![f234889BD4ABCCEDEFA6B333C6D0E6 [1]](https://babyben.ru/images/babyben/2017/09/f234889bd4abcccedeffa6b333c6d0e61.jpg)
Detailed information about mushrooms of honey agarics: types, photos, places and terms of growth, distinctive signs of inedible.
The content of the article
- Types of edible mushrooms - Assumption, summer, meadow, Chinese, autumn, winter, thick -legged, mucous mucous membranes, scum garlic: description, photo
- How to determine false mushrooms: signs
- How to distinguish the guesses from the actual mushrooms?
- What stumps are mushrooms of honey mushrooms grow on?
- When they appear, and how much, and where the mushrooms are growing in autumn, winter, spring and summer in the forest, and when to collect them?
- Can there be poisoning mushrooms with mushrooms: what are the symptoms of poisoning, after what time they appear?
- Video: Mushrooms of October: Autumn mushrooms
Nedata is the most common mushrooms. They are familiar even to a novice mushroom pipe. But their diversity, sometimes, even scientists involved in the study of mushrooms, introduces into doubt in determining their species. But honey mushrooms are not only edible, but also deadly poisonous.
Therefore, before going to the forest, get acquainted with the main, most often encountered species of mushrooms.
Types of edible mushrooms - Assumption, summer, meadow, Chinese, autumn, winter, thick -legged, mucous mucous membranes, scum garlic: description, photo
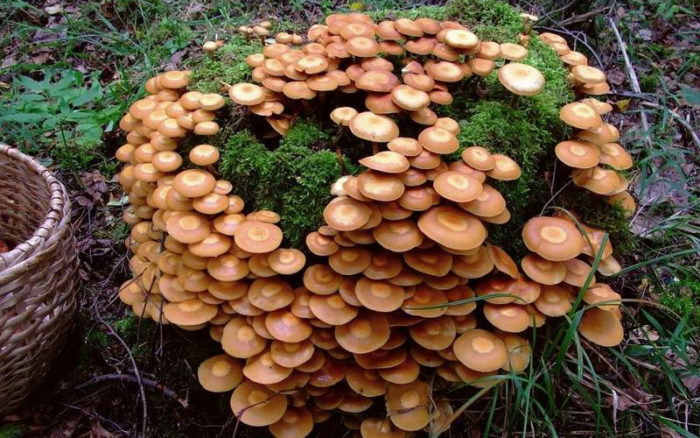

Summer (Kuehneromyces Mutabilis)
| Hat | Plates | Leg |
|
|
|
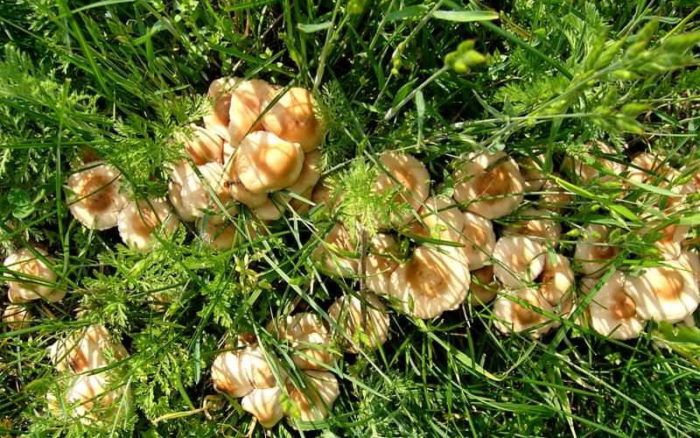

Meadow (lat. Marasmius Oreades)
| Hat | Plates | Leg |
|
|
|

Seddle -toe scales (lat. Pholiota Nameko)
| Hat | Leg |
|
|
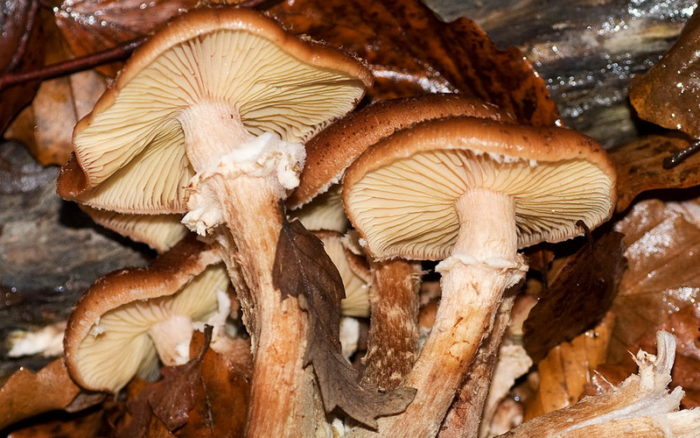

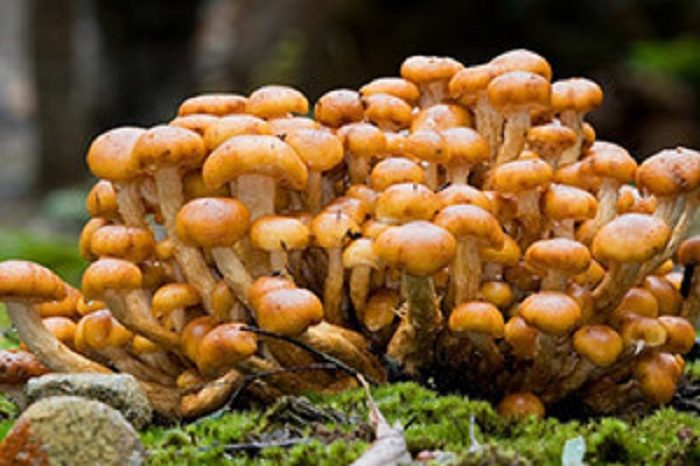
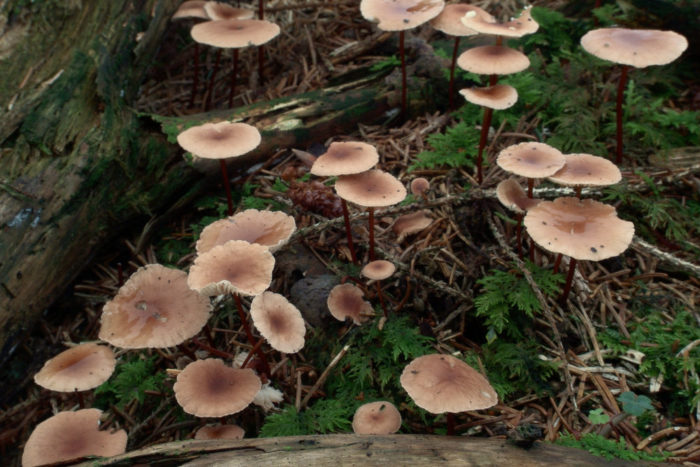
Autumn (Armillaria Mellea) or Assumption
| Hat | Plates | Leg |
|
|
|
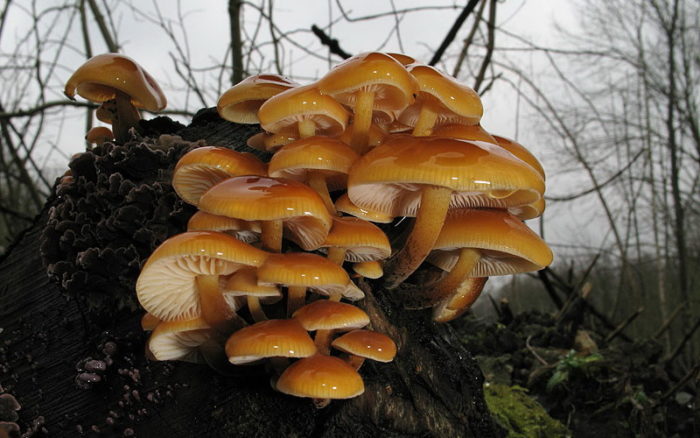

Winter (Flammulina Velutipes)
| Hat | Plates | Leg |
|
|
|
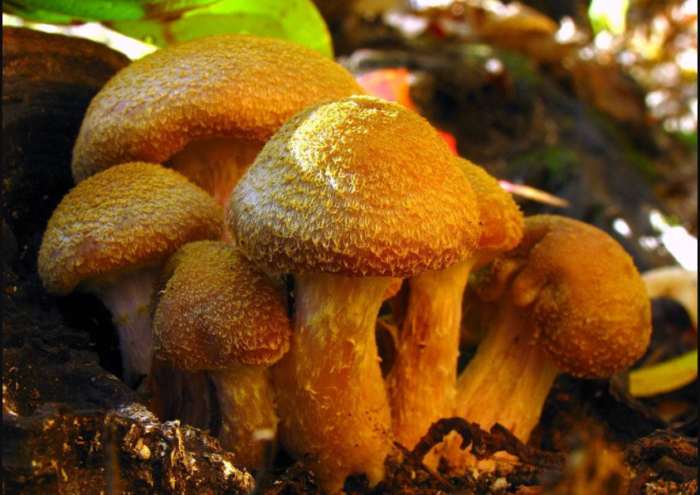

Thick -legged (lat. Armillaria lutea, Armillaria gallica)
| Hat | Plates | Leg |
|
|
|
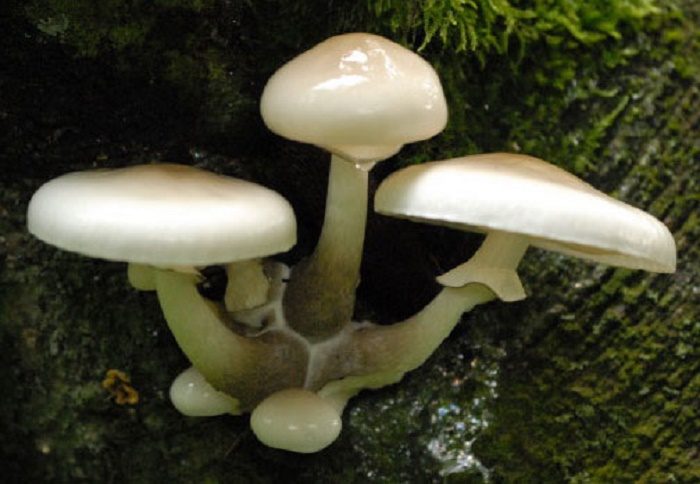

Mucous or udemansella mucous membrane (lat. Oudemansiella mucida)
| Hat | Plates | Leg |
|
|
|

Garlic ordinary (lat. Mycetinis scorodonius, Marasmius scorodonius)
| Hat | Plates | Leg |
|
|
|
How to determine false mushrooms: signs
- The most important feature is that false mushrooms do not have a captured ring (skirt) on the leg
- Have an unpleasant earthy smell
- The color of the hats is bright
- Smooth hats without scales
- The plates are yellow, as they grow, they become greenish or olive-black
- When eating bitterness
How to distinguish the guesses from the actual mushrooms?

note
| Edible | False |
| A ring on the leg | |
|
|
| Left of the legs, cm | |
|
|
| Plates | |
| Pale yellow or creamy |
|
| Hats | |
|
|
| Taste qualities | |
|
|
| Smell | |
|
|
| When getting into the water | |
|
|
What stumps are mushrooms of honey mushrooms grow on?
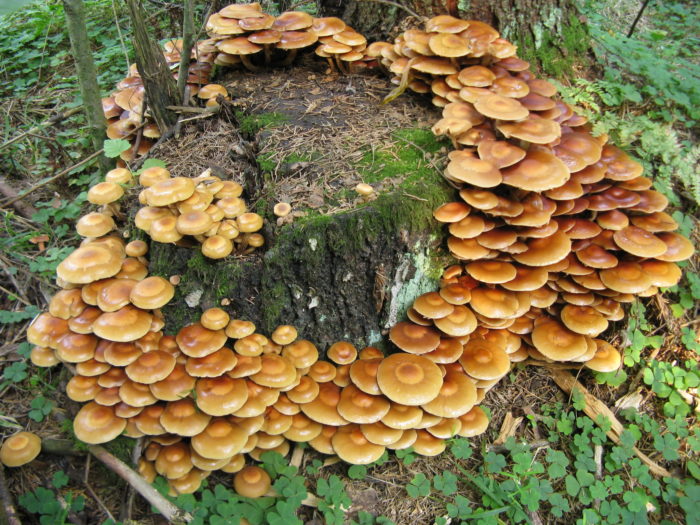

Beautiful necklace
- Parasitizing mushroom individuals multiply mainly on the dead remains of the trees
- They grow on wood of about two hundred different breeds
- Summer species of mushrooms can be found near deciduous stumps: birch, linden, aspen, etc.
- Autumn mushroom is found everywhere, on any species of trees
- To collect a good crop of mushrooms, it is not necessary to look for them next to a certain breed of trees, you just need to know the places where they are more likely to come across:
- on cornflowing snags or fallen logs in deciduous forests
- in cuts and ravines
- Having discovered the first find, inspect this site - there will definitely be others nearby
When they appear, and how much, and where the mushrooms are growing in autumn, winter, spring and summer in the forest, and when to collect them?
- The most important factor in mushroom growth is the temperature regime: most mushrooms require +15-26 ° C.
- Autumn, spring and winter mushrooms are enough +3-5 ° C.
- The optimum summer reproduction temperature is +23 ° C, and there is enough autumn and spring - +12 ° C.
- In addition to optimal temperature conditions, good humidity is necessary for successful growth.
- In the presence of optimal warm and wet conditions, they are stretched in a day.
- The lifetime of mycelium depends on their belonging to the form.
- Fluctuates within 11-14 days.
| Category of mushrooms | When appear when they collect them | Where they grow | How much is growing, days |
| autumn |
|
|
6-8, you can find bypassing the day from the moment growth |
| summer |
|
|
9-12, ready to collect after 1-3 days |
| winter |
|
|
9-12, ready to collect after 2-3 days |
| spring |
|
|
9-12, the first myceliums appear after 2-3 days |
Can there be poisoning mushrooms with mushrooms: what are the symptoms of poisoning, after what time they appear?

Be carefull
Poisoning can be obtained both poisonous and edible varieties of a mushroom, the last in case of their poor quality.
- The first symptoms of poisoning with rotten boiled or poor edible individualsappear 1-2 hours after their use, in the form:
- Sickening attacks and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Pain in the gastric and intestinal zones
- Heartburn and belching
- General weakness
- Headache
- Increasing body temperature to 37.5 degrees
- Increased gas formation in the intestines
- False mushrooms, Mistakely accepted for food, cause the first symptoms of poisoning after 15-20 minutes. Develop brightly, instantly violate the patient's condition, expressed:
- Strong dizziness and impaired coordination
- Nausea and vomiting. First, food residues come out, then gastric juice and bile
- Violation of breathing - turns into superficial, frequent, accompanied by shortness of breath, there is a lack of air
- Bright mirage - auditory, tactile or audience
- Abundant and multiple diarrhea
- Convulsions - partial or common
- Impaired awareness, even a coma is possible
Popular gifts of nature are unusually appetizing in any form:
- fried
- stewed
- pickled
- salted
In time, a well -collected successful crop will enjoy yourself and treat the guests with useful gifts of nature in winter.