In the article, you will find answers to questions about how the auditorium affects the ability to learn how to develop and train the auditorium of the child from an early age.
The content of the article
- The shape, as a way to analyze and preserve information, is most pronounced in children's and adolescence. Over time, this type of memorization replaces the logical memory, which is not based on the visual image of items, and on its functional purpose
- Developed since childhood, the shaped memory can be very useful in certain professions and hobbies - creative, analytical, technical
- With an effective training workout, you can develop the ability to spatial thinking, memorizing and visual reproduction of a large amount of information.
Summary memory, features
Summary memory is one of the forms of shape. A characteristic feature of the visual memory is a certain conversion of an object visualization during its retention period.
In the process of conservation of visual information, the following modifications of the object presentation occur:
- simplification (discarding unnecessary parts)
- exaggeration (most significant image items)
- mysterious creation of symmetry (necessary for form perception)
- change color color
Such transformations make an image less accurate compared to descriptive characteristics, but at the same time turn it into a certain character, firmly fixed in memory and associatively causing qualified quality inherent in it.

Memorization of bright images is typical for the child's visual memory
Summary memory, memorization
Memorization is a function of displaying past practical experience, events, images with their declamation and more or less accurate reproduction. The basis of the science memorization mechanism are stable associative connections connecting real and general phenomena.
Fixing once a subject or image, the memory then parallel to other objects or events associated with it. Associations are formed involuntarily, and can be specifically selected to memorize certain information and classified:
- by adjacentness - bind 2 or more phenomena in time or space, for example, performing a sequence of operations, the assimilation of verbal material, a certain response to sounds, danger
- by similarity, some phenomena with similar features are associated. They are based on the identity of nervous connections caused by objects or events
- in contrast - combine 2 or more opposite phenomena. Most often, contrasting objects or events cause emotional bursts, then mentally analyzed and compared, due to which the formation of new nervous ties occurs.
More complex associations connect the phenomena associated in reality, but possessing various properties, origins, classification. For example, the genus and view (bird is swallow), the whole and part (lemon - slice), the cause and consequence (rain - rainbow), the subject and definition (ice cream is cold).

Set of pictures for training associative visual memory
To create sustainable associations, multiple repetitions are needed. Sometimes the connection may arise quickly if the event made a strong impression or caused an emotional experience.
Then in the cerebral cortex form an active focus of excitation, which is responsible for the formation of strong ties. To develop an associative memorization, special games should be carried out with a child in the form of questions and search for answers:
- "What does this subject look like?"
- "Find suitable to it in shape, color, smell, taste, etc."
- "What parts can be split this figure?"
- "Find the missing fragment of a whole (group of subjects)"
Views of visual memory
Almost every impression, an emotional experience, seen the image is left in the mind of a person a trail, which can be stored for a long time and used in appropriate situations. Studying the functioning of memory is aimed at managing psychological techniques and physiological mechanisms that allow to hold and reproduce a large amount of material.
Such skills are especially necessary during the period of training and active cognitive activity. Species of visual memory are divided into the following:
- Long term memory - Saves and holds information for quite a long time. All accumulated practical experience, horizons, reproduction functions of visual images are based on this type of memory.
- RAM - Starts processes to perform current actions with subsequent forgetting intermediate information. The storage of RAM data can be from a pair of seconds to several days
- Emotional memory - Memorization of feelings and experiences. Emotional signals stored in memory encourage people to act or hold from any actions. The ability to empathy - empathizing another person, a fictional literary or film representation is a manifestation of emotional memory.
Summary motor memory
- Motor (Motor Memory) - the ability to save and reproduce basic and special motor functions, both own and seen. This type of memory is the basis for the development of walking, letters, domestic skills, manual labor, creative activities, performing sports exercises
- Bad motor memory is usually expressed "clumsy" and lack of clear, coordinated movements
- The development of this type of memory is based on observations and multiple repetitions of movements. The errors allowed in exercises shape the development of movements and stable memorization

Development of visual memory - the main element of learning reading and writing skills
Short-term visual memory
Short-term memory - Reflects not the full content of phenomena, but only their interpretation. For example, several words are stored in the memory of the phrase or the most bright, not complete, and the general image of the image seen.
This type of memorization allows you to identify items based only on visual perception of shape, color, content, orient in space using visual images.
Volume of visual memory
The volume of short-term visual memory of an adult is approximately 7 ± 2 units. For a child, this figure is approximately equal to its age. For more accurately, a special technique is used, which includes the test of the test in the form of a picture.
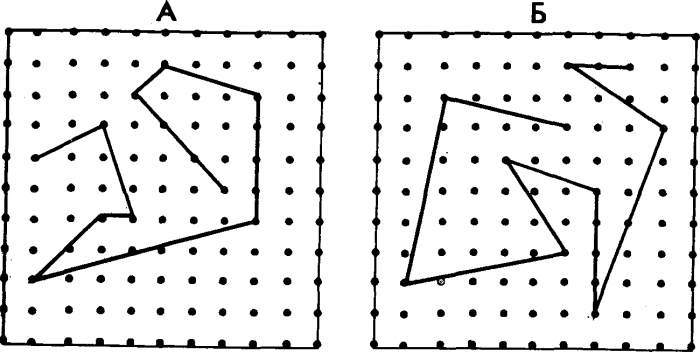
Pictures for testing for the volume of visual memory
The child is invited alternately to consider 2 images, and then on an empty stencil reproduce all stored lines from each part. As a result, the average number of correctly depicted lines is calculated.
The correct is also considered the line, length and location of which is slightly different from the original. The resulting indicator is considered the volume of visual memory in units and is estimated at a 10-bital scale:
- 10 points - if a child of 10-12 years old has an indicator of more than 8 units, aged 6-9 years - 7-8 units
- 8 - If a child of 10-12 years has an indicator of 6-7 units, aged 6-9 years - 5-6 units
- 4 - If a child is 10-12 years old, has an indicator of 4-5 units, aged 6-9 years - S-4 units
- 0 - If a child of 10-12 years old has an indicator of 0-1 units, aged 6-9 years - 0
Diagnostics of visual memory
The diagnosis of visual memory in preschoolers is important from the point of view of determining the degree of readiness of the child to school and form the skills necessary for the learning process.
For the diagnosis and study of the figurative memory in children, the D. Waxer technique is used. The results of such a test will allow parents to pay attention to the presence of certain problems and in time to adjust the preparatory period.
Spectacle Test
The child is offered to look at 10-15 seconds each of the 4 images. Then he is asked to reproduce everything he remembered on a pure sheet of paper. As a result of the test, the corresponding scores are charged according to the degree of accuracy.
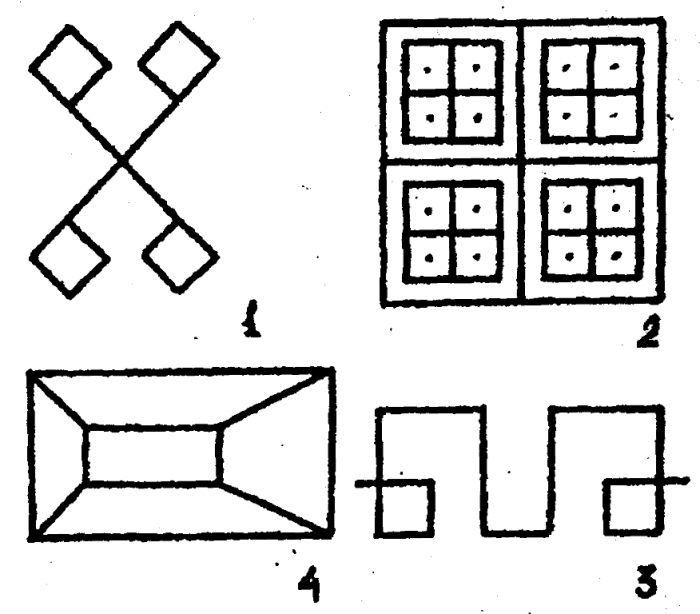
Test for visual memory according to the method of D. Waxer
1st image - The maximum score is a point:
- 2 Intersecting lines and 2 checkbox - 1 point
- correct orientation and selection of flags - 1 point
- similar angle crossing straight lines - 1 point
2nd image - The maximum score is 5 points:
- large square crossed 2 lines - 1 point
- 4 smaller squares in more - 1 point
- 2 intersecting straight lines and 4 small squares - 1 point
- 4 points in the center of each square - 1 point
- preservation of image proportion - 1 point
3rd image - The maximum score is a point:
- little rectangle inside Big - 1 point
- the tops of a smaller triangle are connected to the tops of more - 1 point
- little rectangle is located exactly in the center of Big - 1 point
4th image - Maximum score from the point:
- both sides of the pictures are located correctly relative to the center - 1 point
- pictured outdoor rectangle with an angle for each edge - 1 point
- correct shape of the figure - 1 point
The total test result is 14 points. For the developed visual memory, the indicator is characterized by 10 points and above, the average result is 6-9 points, low - 0-5 points.
Violation of visual memory
- Violations of visual memory in children may be a consequence of pathologies for the formation of mental functions, be caused by diseases of the nervous system and brain due to transferred infections and injuries
- A child with a weak visual memory is usually behind in the assimilation of the school program, distracts and disturbs discipline during occupation. As a result, such children poorly remember the content of the lesson, explaining the teacher and the essence of the tasks, which leads to serious problems with performance
- In elementary school, the violation of visual memory is manifested in difficulties with the perception of the sequence of symbols, slowing the acquisition of reading skills, letters, drawing. In high school, there may be problems with the assimilation of a large amount of information, logical thinking and analysis
Exercise of visual memory
- To help the child, it is necessary to draw attention to his ability to memorize visual images back in preschool age
- If you notice some difficulties, you need to contact a neuropathologist and neurologist to consult and conduct a survey for possible diseases
- Along with this, you can train the visual memory of the baby, starting from the very early age

Sample set of cards for games developing visual memory
Games for viewing
Training the visual memory of the child using the gaming methods:
- Prepare pair pictures of familiar items. At one, the object should be depicted, better than a bright color and simple shape, on the other - the same item, but with the lack of some elements. First offer the baby the first image and let the time for consideration (about 1 minute), then remove the first picture and give another, asking to call differences
- Spread up to a child up to 10-12 pictures with images of simple familiar objects or items themselves (it can be cubes of different colors, balls, small toys, dishes). After the kid carefully considers them carefully, remove everything and ask to call those that he remembered. At the age of 5-7 years, there will be a good result if the child calls 6-8 items
- Another option of this game will be called pictures or items with the child in turn. Will lose one who will not be able to remember the next subject
- Take 5-8 items, spread them on a flat surface and allow the baby well to consider them well. Then ask him to turn away and change 2 items in places, remove or add one. Offer the child to tell what has changed
- Play in superagents. Tell your child about secret agents who know how to memorize the first time. Now offer the baby carefully consider a picture or photo, such as a children's magazine. Ask a child to tell in detail everything he remembered - who is dressed in which position is, which items were in the back background, etc. If the picture was simple, ask the child to draw it in memory, using seen colors
- Take the counting sticks and fold the simple figure (square, triangle, lodge, Christmas tree). Ask the child to remember the figure, and then fold the same. The baby must use the same amount of chopsticks and the location of colors

Set of images for training visual memory
Exercises for visual memory
For school age children, in addition to games, special exercises will be useful for training visual memory. To conduct such activities, you will need to prepare and form material in the form of special cards and drawings.
- Show the child sheet, which shows a variety of geometric shapes or patterns, both symmetrical and arbitrary shape. After he is well considering the image, ask to play seen on the pure sheet. The complexity and number of figures depend on the age and preparing the child. Start with a few simple forms, gradually complicating the task
- Prepare cards with digital rows containing different number of digits. Show the child a card, then ask to call the numbers in a row. Start with 2-3 digits, gradually increasing their number. Similarly, you can train memory, memorizing the sequence of letters and words.
- Train associative memory. Make cards on which the word will be written on one side, and to another - a clear child definition for this word
For example, morning - foggy, friend - reliable, table - round, etc. Repeat together words and definitions, then show the child only definitions and ask to restore words along it. Simultaneously use 20-30 cards