In the article, you will get acquainted with the structure of a skeleton of a person and recognize the names of the bones.
The content of the article
- The skeleton of man is a building with the title of bones: a scheme, photo in front, side, rear, description
- Main parts of a human skeleton, quantity, bone weight
- What fabric is the basis of the skeleton bones, which substance gives human skeleton strength, what is the composition of the bones?
- Anatomical skeleton of chest, human pelvis: scheme, description
- Anatomical skeleton of hands, human brushes: scheme, description
- Anatomical skeleton of shoulder and forearm of a person: scheme, description
- Anatomical skeleton of neck, human skull: scheme, description
- Anatomical skeleton legs, feet of man: scheme, description
- What bones in the skeleton of a person are connected moving using the joint and motionless?
- What is interconnected by the bone of a skeleton of a person?
- What is the role of a human skeleton, which ensures mobility, belong to the mechanical function of the skeleton bones?
- What are the features of the structure of a skeleton of a person associated with straightening?
- How many years does a human skeleton grow?
- What bones are tubular in a human skeleton?
- What is the longest, massive, strong and small bone in a human skeleton?
- Video: "The structure of the skeleton"
The skeleton of man is a building with the title of bones: a scheme, photo in front, side, rear, description
Everything is known that the skeleton is the bone system of man. The skeleton is a totality consisting of passive and moving bones. Without a skeleton, the body of a person simply will not be able to hold: all its internal organs and soft fabrics, muscles.
Interesting: in the human adult formed body, a total of about 200 bones are contained. But in the body of a newborn, the number of bones is significantly more - their 270! It is very easy to explain - through time small bones are formed into large.
All bones in the skeleton are connected by ligaments and joints (types of connective tissues). Surprisingly, at different stages of life, a person experiences many transformations of his skeleton. The most amazing of them is the transformation of the cartilage skeleton into the bone.
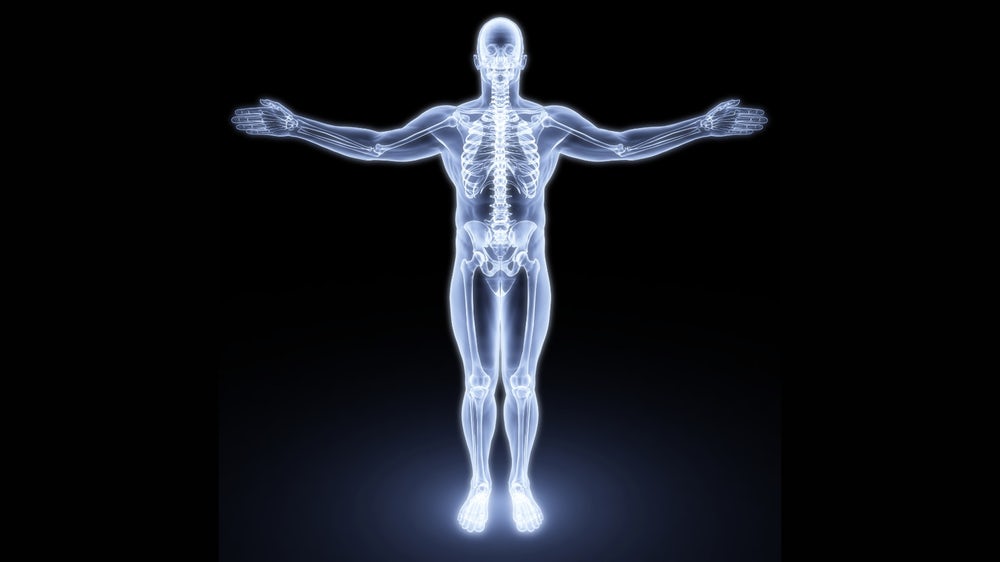
Projection of the skeleton from all sides
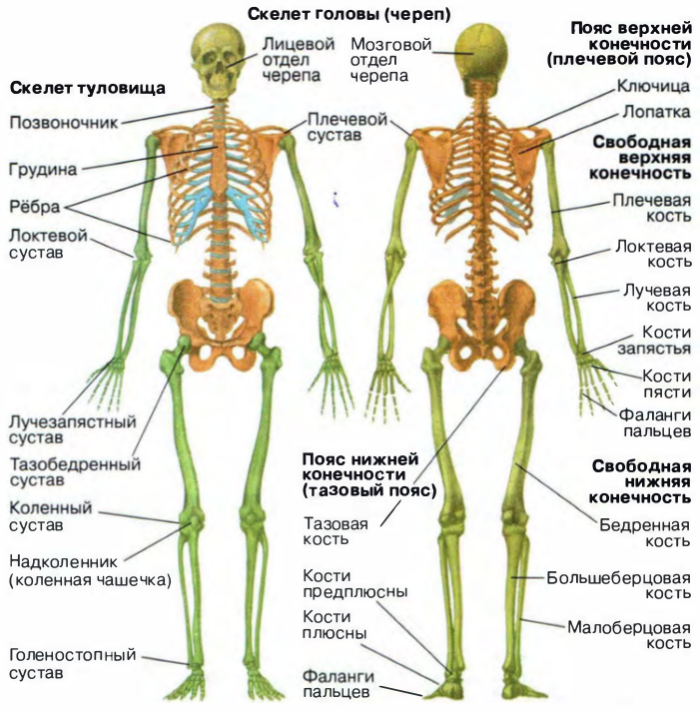
Main parts of a human skeleton, quantity, bone weight
The skeleton is divided into two groups:
- outer coat
- Additional
Outer coat skeleton:
- Scull -"Bone" of the head. It is in this bone is placed one of the most important internal organs of the human body - the brain.
- Rib cage -"Receptacle" major internal organs, their "body" and protection. In the cell 12 of the vertebrae and the same number of pairs of ribs.
- Spine -this axis of the body, in which the spinal cord passes.
Secondary skeleton:
- upper limb girdle(Scapula and clavicle)
- upper limbs
- lower limb girdle
- lower extremities
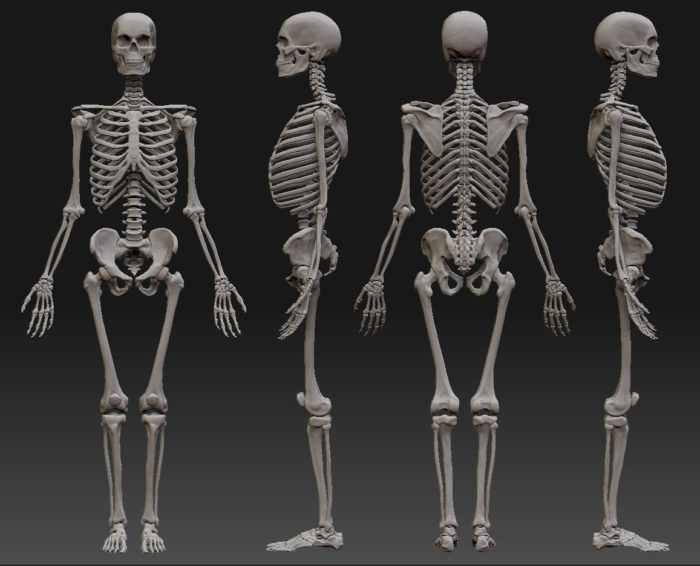
A description of all human bones
What fabric is the basis of the skeleton, which substance attaches human skeleton strength, what is the composition of bones?
Skeleton - the solid, sturdy and strong foundation of the body. He has the most important functions, without which human life would be impossible. It provides support, the ability to move and protects the internal organs.
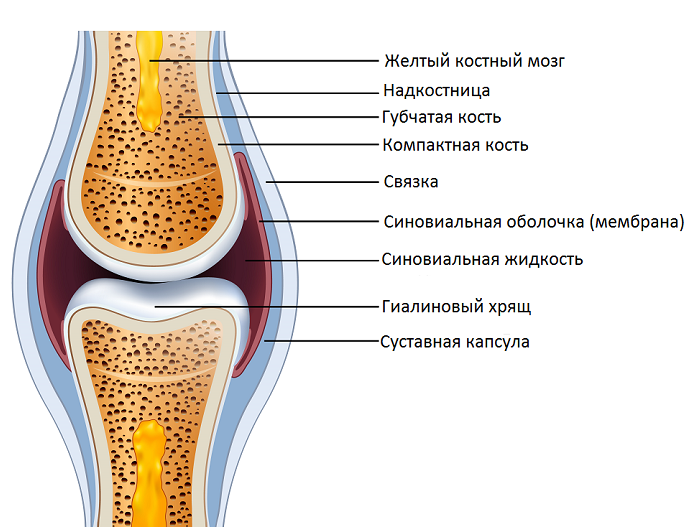
The skeleton is composed of bones and bone from the bone. What is a bone? This type of connective tissue. Few people know that inside the bone has nerves and blood vessels. In bone cells there is a large number of shoots, surrounded by special "channels" with the liquid. It is through this liquid, and there is a "breathing" of the cells.
This liquid is called "intercellular" and it consists of organic substances (protein) and inorganic (calcium and potassium salts). This structure allows the bones to be flexible and elastic at the same time.
INTERESTING: It is surprising that children's bones differ in that they are more flexible, and the bones of adults are much stronger.
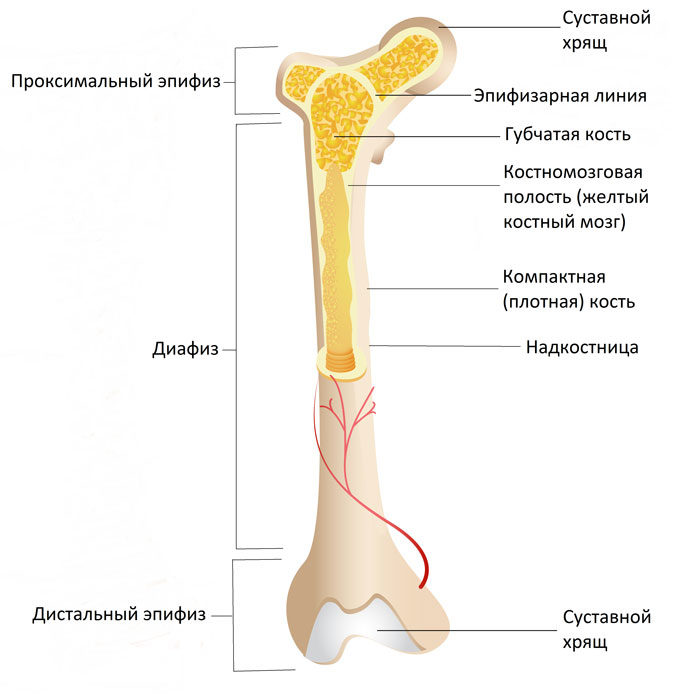
And bone structure
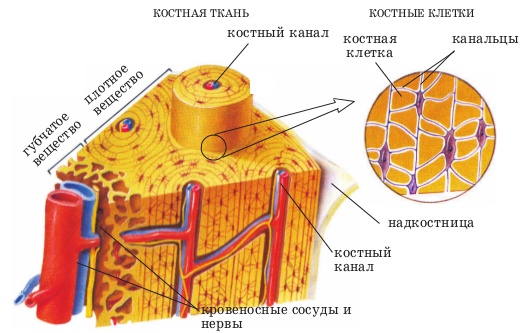
internal tissues
Anatomical skeleton chest, pelvis person: circuit description
Explore a detailed picture of the chest, to see every bone and learn its name.
Human thorax:
- The two sides
- Backside
- Front side
The thorax consists of:
- thoracic vertebrae
- ribs
- Breastbone (sternum)
- Upper and middle handle
- xiphoid
Features of the structure of the chest:
- The first edge is horizontal
- The ribs are connected to the sternum cartilage
- The chest "hide" the most important organs
INTERESTING: The rib cage helps a person breathe, helping the movement to reduce or increase the volume of air in the lungs. Thorax more men than women, but women - wider.
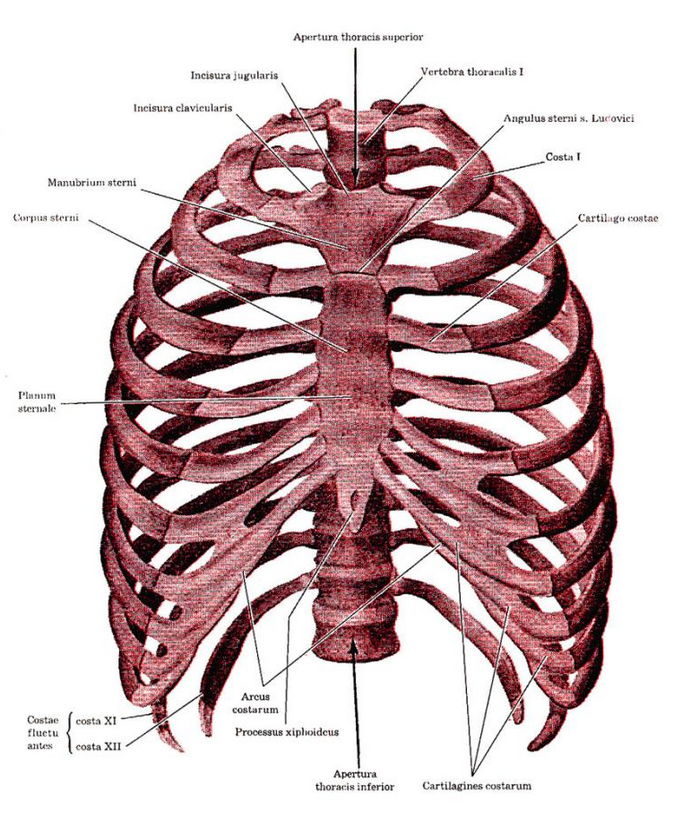
Rib cage
Anatomical skeleton hands, human hand: the scheme, the description
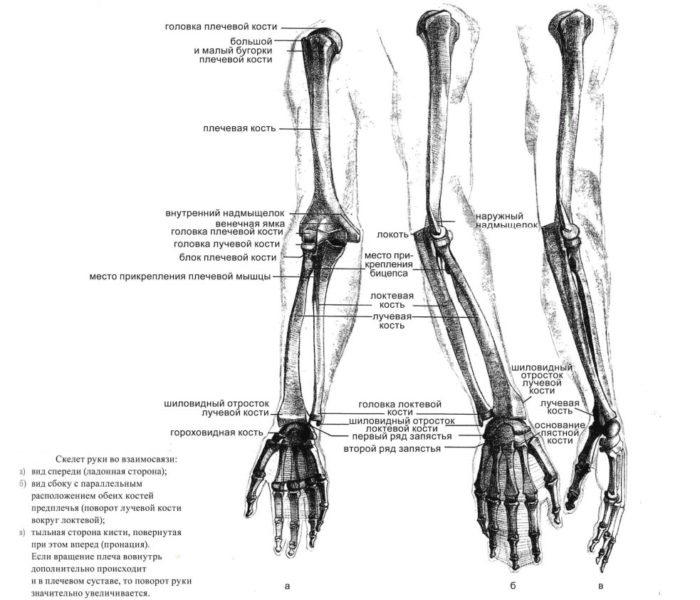
The hand of man is composed of many bones.
The hand is divided into three parts:
- Shoulder
- Forearm
- Brush
It's important to know:
- Bone Base Shoulder - Shoulder Bone
- Bone base of the forearm - elbow and radiation bone
- Brush consists of 27 separate bones
- Pyh contains 5 bones
- The skeleton of fingers consists of 14 phalanx
Bones of hand
Anatomical skeleton of shoulder and forearm of a person: scheme, description
Here you can consider the shoulder bones and forearm with names.
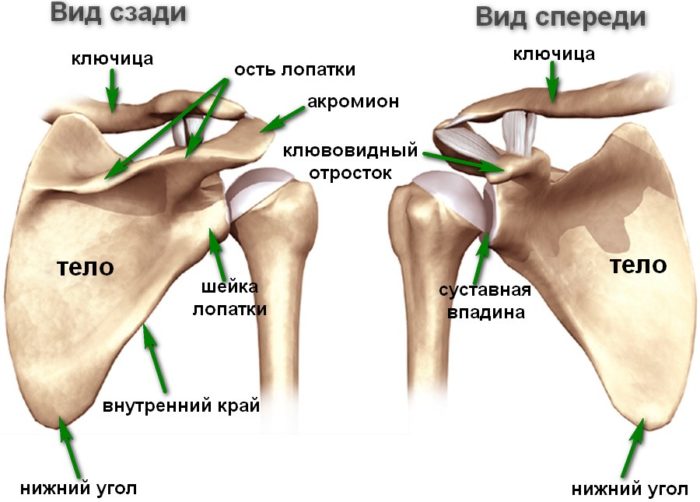
Shoulder and forearm
Anatomical skeleton of neck, human skull: scheme, description
In the pictures, all important bones of man are depicted in detail.
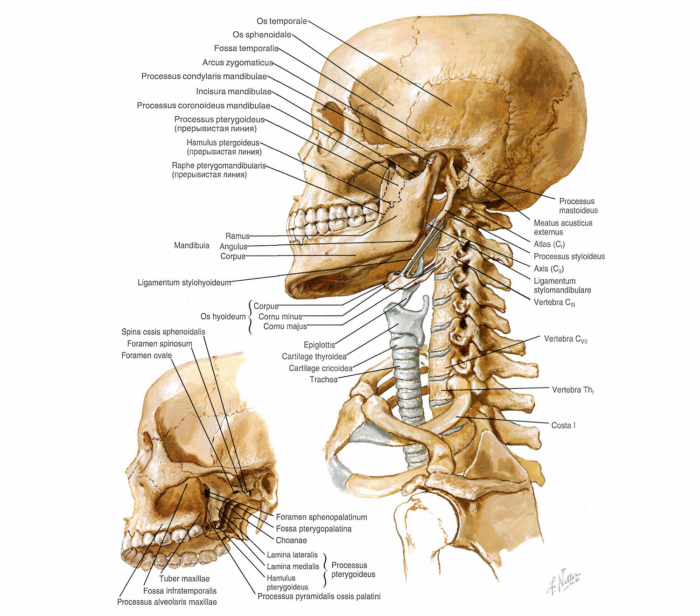
Head bones
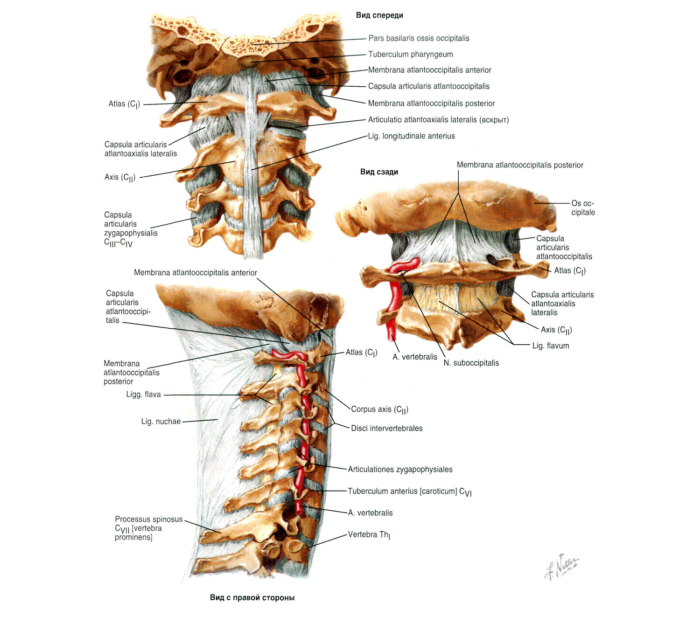
Bones of Neck
Anatomical skeleton legs, feet of man: scheme, description
Man's leg also has many bones.
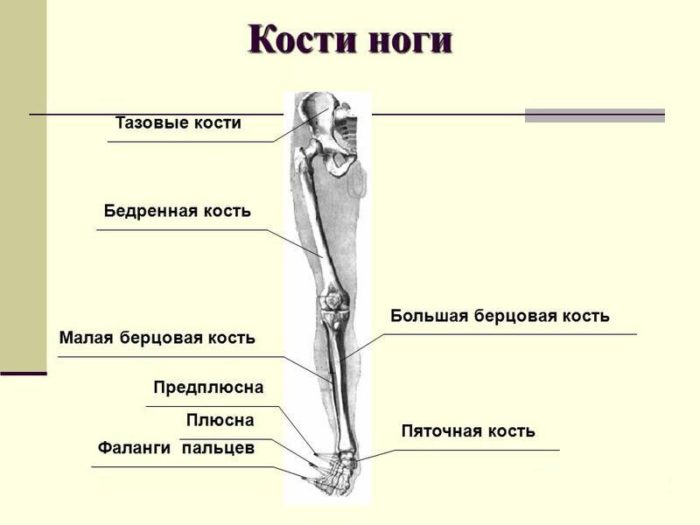
Bones of foot
What bones in the skeleton of a person are connected moving using the joint and motionless?
It is important to know what bones in a human skeleton are movably connected by joints or motionless.

Bones in tele
What is interconnected by the bone of a skeleton of a person?
The bones in the human body can be connected with:
- Joints
- Bonds
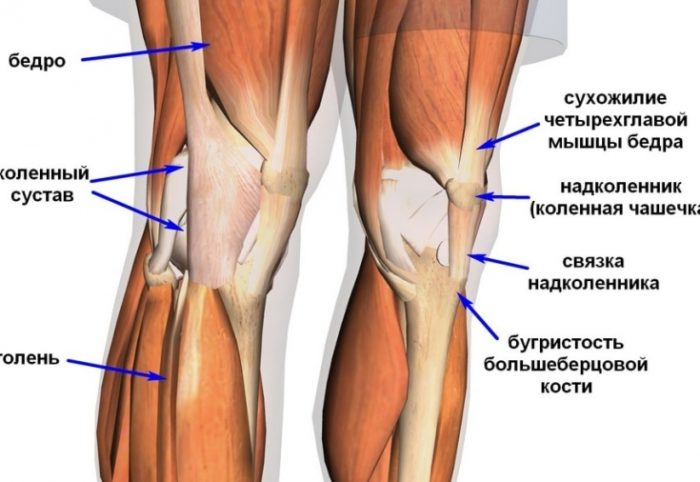
Bundles
Joint
What is the role of a human skeleton, which ensures mobility, belong to the mechanical function of the skeleton bones?
Functions:
- Musculoskeletal (body support and fastening of soft tissues, organs, body mobility).
- Movement (body transportation)
- Spring (softening the shock point)
- Protective (protection of internal organs from injuries)
What are the features of the structure of a skeleton of a person associated with straightening?
The human skeleton can be characterized by the fact that it has a vertical position. The spine holds straight, but has bends. During going, he is able to "spring", softening all the shocks. Due to the fact that the person goes straight, the chest is expanded.
The hand is the body of labor, the thumb is removed and developed so that it is convenient to capture and keep the subject. The belt has the form of a bowl and is a support for the pelvic organs. The lower limbs are stronger than hands and confidently hold the "heavy" body.
How many years does a human skeleton grow?
The human skeleton is experiencing several active formation stages:
- First "Early": from 0 to 7 years
- The second "teenage": from 11 to 17 years
- The third "final": in women until 25 years, in men up to 30.
What bones are tubular in a human skeleton?
Long tubular:
- Femoral
- TBERBERS
- Maloberstovaya
Short-cutting:
- Tweet
- Falangovye
- Metro
What is the longest, massive, strong and small bone in a human skeleton?
- The longest bone -femoral
- The most B.oLAL -tBERBERS
- The strongest -femoral
- The smallest -"Anvil" or "elder" (in the ear)