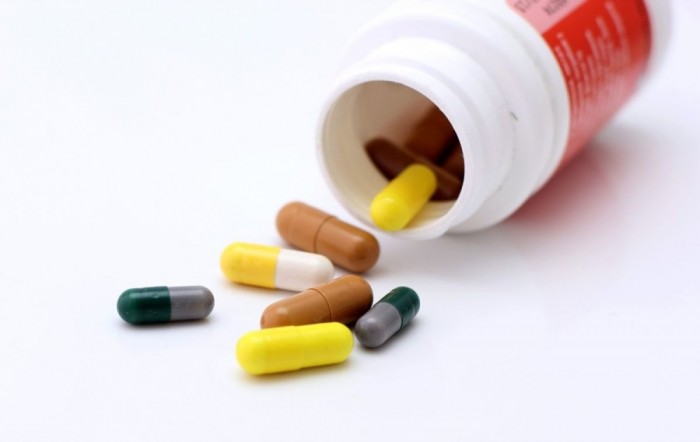
To increase the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood, it is recommended to take iron -containing drugs or syrups. In severe cases or with peptic ulcer, the doctor may prescribe iron in injections. Get ready for the fact that taking the drugs lasts from 30 to 60 days, since they have a cumulative effect. Be prepared for the side effects of iron -containing drugs, one of them is the darkening of the chair.
Iron is combined with drugs that contribute to its absorption in the body (folic acid and vitamin C), however, there are a number of drugs with already combined necessary combination:
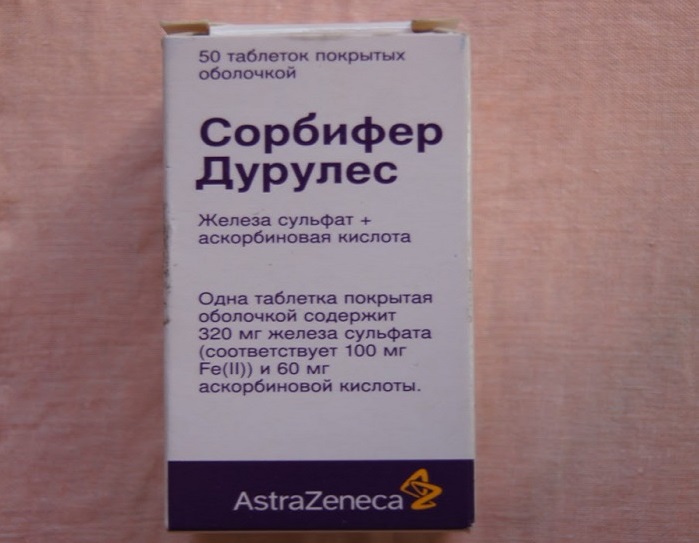
- Sorbifer - 100mg of iron+vitamin C
- Totem - 50mg iron
- Fenyuls - 45mg of iron. This drug is prescribed both for the treatment of anemia and for its prevention
- Ferrum Lek - tablets 100 mg, syrup 50 mg/5ml
- Maltofer - 10 mg/ml syrup
Important: when taking a totem (drug in ampoules), use a tube or rinse your mouth after each use of the drug. This tool adversely affects the teeth.
Taking iron -containing drugs is not combined with milk products.
Pregnant nutrition for low hemoglobin
Taking vitamins and iron -containing drugs may not bring the desired effect and two months later, if you bypass a full nutrition. The diet of a pregnant woman must include products with a high content of protein and iron:
- Grain
- Fruits and vegetables
- Low -fat meat (beef, pork)
- Offal (liver, tongue, heart)
- Eggs (the yolk is especially useful)
- Fish
- Milk products
With reduced hemoglobin, minimize fat consumption (up to 80g per day), exclude even the idea of \u200b\u200bvegetarianism during pregnancy.

Food during pregnancy
Iron in products, table
| The amount of iron mg/100g product |
Products |
| Very big | Pork liver (12), beef liver (9), beef tongue (5); Meat: rabbit (4.4), turkey (4); Beans (12.4); Group: buckwheat (8), barley (6.4), oat (3.9), millet (7); Blueberries (7), peaches (4.1) |
| Large (2-3) | Meat: chicken, ducks, beef, lamb, smoked sausage; Mackerel, pink salmon; Eggs; Group is semolina, wheat bread; Pears, apples, plums, aiva, apricots |
| Moderate (1-1.9) | Pork, boiled sausage; Rice, pasta; Tomatoes, beets, onions, spinach, dill, cabbage, carrots; Cherry, gooseberries, watermelon, blackcurrant, strawberries |
| Small (0.4-0.9) | Fish: Sardina, Saira, Paltus, herring; Cheese, cottage cheese; potatoes, cucumbers, pumpkin; Cranberry, grapes, lemon |
| Extremely small (0.1-0.3) | Milk, kefir, sour cream; Oranges, tangerines |
Iron rate during pregnancy
- The daily iron rate in pregnant women is twice as high as in the usual state and is 25-30 mg per day. This does not mean that it is necessary to receive such an amount of iron every day every day. For example, if today 10 mg enters your body today, and tomorrow - 40, then the daily norm is compensated for two days
- Lack of iron leads to a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood and an disappointing diagnosis - iron deficiency anemia
- You can determine the content of iron in the body using a blood test. It seems on an empty stomach, on the eve it is not recommended to drink alcohol and aggressive food (overly spicy, salty, sweet). In normal condition, the level of serum iron in the blood is 15-30 mkmol/l
- A sufficient level of iron in a woman’s blood will help the normal course of pregnancy and contribute to the birth of a healthy child
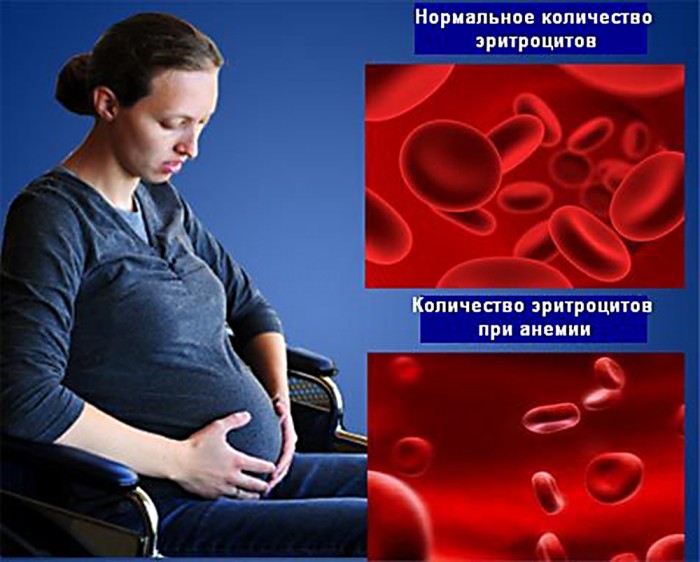
Anemia
Can there be a high hemoglobin during pregnancy?
A serious danger to a pregnant woman is fraught with an increase in hemoglobin concentration. In this case, the blood becomes thicker, which leads to the formation of blood clots in the vessels. An increase in hemoglobin is also unsafe for the fetus: due to poor blood circulation, the baby can receive an insufficient amount of nutrition.
Causes of increased hemoglobin:
- Kidney diseases
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system
- Deficiency of vitamin B12
- Disadvantage of folic acid
- Heredity
- Place of residence (for example, highland areas with sparse air)
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Lethargy, drowsiness
- Lack of appetite
- Pallor
- Vision problems

High hemoglobin during pregnancy
What to do if hemoglobin is increased during pregnancy?
The indicator of the norm of hemoglobin varies throughout pregnancy:
- 1st trimester-115-160g/l
- 2nd trimester-108-144g/l
- 3rd trimester-100-140g/l
An increase in the level of hemoglobin in the first trimester should not cause serious concerns, because further, with the course of pregnancy, the needs of the baby will eliminate its surpluses. If this indicator remains much higher than the norm for a long time, then measures should be taken. Often this is due to the disadvantage of vitamin B12 or folic acid, therefore, the expectant mother is recommended to make up for the lack of these substances in the body.
Important: do not panic if the hemoglobin level is only 10-15 units higher than normal. Over time, it stabilizes.
Taking medication during pregnancy is with particular caution: they act, liquefying blood. It is best to cope with increased hemoglobin is helped by frequent walks in the fresh air and a healthy diet that provides the body with vitamins.

Walks with increased hemoglobin
Drugs to reduce hemoglobin
Preparations for reducing hemoglobin, which dilute blood, are recommended only in extreme cases, they can harm both the expectant mother and the health of the fetus.
Important: consult your doctor about taking vitamin complexes with increased hemoglobin. Most of them contain vitamins and substances that help the body absorb iron, which helps to increase the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood.