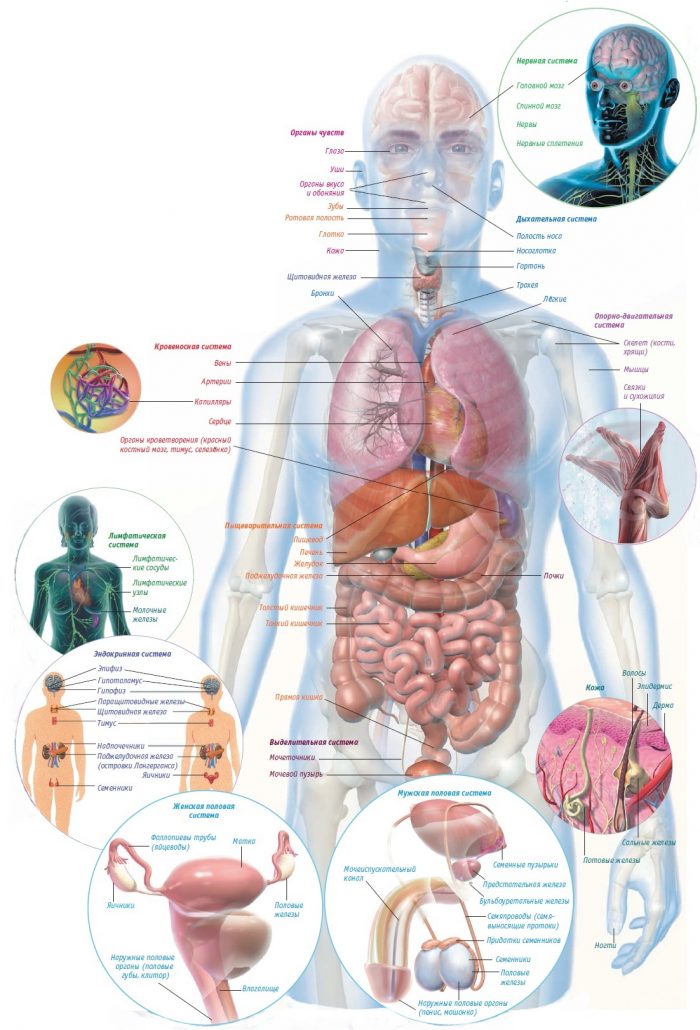
The content of the article
- The location of the human organs: photo with inscriptions
- What organs are located in the chest: scheme with inscriptions
- What organs are located in the abdominal cavity: scheme with inscriptions
- The structure of the pelvic organs: scheme with inscriptions
- Video: human anatomy. Where and what is located?
A set of mandatory knowledge for a person is constantly expanding. However, without a clear understanding of the functioning of the body, its needs and interconnection of organs, all other achievements of science and progress are useless.
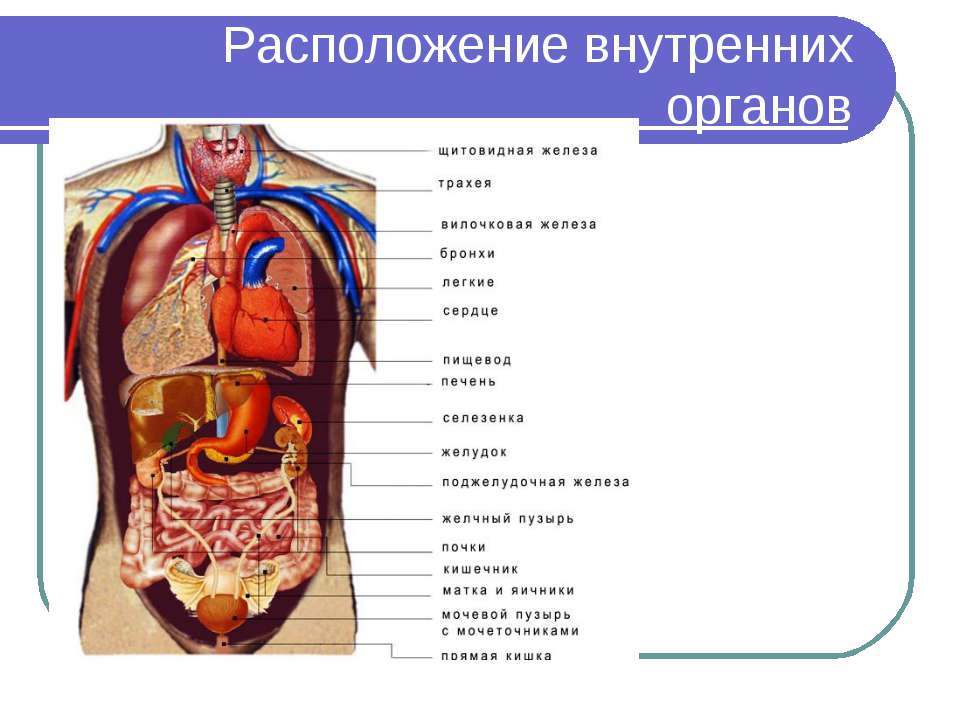
The location of the human organs: photo with inscriptions
the distribution scheme of organs inside the human body
- thoracic
- abdominal
- large and small pelvis
The thoracic region, in turn, consists of:
- 2 lung spaces
- heart zone
- directly abdominal
- rubbing
So the chest organs are responsible for:
- breath
- oxygen absorption and getting rid of the exhaust air
- blood pumping
- digestive processes
- the absorption of useful substances
- immunity fortress
- filtering toxins, poisons
- participation with the bloodwalk of your body, and in the female version - the fetus
- acid formation for digestion
- hormonal regulation of the correct operation of all abdominal organs
- selection of spent substances
- reproduction
- hormonal management of the work of the body in question
- tubular, or hollow - for example, stomach
- solid that do not have a cavity - for example, the liver
- muscles contribute to the abbreviations of the organ,
- mucous membranes - moisturizing and absorption of substances,
- the slippery outer layer is the lack of friction between the organs.
In our body, part of the organs are paired, for example, light, part without a couple, for example, a heart.
version of the internal structure of the human body
What organs are located in the chest: scheme with inscriptions
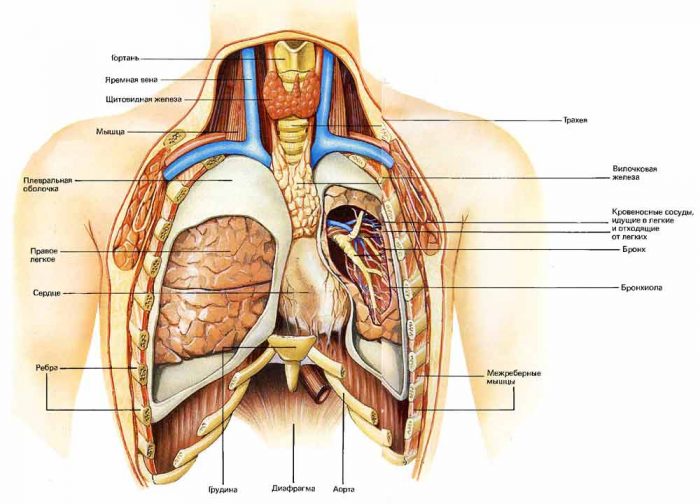
the structure of the human chest, the view from the inside
- They occupy almost all of its space, especially at the time of inspiration. From below, the lungs rest on the diaphragm. Around them - protection from the ribs.
- The bronchial tree branches inside the lungs and connects them to the trachea.
- In this case, its left branch is thinner and longer than the right.
The thymus gland is the mysterious organ of the chest. It is located in the upper part of the latter over bronchial branching into the lungs. Participates in the work of the human immune system.
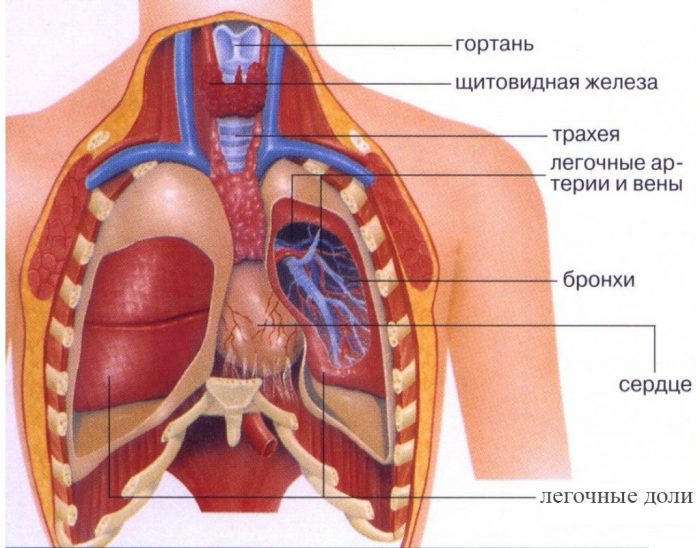
the enlarged diagram of the organs inside the human chest
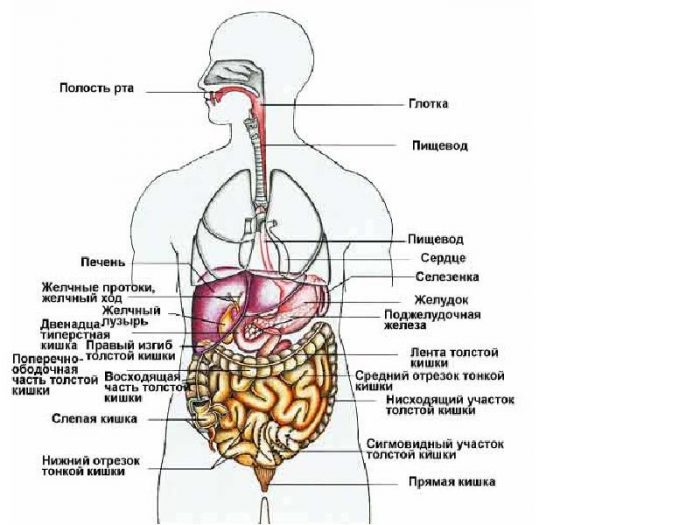
What organs are located in the abdominal cavity: scheme with inscriptions
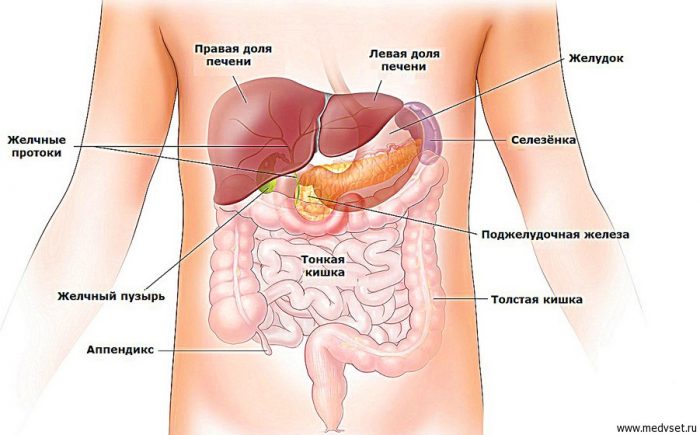
abdominal scheme: arrangement of organs
- in the center
- to the right of him
- left
The first category is the intestines.
- The small intestine in appearance is a thin mixed tube. It is formed at the place of narrowing of the stomach and can reach 6 m in length. It smoothly expands into the large intestine on the right below. The latter forms a semicircle clockwise throughout the abdominal space and ends with an anus.
The second category is the stomach, pancreas, spleen.
The stomach is the expansion of the esophagus resembling a bag. It is immediately under the diaphragm.
- As it is filled, he is able to change his size. In people with addiction to the absorption of a large amount of food, the stomach is increased.
- It is a reservoir for the accumulation and digestion of food, passing the first stage of mastering nutrients.
The stomach is a complete organ with several layers of muscles. Due to the reduction of the latter, food moves along the organ and further into the intestines.
The pancreas is located slightly below under the stomach. She is:
- participates in the process of digestion of food,
- produces juice for its splitting,
- provides metabolic processes in the body, namely protein-carbon and fat.
Spleen:
- is responsible for the production of lymphocytes
- accumulates platelets
- captures harmful substances and bacteria, filters them
- member of the metabolic processes of the body
- ambulance for red blood cells and platelets with damage to the membranes
The liver is a vital human organ. It consists of 2 shares, of which the right is much smaller than the left.
- maintaining lipid balance
- assimilation of cholesterol and glucose
- the conclusion of an excessive amount of vitamins and substances of internal metabolism
Its task is to accumulate bile coming from the liver, and send it to the intestines. It helps to digest food at all stages of its movement, starting with the stomach.
The kidneys are similar in shape to beans.
- They are located behind the abdominal organs closer to the lumbar zone.
- The right kidney is smaller than the left. The weight of one ranges between 100-190 gr, and the size is about 10 cm.
- The purpose of the kidneys - filtering and secretion of urine, regulation of chemical processes.
- adrenaline
- sexual - androgens
- corticosteroids
- cortisone and cortisol
- norepinephrine
Visually, the scheme will help you visually remember the location of the abdominal organs.
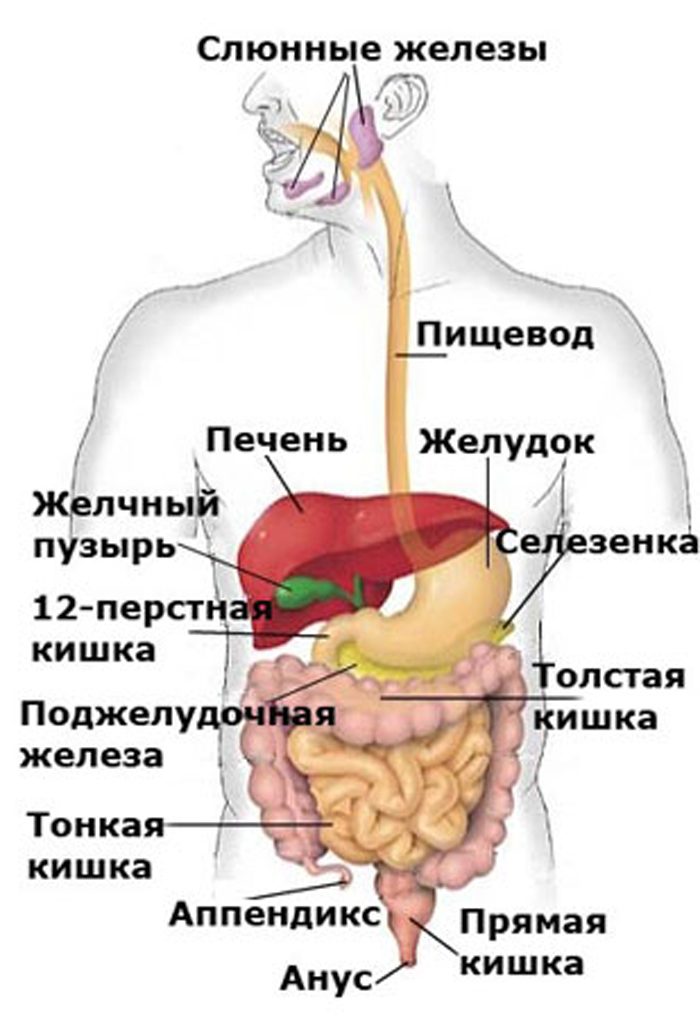
abdominal organs: scheme with inscriptions
The structure of the pelvic organs: scheme with inscriptions
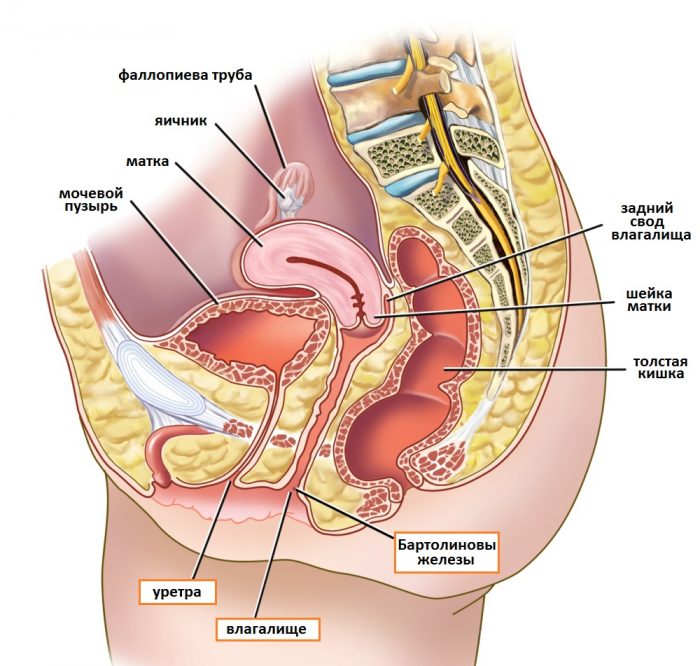
a schematic image of the structure of the internal organs of a small pelvis in a woman
In the small pelvis are located:
- bladder and rectum - general
- uterus and ovaries - in women
- playing gland and testicles - in men
The bladder is piled on the pubic area. In an empty state, it seems to be flattened, and in filled, it has the shape of an oval container.
The rectum is a continuation of the large intestine. It is located vertically down the far wall of the pelvis.
Its task is to collect and withdraw the developed material after the digestive process.
- uterus in women
- prostean gland in men
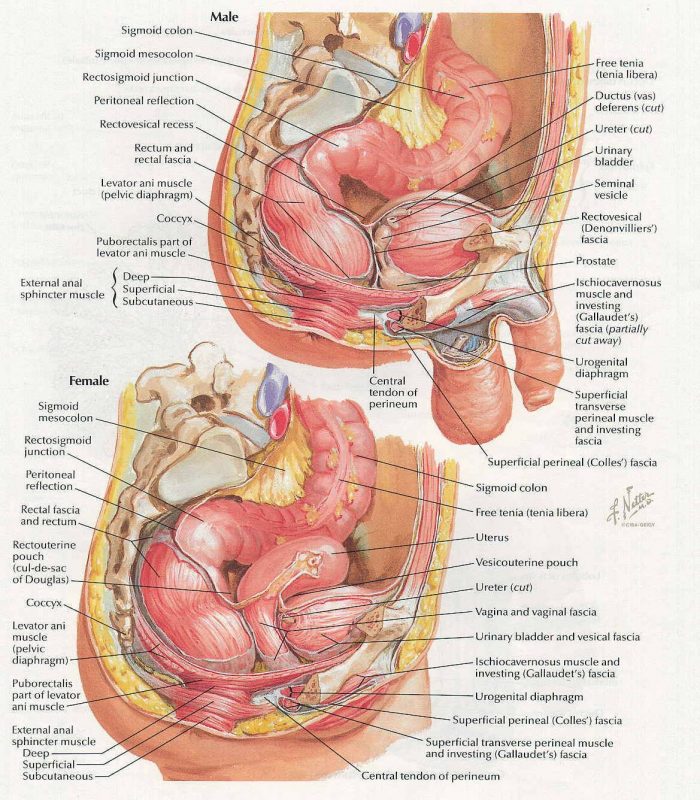
the structure of the internal organs of the pelvis in men and women
Study the structure of your body consciously. Learn to listen to his needs and live in harmony with him!