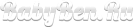In this article, the young mother can find out which tests will be required to hand over her newborn baby, and that they can show.
The content of the article
- What tests taken from a newborn?
- Analysis of the heel of an infant or neonatal Screening
- VIDEO: Taking blood from the heel
- Analysis of blood from a vein or finger
- Where to get tested a newborn?
- How to collect a urine sample to the newborn and how much?
- VIDEO: urinal children Apexmed: instructions for use
- blood test norm newborn
- Analysis for genetic diseases newborn: normal
- hormones newborn Analysis: normal
- How to collect the feces of the newborn in the analysis?
- Tests of dysbacteriosis newborn - norm
- VIDEO: The study of feces for dysbacteriosis
As soon as the baby was born, he was immediately subjected to some manipulations necessary to adapt the little creature in the outside world, in which he had just emerged. These manipulations include umbilical cord cutting, wiping, weighing, eye instillation, etc. including a newborn take a blood test.
What tests taken from a newborn?
To check the health of the newborn, analyzes of his blood, urine, feces.
Also conduct some specific tests.
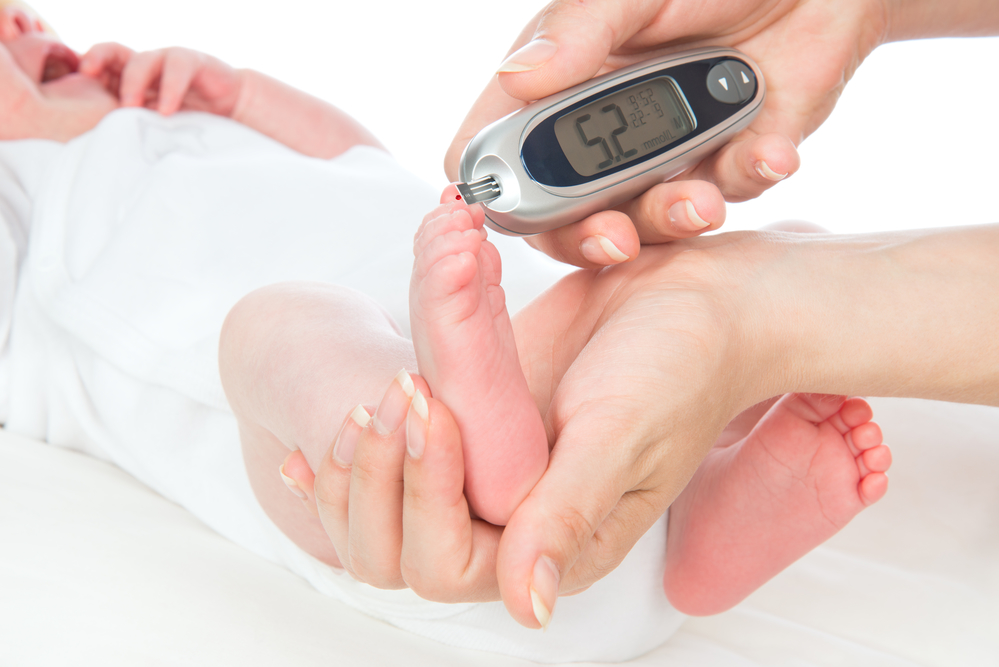
Analysis of the heel of an infant or neonatal Screening
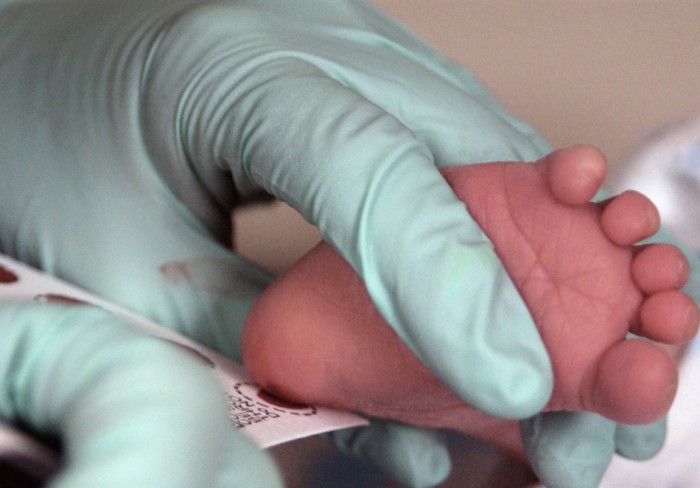
This assay, as previously reported, carefully carried out in the hospital for 4 - 5 days of life an infant or a 7 - 10 days (if the baby is born prematurely) for timely detection of genetic diseases (for more details see above.).
Analysis of the heel of the newborn takes a few days after birth to identify possible genetic abnormalities.
- Since the baby is still very tiny, blood samples have to be taken from his heels. First blood tests baby for genetic abnormalities are called screenings
- Such an analysis makes it possible to identify hypothyroidism, phenylketonuria and several other severe congenital hereditary diseases in the earliest stages, if any
- Analysis of blood taken from the heel at the baby on the 4th day of stay in the hospital, preterm infants - 7 day
Screening allows you to identify hidden health problems in a newborn.
What is hypothyodesis?
- Pretty rare (1 case per 5,000 babies), but an unpleasant congenital disease associated with the insufficient development of certain hormones. At the initial stage, before the manifestation of symptoms, on the basis of the analysis, if it is detected, appropriate treatment is assigned, which avoids the development of the disease
- The disease itself in the untimely identification or absence of adequate treatment can lead to defects in the physical, intellectual and mental development of the child
What is phenylketonuria?
- With phenylketonuria, the child does not produce an enzyme that cleaved the amino acid phenylalanine. This amino acid is part of protein products. If it does not split and accumulates in the body, then, in the end, becoming extremely toxic, the brain and the nervous system of the kid is striking. As a result, the child develops mental retardation
- Phenylketonuria is successfully treated with early detection and timely treatment. The problem remains only that, having matured, a person remains a carrier of the disease
- Fortunately, the disease occurs in a ratio of 1: 10,000 and is detected, due to the first test of blood from the heel
Other congenital diseases, to identify which allows the analysis of heel
Other congenital diseases that can be immediately identified at the newborn and subsequently to successfully treat, are galactosemia, adrenogenital syndrome and fibergation. These diseases also have a congenital hereditary nature and may have sad consequences in the form of anomalies of the child's development, and, as in the case of Galaktozhemia, and the fatal outcome.
VIDEO: Taking blood from the heel
Blood test or from veins
Sometimes, not all children are analyzed, taking blood from a finger or from veins. In children whose moms have a negative group of blood, take blood test from the umbilical cord to check and avoid reserves conflict.
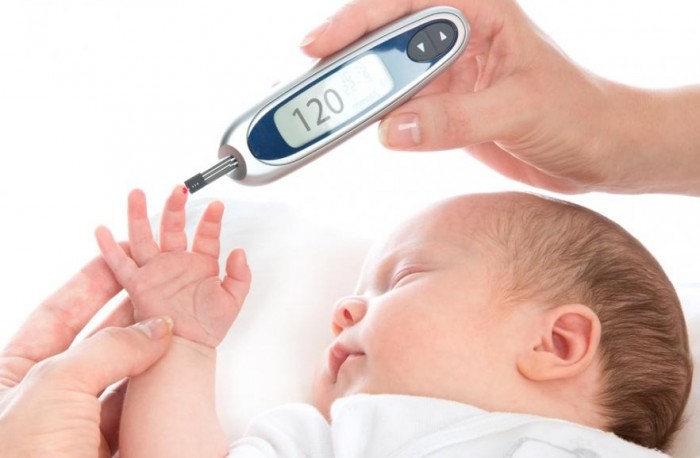
The blood test from the finger is taken from a newborn with a jaundice.
- The reason for the analysis of blood from a finger or vein becomes the jossing of newborns
- As you know, the jaundice may occur in the infant due to the non-formation of the body's functions due to the increase in the level of bilirubin. Such a jaundice is physiological and passes by itself somewhere two weeks after the child's birth. This promotes maternal milk and outdoor walking
- If, in some cases, the jaundice does not pass at the specified period, then this is a reason to carry out a further examination of the child in order to identify the level of bilirubin, pathologies in the development of liver and biliary tract. For this, additional blood tests are required.
Where to pass the tests of the newborn?
In newborns, tests are taken right in the maternity hospital.
A month later, on the need for tests can be handed over in the district children's clinic.
How to assemble urine on the analysis of the newborn and how much?
For the collection of urine in young children in pharmacies, special urinary workers are sold, which are attached to diapers.
Experienced mothers suggest other ways to collect urine. To do this, it is necessary to free the baby from the diamers in the morning, wipe the genitals with a children's damp napkin and start feeding.
At the same time, another person, for example, dad or grandmother, keep a jar for a boy or a deep plate for a girl. As a rule, the baby, as soon as it starts to eat, immediately empties.

Collect urine in the newborn will help a special urinary.
After that, urine needs to be pouring into a sterilized jar or a special container, which is also sold in a pharmacy.
For the urine analysis of the newborn, it is enough 10-20 ml, but not less.
VIDEO: bid Children's ApexMed: Application Instructions
Blood analysis rate in a newborn
Norms of general blood test for children from birth to 1 month
Newborn 0-7 days 7-30 days
- Hemoglobin 180-240 134 - 198 107 - 171
- Erythrocytes 3.9-5.5 4.0-6.6 3.6-6.2
- Color indicator 0.85-1.15 0.85-1.15 0.85-1.15
- Reticulocytes 3-15 3-15 3-15
- Leukocytes 8.5-24.5 7.2-18,5 6,5 -13.8
- Palcoidal 1-17 0.5- 4 0.5-4
- Segmented 45-80 30-50 16-45
- Eosinophils 1 - 6 1 - 6 1 - 5
- Basophiles 0 - 1 0 - 1 0 - 1
- Lymphocytes 15 - 35 22 - 55 45 - 70
- Platelets 180-490 180-400 180-400
- SE 2-4 4-8 4-10
- As is well known, the main indicators in the overall blood test are hemoglobin, red blood cells, leukocytes. Reduced or increased content may indicate some deviations in the functioning of the children's body
- For example, the increased content of erythrocytes in the blood may indicate a lack of fluid in the body, which happens at elevated temperatures, with intestinal infections, diarrhea, vomiting
- The reduced erythrocyte content may be due to a lack of protein and iron child, that is, insufficient nutrition and anemia. It may also indicate some serious diseases. Therefore, it is standing after some time to repeat the analysis in order to trace the dynamics of the blood erythrocyte level in a child
- The low content of hemoglobin also suggests that a child has anemia, and in its diet additionally products containing iron, magnesium and other minerals should be included.
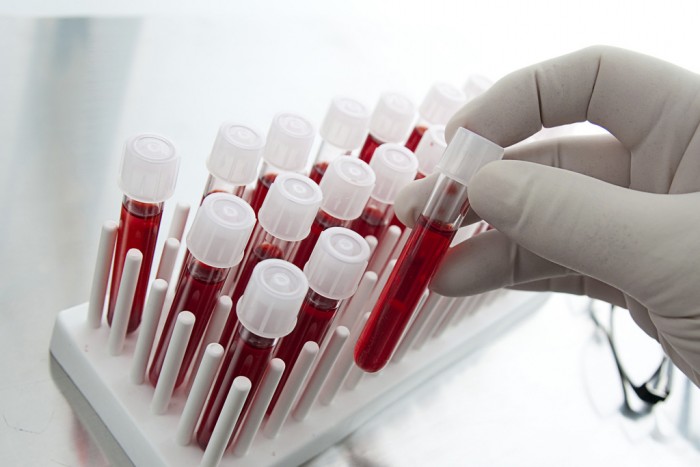
Blood indicators of the newborn say a lot about his health.
- If the blood test shows an increased leukocyte content, then this is evidence of the inflammatory process in the body. Need consultation and doctor assistance
- An increase in the content of leukocytes in the blood may be after vaccinations. This is a completely normal process, because a foreign substance was introduced into the child's body, and he responds to it with a completely physiological way.
Important: Another indicator of blood, about which parents should be aware is the content of eosinophils. If the indicator is exceeded, an allergic reaction occurs in the child's body, or it has worms
Analysis on genetic diseases Newborn: norm
- Analysis on genetic diseases Newborn is the same screening, blood for analysis of the heel. It is carried out as follows. The baby's heel is treated with alcohol and punctured in order to collect 5 blood droplets (one to identify genetic diseases described above). Blood is collected on a special test form. It is paper, so blood absorbed immediately
- After that, the filtered test form with the collected analysis is sent to a special laboratory and is investigated. Results are not used earlier than 10 days or month
- If the analysis is normal, the parents do not inform about it. If any deviations are revealed, this is immediately reported to the clinic of a child and parents for the passage of compulsory treatment.
- If the analysis gave a positive result, then further, more thorough examination of the baby in the endocrinologist, X-ray of the thyroid gland and ultrasound, additional analysis of hormones
Hormone analysis newborn: norm
The hormones of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland are investigated.
So, TTG and T4 are investigated.
- TTG - thyrotropic hormone
- T4 - Tyroxin
The rate of TSH in a newborn - up to 17 mm / l.
More than 50 - there is a suspicion of hypothyeriosis.
More than 100 - hypoteriosis is diagnosed.
How to assemble the feces in a newborn for analysis?
If you collect urine analysis, especially in newborn girls, there may still be a problem, then the feces analysis is going with diapers, from the middle. It will take a volume of approximately equal volume of the teaspoon.
Important: If necessary, storage material for analysis in a closed container can be kept some time in a cold place.
Container for feces.
Tests for dysbacteriosis newborn - norm
- Today, many parents use the word dysbacteriosis, since it is a rather frequent phenomenon associated with incorrect nutrition, an individual state of health, environmental factors, and the like.
- The analysis of dysbacteriosis allows us to find out the number of normal and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms in the child. Additionally, it turns out the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics, and this is important for the purpose of proper treatment.
Useful microorganisms include bifidobacteria, lactobacillia, intestinal sticks. To conditionally pathogenic - staphylococci, enterobacteria, mushrooms - Pathogenic include Salmonella and Shigella
- If the baby is constipation or, on the contrary, diarrhea, allergies or intolerance of some products in the idea of \u200b\u200bintestinal disorder or spindles on the skin, he needs to make an analysis on dysbacteriosis
How to assemble the feces to dysbacteriosis, will tell a nurse. Mom warn that the baby does not need to give any new products 3 days before analysis.
Normally, the analysis of newborns will show:
- biofidobacteria - 1010-1011 Come
- lactobacilli - 106-107 Come
- escherichia - 106-107 Come
- bacteroids - 107-108 Come
- enterococci - 105-107 Come
- saprofit staphylococci - up to 104
- pathogenic staphylococci - no
- pathogenic enterobacteria - no