In order to correctly diagnose a particular disease, it is necessary to donate blood for analysis. What tests to take and what they mean to learn below.
The content of the article
- General blood test (UAC) in children - norm and decoding results: table
- Biochemical blood test in children - decryption and norm in the table
- Hematological blood test in children decryption
- Blood test for allergens in children
- Blood test for tuberculosis for a child instead of a mantu
- Blood test for leukemia in children
- Blood test for worms in children
- Blood test for lamblia in children
- Blood test in chlamydia in children
- Blood test for sugar in children
- Blood test for hidden infections in children
- Staphylococcus a test in children
- Analysis for lead in the blood in children
- Analysis for amino acids in a child
- Blood test for scarlet fever in children
- How to take an analysis for whooping cough child
- Blood test for chickenpox in children
- Analysis for mycoplasma in children
- Blood test for appendicitis in children
- Blood test for rickets in children
- Video. Clinical blood test
Important: any blood test is given strictly on an empty stomach and fried, acute and fatty dishes are excluded from the diet a couple of days before it.
General blood test (UAC) in children - norm and decoding results: table
General blood analysis
A general blood test or clinical is the most affordable and capacious method of blood test. The results of this analysis may indicate various deviations in the state of health of the child. Proper decoding of indicators is able to diagnose the disease, direct the child to the desired specialist and prescribe the necessary treatment.
| Index | General blood test - norm | ||||||
| 1 day | 1 month | 6 months | 12 months | 1-6 years | 7-12 years | 13-15 years | |
| Hemoglobin, HB | 180-240 | 115-175 | 110-140 | 110-135 | 110-140 | 110-145 | 115-150 |
| Color indicator | 1,2 | 1,1 | 0,8 | 0,9 | 0,95 | 1,0 | |
| Hematocrite, % | 56 | 45 | 35 | 37 | 39 | 47 | |
| Red blood cells, RBC | 4,3-7,6 | 3,8-5,6 | 3,5-4,8 | 3,6-4,9 | 3,5-4,5 | 3,5-4,7 | 3,6-5,1 |
| Platelets, PLT | 180-490 | 180-400 | 180-400 | 180-400 | 160-390 | 160-380 | 160-360 |
| Retikulocytes, RTC | 3-15 | 4,5-21 | 2-10 | 2-10 | 2-7 | 2-13 | 2-11 |
| ESR, ESR | 2-4 | 4-8 | 4-10 | 4-12 | 4-12 | 4-12 | 4-10 |
| White blood cells, WBC% | 8,5-24,5 | 6,5-13,8 | 5,5-12,5 | 6-12 | 5-12 | 4,5-10 | 4,3-9,5 |
| Lymphocytes, Lym % | 12-36 | 40-76 | 42-74 | 38-72 | 26-60 | 24-54 | 25-50 |
| Monocytes, mon % | 2-12 | 2-12 | 2-12 | 2-12 | 2-10 | 2-10 | 2-10 |
What do these indicators say and what does deviations from norms lead to?
- Hemoglobin - Two -component protein, consisting of protein and atomf iron, as part of red blood cells. The main function: transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide between organs and light.
Reduced level - a sign of the development of iron deficiency anemia.
Increased level -speaks of the lack of water in the body and a violation of the activity of the cardiovascular system - Red blood cells - Red blood cells, the basis of which is hemoglobin, and therefore their functions are the same. Participate in oxygen breathing and metabolism
Reduced level - development of iron deficiency anemia, liver disease and a sign of poisoning
Increased level - A slight increase indicates dehydration. Exiled indicators indicate a disease of blood or heart, or the development of cancer processes in the liver and kidneys, as well as a violation of the respiratory system for the respiratory system - Platelets - The main participant in the process of blood coagulation.
Reduced level leads to poor blood coagulation (with the exception of the menstrual cycle in women)
Increased level It can cause the development of blood clots in the vessels (with the exception of the menstrual cycle in women) - Reticulocytes - bone marrow cells from which red blood cells are formed in further
Reduced level - provokes damage to the kidneys or bone marrow, which leads to further depletion.
Increased level - deficiency of iron and folic acid, accelerated erythropois - ESR - indicator of the velocity of erythrocyte.
Increased level speaks of any inflammatory and pathological processes in the body - Leukocytes - white blood cells, the main function of which is the protection of the human immune system
Increased indicator Leukocytes are considered the norm for any physical exertion, during pregnancy. Attention should be paid to the lack of provoking factors., Because This may indicate the development of viral and bacteriological infection, allergies
Reduced level - Low immunity factor - Lymphocytes and monocytes- The cells of the leukocyte row, perform a protective function. Increasing and lowering the level indicates the same as leukocytes
Biochemical blood test in children - decryption and norm in the table
Blood chemistry
Biochemical blood test - analysis with which it is possible to identify a violation of the work of a particular organ of the child, the early development of pathological processes in the body, and determine the lack of trace elements.
Blood biochemistry includes more than 100 indicators, consider the most commonly encountered in the table.
|
Index |
Norm |
||
| 0-1 months | 1-12 months | 1-14 years | |
| Total protein, g/l | 49-69 | 57-73 | 62-82 |
| Albumin, g/l | 34-44 | 36-49 | 37-55 |
| Seromucoid, unit/l | 0.13-0.20 | ||
| Timille test, e/l | 0-4 | ||
| C-reactive protein | Negative | ||
| General bilirubin, μmol/l | 17-68 | 3,4-20,7 | |
| Direct bilirubin, μmol/l | 4.3-12.8 | 0,83-3,4 | |
| Indirect bilirubin, μmol/l | 12.8-55.2 | 2,56-17,3 | |
| Amylase, e/l | up to 120 | ||
| Alt, unit/l | up to 40 | ||
| AST, unit/l | up to 40 | ||
| Creatinin, mmol/l | 35-110 | ||
| Urea, mmol/l | 2,5-4,5 | 3,3-5,8 | 4,3-7,3 |
| Glucose, mmol/l | 1,7-4,7 | 3,3-6,1 | |
| Uric acid, mmol/l | 0,14-0,29 | 0,14-0,21 | 0,17-0.41 |
| Calcium, mmol/l | 2,2-2,5 | 2,3-2,87 | |
| Phosphorus, mmol/l | 1,8-2,7 | 1,3-2,3 | 1,0-1,8 |
| Sodium, mmol/l | 135-155 | 133-142 | 132-156 |
| Potassium, mmol/l | 4,5-6,5 | 4,0-5,6 | 3,6-5,1 |
| Magnesium, mmol/l | 0,66-0,95 | 0,7-1,2 | |
| Copper, MKMOL/L | 1,9-10,5 | 4,2-24,0 | 11,0-25,0 |
| Iron, MKMOL/L | 9,8-33,0 | 6,3-15,0 | 9,3-32,0 |
| Chlorides, mekv/day | 0,3-28,2 | 14,1-169,2 | |
| Oksalates, mg/day | 8,0-17,0 | ||
| Ammonia, mm/day | 4,0-15,0 | 35,0-59,0 | |
| p | 5,0-7,0 | ||
Hematological blood test in children decryption
Hematological blood test
A hematological blood test is carried out using a modern device - hematological analyzer. The device measures the level of hemoglobin and hematocrit, provides information about the morphological condition of blood cells and their quantity, calculates the leukocyte formula. The advantages of this equipment are time, the procedure takes 10-15 minutes.
More modernized models of analyzers are able to calculate the amount of granulocytes and agranulocytes, and distinguish between blood cells among themselves.
All information is transferred to the device to the form. What does it include and how to decipher the data obtained?
- WBC (White Blood Cells) " - Leukocyte level
- RBC (Red Blood Cells) - erythrocyte level
- Re (Reticulocytes) - content of reticulocytes
- HGB (Hemoglobin) - hemoglobin
- PLT (Platelet) - platelet level
- Mch (Mean Cell Hemoglobin) - degree of hemoglobin content in one erythrocyte cell
- HCT (Hematocrit) - hematocrite
- Gran (Granulocytes) - content of granulocytes
- Mxd, Mid (Mixed Cells) - the content of monocytes, basophils and eosinophils
- Lymp (Lymphocytes) - lymphocytes
- Mon (Monocytes) - monocytes
- Ba (Basophils) - basophils
- Ne (Neutrophils) - neutrophils
- EO (Eosinophils) - eosinophils
Blood test for allergens in children

Allergens
An important indicator when examining blood for allergens is The level of immunoglobulin E.The norms of its content are given below.
| 1-3 months | 3-6 months | 1-5 years | 5-15 years | 15-18 years |
| 0-2 | 3-10 | 8-20 | 10-50 | 16-60 |
Immunoglobulin E is an antigen protein that protects the body from foreign particles. Increase This indicator indicates the development of an allergic reaction of various kinds of manifestations (asthma, rhinitis, bronchitis, food allergies), the presence of helminthic invasions. In addition, the level of immunoglobulin increases with anaphylactic condition, atopic dermatitis and immunopathological diseases. Decreasethe level of immunoglobulin speaks of congenital or acquired immunodeficiency, and may also indicate a hereditary disease-Louis Bar syndrome.
Blood test for tuberculosis for a child instead of a mantu

Diagnosis of tuberculosis
Currently, in order to identify a disease such as tuberculosis, it is enough to donate blood for analysis. It is carried out in the event of a positive reaction of the body to a previously introduced manti test. Of course, instead of vaccination, you can immediately give blood, but still a mantle has confirmed the diagnosis.
When taking blood, two laboratory analysis is carried out: immunosorbent and PCR diagnostics for tuberculosis.
Important: Analysis of PCR - Tuberculosis is diagnosed in the presence of more than 10 mycobacteria in one sample
Advantages of blood test:
- the speed of the procedure and obtaining information (no more than 5 hours)
- identification of pulmonary tuberculosis in the analysis of PCR
- accuracy up to 98%
Blood test for leukemia in children

Leukemia in children
Leukemia is the formation of malignant cells in the blood system of the body, due to an increase in leukocytes in the bone marrow. Diagnosis of the disease is possible at the level of a general (clinical) blood test. If the data obtained indicates the development of the disease, the delivery of a biochemical blood test is prescribed. What data indicates leukemia?
- Very low hemoglobin level (anemia)
- Low level of red blood cells and reticulocytes
- Reduced or increased amount of leukocytes
- Manifestation of thrombocytopenia
- Increase in the indicator of ESR
- The difference in the size of white blood cells
- Lack of leukocyte series cells - eosinophils and basophils
Blood test for worms in children
Helminthosis
Helminthosis in young children is the most frequent disease. This is due to the fact that parasites easily move through the air and thus fall into the child's body.
Lethargy, moodiness, poor sleep, grinding with teeth during sleep, itching of anal passage and the appearance of parasites in feces are signs of infection with helminths.
Helminthosis will most accurately determine a blood test. The first line is a general analysis. Secondly-immunosorbentity analysis for parasites (ELISA). It is the latter that reveals helminths and determines their type, as well as their number and ability to reproduce. For analysis, venous blood is taken.
Blood test for lamblia in children

Helminthosis prevention
Of all parasitic diseases, lambliosis is diagnosed much more often. Lambia - microorganisms that affect the small intestine, thereby create an obstacle to digestion and absorption of food.
In the case of signs, such as: high temperature (38 degrees and above), nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, acute pain in the umbilical zone and a decrease in body weight, it is necessary to take a blood test for parasites by ELISA. Blood is taken venous. The essence of the analysis is the study of IGG and IgM immunoglobulins.
Decoding the data obtained:
| Less than 0.9 cu | lambiosis is not detected |
| More than 1.1 cu | lambiosis is detected |
| From 0.9 - to 1.1 cu | doubtful lambliosis (repeated testing) |
Blood test in chlamydia in children

The study of chlamydia
Chlamydia - microorganisms that mainly affect the respiratory system in children. Chlamydia in the form of bronchitis, conjunctivitis and pneumonia manifests itself.
In order to diagnose chlamydia, blood is donated from vein. Several types of tests are presented:
- ELISA (immunoformontal). The presence of antibodies IgM, IGA and IgG is checked - their presence speaks of infection. This analysis reveals the stage of the disease
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction). The most accurate analysis based on the genetic material of microorganism
- RIF (reaction of immunofluorescence). The analysis is taken from the urethra, painted with special reagents and is examined under a fluorescent microscope
Important: IGM detection is the initial stage, Iga is progressive, IgG is chronic. The norm is a negative result on all antibodies.
Blood test for sugar in children
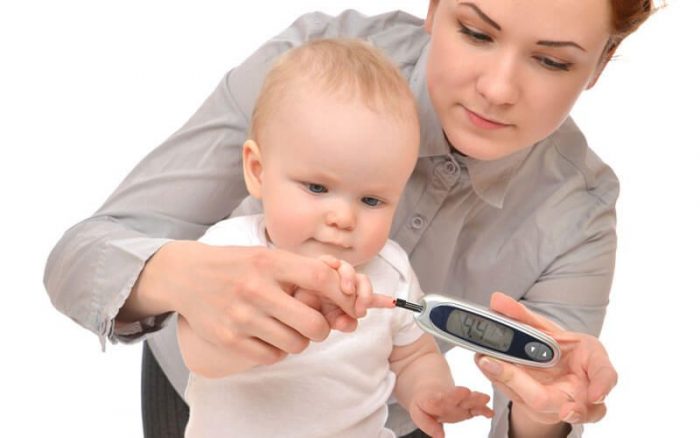

Blood test for sugar
Diabetes mellitus is a disease that disrupts the functioning of the pancreas and other organs of the body. Teenage children from 6 to 10 years are most susceptible to the development of diabetes, so it is important to donate blood for analysis at least once a year.
| The age of the child | Sugar level (norm), mmol/l |
| 0-2 years | 2,78-4,4 |
| 2-6 years | 3,3-5 |
| from 6 years | 3,3-5,5 |
Important: Improving the rate of the submitted analysis of more than 5.5 mmol/l speaks of diabetes mellitus
Important: sugar level more than 7.7 mmol/l after two hours of introduced glucose also indicates the disease
Before passing the blood test for sugar, several rules must be observed:
- The last meal 12 hours before the analysis. Only pure water is allowed
- Do not brush your teeth and do not chew gum, because They contain sugar
Blood test for hidden infections in children

Analysis for hidden infections
Many microorganisms, having settled in the body, feel quite comfortable, causing a particular disease asymptomatic. In this regard, it is necessary to take an analysis for “hidden infections”, these include: herpes virus, cytomegalovirus, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, ureapaplasmosis, etc.
The main types of blood tests for the identification of diseases:
- Immunoformal analysis (ELISA). Determination of antibodies Iga, IGM, IgG, the presence of which indicates infection
- polymerase chain reaction method (PCR).The study of the genetic material of the microbe in the blood (if it is detected). The analysis is the most accurate, but expensive
Staphylococcus a test in children
Golden staphylococcus
Staphylococcus is a microorganism that enters the microflora of the body. But, at the same time, an increase in their number threatens with serious consequences. Staphylococcus causes respiratory tract diseases, skin, gastrointestinal tract and others. There are several types of microorganism, the most dangerous of them is the golden staphylococcus.
To diagnose an infectious disease, laboratory studies of biological material are carried out:
- Bacterial sowing (The material is blood, feces, nasal mucosa or throat, pus, skin surface)
- Serological blood test (blood serum for the presence of antibodies is examined)
- PCR method
Analysis for lead in the blood in children

Lead
Lead is heavy toxic metal, which accumulates in the bones and is slowly excreted from the body. It mainly affects the synthesis of hemoglobin and the nervous system, thereby causing a developmental delay in children. Intoxication can be asymptomatic. To diagnose poisoning with this metal, a blood test is carried out, which is taken from a vein or finger (in newborn from the heel). According to its results, they indicate the content and degree of poisoning by lead.
Important: the rate of lead 10 μg/1 blood
Analysis for amino acids in a child

Amino acids in products
Amino acids are the basis of protein protein. Their imbalance leads to a violation of the work of the kidneys and liver. For the study, venous blood is taken and the following 20 acids are clinically checked:
| Amino acid | Content rate, μmol/l |
| Alanin | 360-630 |
| Arginin | 92-172 |
| Asparaginic acid | 2-30 |
| Glutaminic acid | 54-175 |
| Glycine | 100-400 |
| Treononin | 160-176 |
| Methionine | 20-34 |
| Tyrosin | 78-83 |
| Valin | 188-274 |
| Phenylalanine | 85-115 |
| Leucin | 130-252 |
| Isolecin | 122-153 |
| Triptofan | 30-90 |
| Lysine | 144-363 |
| Faciline | 110-135 |
| Prailin | 50-200 |
| Serin | 70-150 |
| Glutamine | 514-568 |
| Asparagin | 50-150 |
Blood test for scarlet fever in children
Symptoms of scarlet fever
Scarlatin is a very serious and contagious disease caused by Streptococcus A. The symptoms of its manifestation are very obvious, so the blood test is given a general (clinical). In diagnosis, there is:
- Leukocytosis
- Neutrophilia with a shift to the right
- Increase in ESR
- General change in hemogram
How to take an analysis for whooping cough child

Cough
Such a bacterial infection as whooping cough is difficult to diagnose. A number of tests are carried out for this:
- Clinical blood test
With the disease, the number of leukocytes increases, especially one of their species - lymphocytes. - Blood chemistry
- General analysis of sputum
Research is carried out using several methods:
- Bacteriological (sowing mucous secretions with coughing)
- Sowing from the nasopharynx and from under the tongue (modern method and the most convenient)
- Immunological (study of the discharge from the nose and blood for antibodies)
Blood test for chickenpox in children
Chicken pox
Wind OSPU is diagnosed according to the clinical picture, a blood test is taken to confirm the disease in its course. A general and biochemical analysis is carried out.
Clinical blood test:
- Decrease in leukocytes
- An increase in lymphocytes
- Decreasing platelets
Biochemical analysis:
- Increasing the level of Alat (temporarily)
- The appearance of antibodies on the 4-5th day IgM and IgG
Analysis for mycoplasma in children
For diagnosis of mycoplasmosis, laboratory research methods are carried out:
- Bacteriological sowing from a oropharynx
- PCR diagnostics
- Linked immunosorbent assay
Blood test for appendicitis in children

Appendicitis
Appendicitis is diagnosed by the clinical picture, a blood test is donated with not pronounced signs.
Clinical blood test:
- Increased leukocytes
- An increase in neutrophils
- Increasing the level of C-reactive protein
Blood test for rickets in children

Rickets in children
Rickets is a disease of the bone system. For its exact diagnosis, a number of studies are carried out, in which a blood test is also included.
- General blood test for the detection of hypochromic anemia
- Biochemical analysis for the content of phosphorus, calcium and alkaline phosphatase
The concentration of phosphorus and calcium with rickets decreases, and alkaline phosphatase increases