Why do people get asthma? How does this disease manifest? Is it possible to cure her? The article has answers to these and many other questions.
The content of the article
- The causes of bronchial asthma in adults
- Video: Elena Malysheva. The causes of bronchial asthma
- Signs of bronchial asthma in adults
- Is it possible to cure bronchial asthma in adults? Complications of the disease
- Diagnosis of bronchial asthma in adults
- Video: study of the function of external respiration spirometry
- Antibiotics in bronchial asthma in adults
- Diet with bronchial asthma to adults
- Video: Bronchial asthma: recommendations for nutrition and lifestyle
- Disability in bronchial asthma in adults
- Treatment of bronchial asthma in adults with folk methods
- Video: How to cure bronchial asthma with folk remedies? Astma cure
- Prevention of bronchial asthma in adults
- Video: prevention of bronchitis and bronchial asthma
- Medicine is developing today with a rapid pace. Despite this, there are still diseases that have not learned how to cure. One of these is bronchial asthma
- Diagnosed once, she will accompany a person all his life. Doctors and asthmatics “with experience” assure: this disease is not a sentence, it does not always mean disability
- Under the conditions of early diagnosis and adequate therapy, restraining asthma and preserve the quality of life will certainly be able to. Experts advise self -figuring on the issues of this disease and leading the right lifestyle, then the diagnosis will exist only on paper
The causes of bronchial asthma in adults
Bronchial asthma is one of the multifactorial chronic inflammations of the organs of the brochure-legive system. The mechanism of the disease is quite complex:
- under the influence of the stimulus (trigger), the mucous membrane sensitive to it, lining the bronchial tree from the inside, hyperreactes and begins to produce sputum in excess
- the muscles of the bronchi is spasmodic
- due to these two processes, the lumen of the bronchi narrows, which prevents normal breathing
- gas exchange in the respiratory system and the body as a whole is violated
- the patient has an attack of suffocation or a strong unproductive cough begins (with cough asthma)
Important: in European countries and the United States, from 4% to 10% of the population suffer from a particular form of bronchial asthma
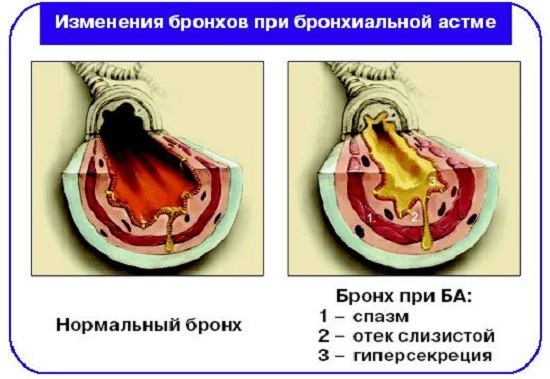
Bronchial asthma - multifactorial, chronic, obstructive, inflammatory disease of the bronchi.
The causal factors provoking the development of bronchial asthma are called triggers (English “to trigger”, which can be translated as “put into action”, “launched”). They are divided into two large groups: internal and external.
The internal attributes:
- Hereditary predisposition. If the child was born in a family where there are allergies or asthmatics, the risk that asthma will be with himself is very high. But he will not get sick if certain external factors that will be discussed below do not affect him
- Floor. Both men and women are sick with bronchial asthma. Moreover, boys more often get sick under the age of 10 years, and women - in the pre -Climacteric period, after 40 years
- Age. The disease is most often manifested in childhood or in the second half of life
- Weight. Obesity determines a person at risk to get asthma. Firstly, because excess weight causes endocrine disorders. Secondly, the diaphragm in fat people is higher, and their lungs are not ventilated enough
In adulthood, women are more likely to suffer from asthma than men.
The external factors of bronchial asthma include:
- allergens
- viruses and bacteria
- contaminated air
- harmful working conditions
- smoking and other bad habits
- long, incorrect or uncontrolled taking certain drugs
- stress and wrong lifestyle
- frequent acute or chronic respiratory diseases
- weather
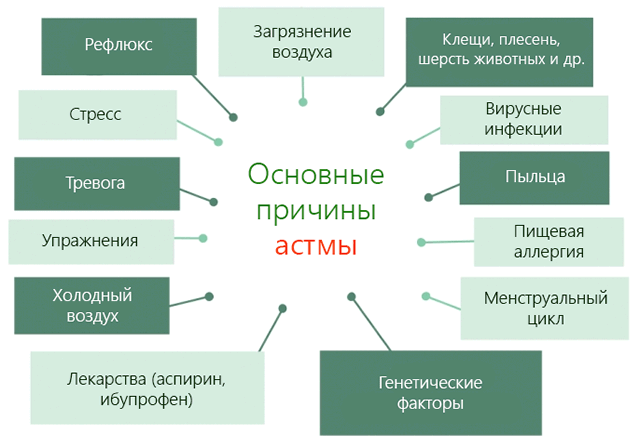
The main causes of bronchial asthma.
Important: the priority task after a person has been revealed in a person, the definition of its triggers is determined. The exclusion of their effect on the patient’s body is half the success of therapy.
VIDEO: Elena Malysheva. The causes of bronchial asthma
Signs of bronchial asthma in adults
If the patient appeals to the therapist or pulmonologist with complaints of a difficult exhalation (expiratory shortness of breath), dry cough, whistles, wheezing and chest pain, periodically arising wheezing and whistles, doctors have every reason to suspect bronchial asthma.
The purpose of the further diagnostic examination is its confirmation and differentiation with other inflammatory and obstructive diseases of the respiratory system.
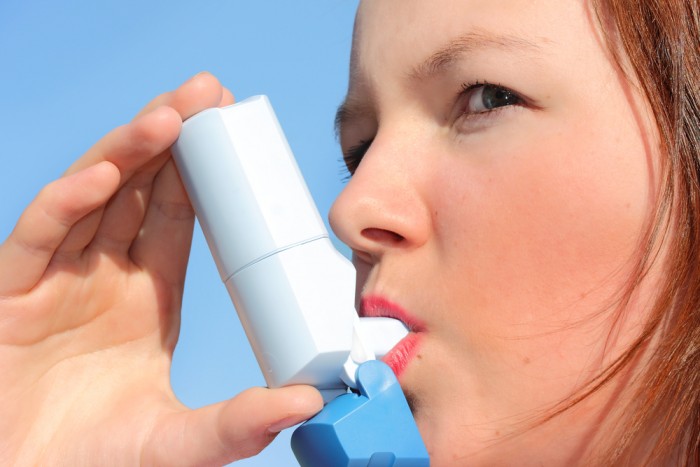

The attack of suffocation is the most striking sign of asthma.
It is necessary to consider in more detail each sign of bronchial asthma:
- Dyspnea. Astmatics show its expiratory version, which is expressed in difficulty exhalation. The patient freely inhales the air with the lungs, and as if something prevents him from exhaling him. Astmatic shortness of breath is acute and increasing. Her respiratory failure may accompany her
- Cough. In asthmatics, it is unproductive, of various intensity. Sputum, distinguished by the bronchi in response to the effects of the allergen, is too thick, clench it and cannot be relieved of the patient. There are also a very special option for bronchial asthma - cough, in which the patient has no other complaints, except for cough. This symptom is especially annoying in the evening and night, which is extremely exhausting a person
- Chest pain. This symptom can be associated with bronchospasm, diaphragm overstrain, as well as complications that asthma gave to the lungs and heart
- Wheezing. They talk about the narrowing of the bronchial lumen and the presence of dense mucus in it
- Attacks of suffocation. This is perhaps the most striking symptom of bronchial asthma. During an attack, the patient is often instinctively, trying to alleviate his breath, takes a position sitting with his hands, his chest becomes cylindrical. Behind a short inhalation is a very difficult, long and intermittent exhalation. You can hear how the patient wheezes everything inside. The body of the asthmatics during an attack is forced to involve additional muscles into the breathing act - the chest, abdominal press and shoulder girdle
Important: a person who suffers from bronchial asthma can also have rhinitis, pain and sore throat. They precede the attack of suffocation or accompany him
In accordance with how often and intensively the signs of the disease are manifested, bronchial asthma is classified according to degrees of severity.
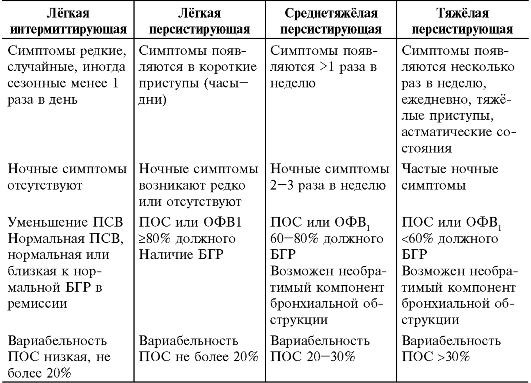
The severity of bronchial asthma.
Is it possible to cure bronchial asthma in adults? Complications of the disease
Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely cure bronchial asthma. But it is quite realistic to achieve its persistent remission, when the attacks of the disease will be absent for many months and years.
If you ignore the treatment of the disease, its numerous complications may appear:
- Bronchial asthma will progress. This means that the attacks of suffocation will fate. They will pass by themselves. A pocket inhaler to stop them will become a constant satellite of the patient. Yes, and he will not always help out. To remove a state of life -threatening human life, it will need to be hospitalized for prolonged treatment in a pulmonological hospital
- Astma will be complicated by pathological conditions of the respiratory system. Due to the extreme narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi, the respiratory function is impaired, as its consequence, acute hypoxia of the body will occur. A lung rupture may occur, accompanied by air entering the pleural cavity (spontaneous pneumothorax). The bacteria that multiply in thick and viscous sputum, which in asthmatics in the bronchi, provoke acute bronchitis and pneumonia in patients. Due to the disease, irreversible changes can occur in pulmonary tissue. Due to the abstraction of the alveoli in asthmatics, emphysema of the lungs often occurs, which, like asthma itself, is not treated, and is a danger to the patient's life
- The heart and blood vessels suffer from asthma. The fault of this is chronic hypoxia, and the frequent use of the beta asthmatic attacks - 2 - adrenomimetics. Heart rhythm disturbances, increased blood pressure-satellite diseases of bronchial asthma.
- The disease gives complications to the brain and the nervous system. Oxygen starvation and hypercapnium of the brain provokes respiratory encephalopathy. Ceremonial edema, increasing intracranial pressure are also possible
- The treatment of bronchial asthma provides for the use of numerous drugs, and this negatively affects the work of the liver and other gastrointestinal tract
- Astmatics often disrupt metabolism. Hypoxia affects the composition of the blood, the body experiences a deficiency of oxygen and potassium, but it receives carbon dioxide in excess. Metabolic pathologies occur at the cellular level
- In addition, suffocation attacks provoke internal bleeding, organs, hernias and genitals in women
IMPORTANT: In patients with severe, immunity suffers greatly. Seasonal SARS and influenza rarely bypass them
Diagnosis of bronchial asthma in adults
Spirometry is a method for diagnosing bronchial asthma.
The diagnosis of asthma in adults is complex, it takes place in several stages.
- Anamnesis collection. According to statistics, it is enough for a doctor to interrogate the patient for 5-10 minutes to suspect bronchial asthma from him. The arguments in confirmation of the diagnosis are the presence in the family of a sick asthmatics and allergy sufferers, frequent diseases of acute respiratory viral infections and bronchitis, the manifestation of atopia in any form, smoking, work in harmful production, so on
- Physical examination. External examination and auscultation allow the patient to identify the above signs of asthma
- Research of external breathing function. It is carried out through a spirometry. The study allows you to determine the degree of obstruction of the bronchial tree, the cross -country ability of the bronchi, on the basis of which concludes the severity of the disease
- X -ray of the chest. This method allows you to distinguish asthma from pulmonary emphysema or pneumosclerosis
- Skin tests and blood test for antibodies like IgE. They allow you to determine allergies and identify allergen
Video: study of the function of external respiration spirometry
Antibiotics in bronchial asthma in adults
Antibiotics do not treat bronchial asthma itself, but its complications in the form of infectious diseases of the respiratory system, in particular, bacterial inflammation of the bronchi.
Indications for the treatment of antibacterial drugs for asthma are a bacterial infection confirmed by laboratory tests.
Important: with bronchial asthma, it is not recommended to take penicillin antibiotics, they can aggravate the patient's condition. Self -medication is not permissible! Only a doctor can prescribe such strong drugs.
As a rule, antibiotics are prescribed antibiotics from groups of cephalosporin, macrolides, as well as lincomicin.
Diet with bronchial asthma to adults
Astmatics recommended hypoallergenic life and hypoallergenic diet.

Astmatika prescribes a hypoallergenic diet.
If the disease is in remission, the patient needs to adhere to the basic rules of proper nutrition, as well as to be from the products that cause him allergies. He must consume:
- complex carbohydrates in the form of cereals (preferably without gluten) and rough grinding bread
- low -fat meat (rabbit, beef, turkey, possibly chicken)
- milk and dairy products
- eggs
- loof fish
- vegetables and fruits
- butter and vegetable oil
They can fall under the ban:
- fat dairy products
- pork
- some types of fish
- citrus and exotic fruits
- vegetables and greens containing sorrel acid (sorrel, trough, salad, spinach, read)
- sharp seasonings and spices
- nuts
- mushrooms
- honey
- berries, pepper and peaches (if asthma is aspirin)
Astmatika is powered according to the following principles:
- the daily calorie content of the diet is based on individual characteristics, but not more than 3,000 kcal per day
- fractional nutrition
- small portion size
- sufficient and correct water consumption regime
- it is not recommended to salt food
Video: Bronchial asthma: recommendations for nutrition and lifestyle
Disability in bronchial asthma in adults
Bronchial asthma and disability are not identical concepts. The presence of only a diagnosis for a medical and social examination is not enough to give a person a disability group.
In order to try to do this, the patient needs to go to an appointment with the therapist or pulmonologist and ask for a referral for examination.
During a visit to ITU, asthmatics must be with you:
- A direction issued by a therapist or a pulmonologist
- A special document in which the diagnosis of “bronchial asthma”, the degree of its severity, the frequency of exacerbations, the severity of suffocation attacks, the presence or absence of a patient with corticosteroid dependence, the presence or absence of asthma complications in a patient are prescribed
- Wage sheet signed by the therapist, cardiologist, neuropathologist, endocrinologist and other doctors - specialists
- Blood tests, cardiogram, radiogram of lungs, spirogram, hormones tests
- Extracts from hospitals in which the patient treated asthma
- An identity document (passport)
- Insurance policy
Important: ITU evaluate not only the state of health of asthmatics, but also the conditions of its labor

With bronchial asthma, you can get disability.
Patient with bronchial asthma can be assigned one of three disability groups:
- The third group is assigned to patients with medium -severity asthma, quickly stopped by suffocation attacks, infrequent hospitalizations. It implies the transfer of the patient to lightweight work or reducing his working day. Harmful work is contraindicated for them
- The second group is assigned to a person with asthma, which was complicated by diseases from other organs and systems. Poor well -being significantly worsened the patient’s physical capabilities, he often needs treatment in hospital conditions, as well as visiting health resorts
- An asthmatist recognizes an disabled person of the first group, in the body of which irreversible processes are launched. He is no longer able to serve himself, move himself, and, moreover, work
Important: if the ITU decision seems to be unfair to the patient with bronchial asthma, he has the right to challenge him in court
Treatment of bronchial asthma in adults with folk methods
Important: any folk method of asthma therapy should be consistent with the doctor, since the products and herbs used for them are often allergens. They will not only help, but provoke an exacerbation of the disease
RECIPE: Milk and pine cones
Need: pine cones - 3 pcs., Milk - 0.5 l
- pine cones wash
- put them in a thermos
- pour hot milk into a thermos
- insist 4-6 hours
- filter the drug
- use a glass of the drug twice a day
RECIPE: Jergery infusion
It is necessary: \u200b\u200bthe root of Jerusalem artichoke is grated - 2 tbsp. tablespoons, water - 200 ml
- topinamybur root is rubbed on grater
- pour it with boiling water
- insist 2-3 hours
- filter
- divided into four portions
- consume during the day
RECIPE: Infusion of herbs
I need: anise, chamomile, calendula, coltsfoot, mint, lobillar, violet, licorice root
- i am mixing herbs
- take them 2 tbsp. tablespoons and pour into a thermos
- pour grass 1.5 l of boiling water
- insist 2 hours
- filter
- drink 50 ml before meals
VIDEO: How to cure bronchial asthma with folk remedies? Astma cure
Prevention of bronchial asthma in adults
Astma prevention in adults can be three types:
- Primary. These are measures aimed at preventing the disease. They imply hypoallergenic life, cleanliness in the house, compliance with personal hygiene rules, proper nutrition, sufficient physical activity, hardening, prevention of seasonal respiratory diseases, rejection of bad habits, so on
- Secondary. These are measures aimed at preventing exacerbations of the disease that has already developed. A doctor or nurse should tell the patient about them
- Tertiary. These are measures aimed at avoiding death at the time of an attack of suffocation or from a complication of the disease